AS AD WARM UP First day after Winter Break ANSWERS
advertisement

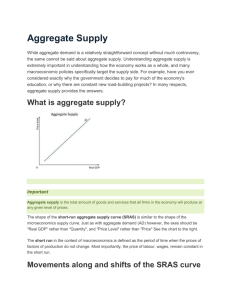
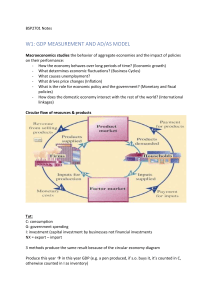
AS/AD WARM UP ANSWERS Instructions: Draw and label an initial AS/AD graph for each, according to the criteria set forth in each. Then make changes as necessary to your graph according to the information in the question. Then answer any subsequent questions, as necessary. #1: Graph an economy that is currently in a recession. During a recession, consumer spending is relatively low and fewer people have jobs. Lower consumer spending means lower GDP and an aggregate demand curve smaller than normal. Therefore, aggregate demand is to the left of its normal position. #2: Suppose the economy of the United State is at full employment equilibrium. If Americans begin purchasing more foreign cars, what will happen to the price level in America? The price level will decrease. An increase in the amount of foreign cars purchased means more imports in America. This decreases America’s net exports, lowering the GDP of America. With a lower GDP, the aggregated demand curve shifts to the left and creates a new equilibrium point at a lower price level. #3: The economy of Japan is currently at full employment. If income taxes increase in Japan, what will happen to the unemployment level in Japan? The unemployment level will increase. With higher income taxes, workers receive less income in each paycheck. Consequently, workers aren’t able to spend as much money as they once could. This will lead to a decrease in Japan’s consumption and investment, decreasing Japan’s GDP. The decrease in GDP will shift the AD curve to the left. A new equilibrium point will be established at a lower economic output level and lower employment rate. If the employment rate decreases, the unemployment rate increases. #4: Suppose Austria is currently operating at maximum capacity. If the size of the labor force in Austria increases, what will happen to the price level in Austria? The price level in Austria will decrease. With an increase in the labor force, the LRAS and SRAS curves will shift to the right as business production increases. The shifts will create a new equilibrium point at a lower price level. #5: The economy of China is currently at full employment. If the price of plastic in China decreases, what will happen to the SRAS Curve? The SRAS curve will shift to the right. With the decrease in the price of plastic, business costs for many Chinese factories decrease. The decrease in business costs will lead to higher supply, and an increase in the SRAS curve.