LR/SR Graph Shifts
advertisement

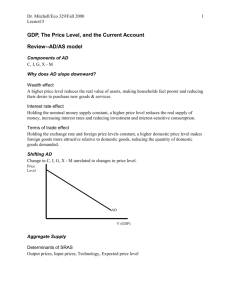
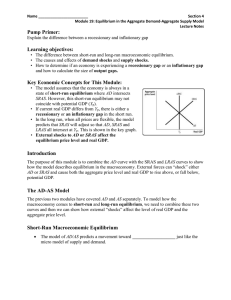
SHORT-RUN/LONG-RUN GRAPHING Summary Why Aggregate Demand Slopes downward? Think about AD from the perspective of the people buying price level = GDP because spending power price level = GDP because spending power Aggregate Price Level AD Real GDP Aggregate Demand Stuff that shifts the curve: Changes in Expectations Optimistic = AD Pessimistic = AD Changes Assets Assets in Wealth = AD = AD Size of the Existing Stock of Physical Capital Small stock = AD Large stock = AD Fiscal Policy G or tax cuts = AD G or tax cuts = AD Monetary Policy quantity of $ = AD quantity of $ = AD Why does Aggregate Supply Slope upward? Think about this from the side of the supplier selling price price level = GDP because selling price price level = GDP Aggregate Price Level because selling price SRAS Real GDP Shifts of the Short-Run Aggregate Supply Stuff that shifts the curve: Changes in Commodity Prices Price falls = SRAS Price increases = SRAS Changes in Nominal Wages Wages fall = SRAS Wages increase = SRAS Changes More in Productivity productive = SRAS Less productive = SRAS Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve Position gives the economy’s potential output Shifts of the curve Increases in the quality of resources, including land, labor, capital, and entrepreurship Increases in the quality of resources: better-educated workforce Technological progress Demand Shock Aggregate Price Level SRAS P1 P2 AD1 AD2 Y2 Positive Shock or Negative Shock? Y1 Real GDP Supply Shock Aggregate Price Level SRAS1 SRAS2 P1 P2 AD Y1 Positive Shock or Negative Shock? Y2 Real GDP Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium LRAS Aggregate Price Level SRAS P1 P2 AD1 AD2 Y2 Y1 or YP Is the initial event a Positive or Negative Shock? Real GDP LRAS Aggregate Price Level SRAS1 SRAS2 P1 P2 AD1 P3 AD2 Y2 Y1 or YP Real GDP