Accuracy, Precision & Sig Figs: Science Presentation
advertisement

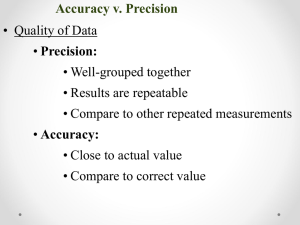
ACCURACY A description of how close measurement is to the true or accepted value of a measurement. Error or Absolute Error = Observed value – accepted value E = O-A Error or Absolute Error = Observed value – accepted value E = O-A • E = 10.2 cm – 10.5 cm E = -0.3 cm • E = 10.8cm – 10.5 cm E = 0.3 cm % ERROR = observed value – accepted value X 100% accepted value % E = O – A x 100% A % E can have + or – value What does negative value mean? PRECISION • The exactness of a measurement. • How closely several measurements of the same quantity made in the same way agree with one another. PRECISION (Uncertainty) 1. Determine average of values 2. Subtract the average from each measured value. (deviation) 3. Add the absolute values of the deviations. (sum of deviations from average) 4. Average of the sum = uncertainty 5. Report result as Average + uncertainty 25.0 + 0.001 cm 25.0 + 0.1cm ACCURACY AND PRECISION Significant Figures = digits of measured value known with certainty and one estimated (doubtful) Significant Figures • What numbers are considered significant? – All non-zero numbers are significant. – Zeroes between significant digits are significant – If there is no decimal point, then trailing zeroes are not significant – If there is a decimal point, then all trailing zeroes are significant – If a number is less than one, then the first significant figure is the first non-zero digit after the decimal point Why are Sig Figs so Important? • We have to interpret measured values made by others • A way to communicate accuracy and precision of data without discussion Trick to Remember Operations with Sig Figs • Addition/Subtraction • Multiplication/Division – Worksheet on operations Practice • • • • • • 1) 6.078 g + 0.3329 g = 2) 8.2 cm - 7.11 cm = 3) 0.8102 m x 3.44 m = 4) 94.20 g ÷ 3.167 22 ml = 5) 1.36 x 10 -5 x 5.02 x 10 -2 = 6) How many grams are in 882 g ?