of the cell
advertisement

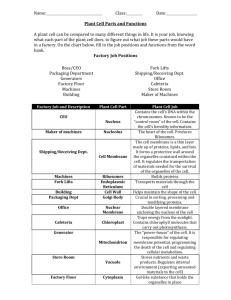
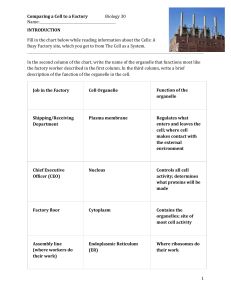
What are cells made of? • All cells are composed of parts, called organelles • The entire cell is made chemically of mainly carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur – These elements are arranged into FOUR classes of molecules – Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids Cells Prokaryotes http://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/iGen3_05-09_Figure-L.jpg Eukaryotes Cells Plants http://blogs.scientificamerican.com/guest-blog/files/2011/08/Plagiomnium_affine_laminazellen.jpg Animals http://www.microscopyu.com/galleries/dicphasecontrast/images/dnarnadic.jpg Cell Membrane • Phospholipid bilayer • Selectively Semipermeable membrane • Contains embedded protein channels that function in transport • Fluid Mosaic Model • “Gatekeeper” of the cell Cell Wall (PLANT) • Provides additional support in plant cells • Made from cellulose (carbohydrate) and proteins Cytoplasm • Consists of cytosol, organelles, and other material • Cytosol - Solute-rich, gel-like substance that takes up most of the cell in volume Nucleus • Contains genetic material (DNA) of the cell • Controls cell activity • “Brain” of the cell • Membrane bound http://stke.sciencemag.org/content/vol2007/issue415/cover.dtl Nucleolus • Ribosomes made here – “Ribosome Factory” Endoplasmic Reticulum • Intracellular transport system • “Highway of the cell” Smooth ER • Smooth ER – where lipids and steroids are made • “Lipid Factory” of cell Rough ER • Rough ER – contains ribosomes, where proteins are made by the cell • “Protein Factory” of cell Golgi Body • Packages and directs movement of materials into and out of cell • “Post Office” of the cell Ribosome • Makes proteins • “Protein Factory Workers” of the cell Lysosome (ANIMAL) • Contain enzymes to break down waste in the cell • “Garbagemen” of the cell Mitochondria • Produce ATP (energy) for the cell • “Powerhouse” of the cell Vacuole Storage compartment for a cell • Plant cells have a large vacuole for storing water • Animal cells have smaller vacuoles Chloroplast (PLANTS) • Site of photosynthesis in plants • Creates glucose using carbon dioxide and water • “Plant food factory” Cytoskeleton • Provides support and structure inside the cell • Allows for movement of vesicles, organelles, and other materials around cell • “Skeleton” of cell Centriole • Divides cells during reproduction