Conversions
advertisement

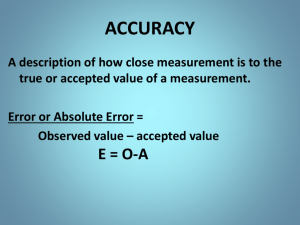
Metric system Measurements Significant figures Relationships Factor Label Method SYSTEM OF MEASUREMENTS (SI) SI Base Units Derived SI Units • Combinations of SI base units form derived units. • pressure is measured in kg/m•s2, or pascals Temperature can be measured using three different units Conversion between T units °F = 9/5 °C + 32 OR °F = 1.8 °C + 32 K = °C + 273.15 T__G__M__KHD_dcm__μ__n__p__f e r a i g a e g a i e e l c k o t a o 1 kg = 1000 g 1 kJ = 1x105 cJ eei cnl i t l i i i c r o a n o i c o 1 dm = 1x108 nm 1 cL = 10000 μL or 1x104 μL e m t o Accuracy and Precision Three students perform the same experiment: The density of the metal is 4.2845 g/mL Density values (g/mL) Joy Taylor Simon Trial 1 2.4563 2.2846 4.2867 Trial 2 1.6798 2.2798 4.2904 Trial 3 4.7893 2.2901 4.2896 Accuracy and Precision, continued Percentage Error • Percentage error is calculated by subtracting the accepted value from the experimental value, dividing the difference by the accepted value, and then multiplying by 100. Percentage error = Valueexperimental -Valueaccepted Valueaccepted 100 • Sample Problem • A student measures the mass and volume of a substance and calculates its density as 1.40 g/mL. The correct, or accepted, value of the density is 1.30 g/mL. What is the percentage error of the student’s measurement? Use of Numbers • Exact numbers – 1 dozen = 12 things for example • Accuracy – how closely measured values agree with the correct value • Precision – how closely individual measurements agree with each other Use of Numbers • Significant figures – digits believed to be correct by the person making the measurement • Exact numbers have an infinite number of significant figures 12.000000000000000 = 1 dozen because it is an exact number!!!! Use of Numbers Significant Figures - Rules • Leading zeroes are never significant 0.000357 has three significant figures • Trailing zeroes only significant if after decimal point. 2.7800 has five significant figures • Use scientific notation to remove doubt 2.40 x 103 has 3 significant figures 2.400x103 has 4 significant figures 2400 has only two significant figures. Use of Numbers • Imbedded zeroes are always significant 3.0604 has five significant figures Use of Numbers • Multiplication & Division rule Easier of the two rules Product has the smallest number of significant figures of multipliers 2.7832 4.242 x 1.23 x 1.4 5.21766 round off to 5.22 3.89648 round off to 3.9 Sample Problem. Calculate the density of a substance with a mass of 14.78 g and a volume of 10.3 mL Use of Numbers • Addition & Subtraction rule More subtle than the multiplication rule Answer contains smallest decimal place of the addends. 3.6923 1.234 2.02 6.9463 round off to 6.95 8.7937 2.123 6.6707 round off to 6.671 Sample problem Determine the perimeter of a piece of paper of 27.94 cm long and 6.92 cm wide. • Sample Problem • How many significant figures are in each of the following measurements? • • • • • a. 28.6 g b. 34.40 cm c. 910 m d. 0.046 04 L e. 0.006 700 0 kg Chapter 2 Direct Proportion •Two quantities are directly proportional to each other if dividing one by the other gives a constant value. Chapter 2 Direct Proportion Inverse Proportion Two quantities are inversely proportional to each other if multiplying one by the other gives a constant value. Chapter 2 Inverse Proportion The Unit Factor Method • Simple but important method to get correct answers in word problems. • Method to change from one set of units to another. The Unit Factor Method • fractions represent unit factors 1 ft 1 ft = 12 in becomes 12 in or 12 in 1 ft The Unit Factor Method • Example: Express 9.32 meters in micrometers. The Unit Factor Method • Example: Express 627 milliliters in L. The Unit Factor Method • Example: Express 45.8 kg in mg. Density conversions • Example: A 20.0 g irregular solid is introduced in a graduated cylinder. The level of water inside the graduated cylinder when from 20.0 mL to 23.3 mL. Calculate the density of the solid. Density conversions • Example: What volume will occupy a liquid with a mass of 15.7 g and a density of 1.34g/mL? Density conversions • Example: Calculate the mass of a gas that occupies 1.5 L and it has a density of 0.00143g/mL?