04. Diagnostic and treatment of urgent condition in mechanical

I.Ya. HORBACHEVSKY TERNOPIL STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Head of department of emergency medicine,
Diagnostic and treatment of urgent condition in mechanical damages.
Speaker: Lyakhovych R .М.
2
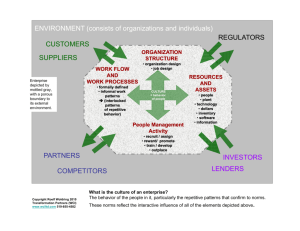
Reasons of origin of hemorrhage are traumatic damages of fabrics of organism and bleeding, which cause traumatic and hemorrhage shocks, in basis of which there is hypovolemia. That is why they in obedience to modern classification are connected in hypovolemia shock.
1. What is depicted at the picture 1?
*Wheelcouch/barrow
2. What is depicted at the picture 4?
*A chair for immobilization and transportation
3. What is depicted at the picture 20?
* Hard shield
4. What is depicted at the picture 21?
*Soft stretchers
5. What is depicted at the picture 40?
*Frame stretchers
6
6. What is depicted at the picture 42?
* Neck Collar
7. What is depicted at the picture 43?
* Pectoral immobilization waistcoat
8. What is depicted at the picture 44?
* Vacuum splints
9. What is depicted at the picture 23?
* Cramer’s Splints
10.What is depicted at the picture 34?
* Elastic splint type Sam Splint
11. What is depicted at the picture 45?
* Elastic splint type Sam Splint
Symptom group of shock determined the type of trauma, volume of mechanical damage of fabrics and organs, size of hemorrhage and hypovolemia by intensity of pain and reaction – answer of organism on aggression by duration of the pathological state.
12. What is depicted at the picture 65?
*Respiratory Ambu-bag with a mask, air-channels/providers, a hose for the serve
13. What is depicted at the picture 66?
* A portable apparatus of ventilation with balloon of oxygen
14. What is depicted at the picture 56?
* A set for conic puncture
16. What is depicted at the picture 2?
* Hand suction-fan
15. What is depicted at the picture 12?
* Laryngoscope with attachments of different size
17. What is depicted at the picture 3?
* Foot suction-fan
12
18. What is depicted at the picture 5?
* Electrosuction-fan
20. What is depicted at the picture 7?
* Pulsoxymeter, located on the finger of patient
19. What is depicted at the picture 6?
*Cardiocomplex
21. What is depicted at the picture 8?
* Medical bag for transference of medical property and medicines
Basic clinical symptoms of bleeding
19
The loss of blood and tissue liquid results in lowering of turgor of hypodermic cellulose, tone of eyeballs, fill blood of hypodermic viens.
The pulsation of peripheral arteries is weak; a pulse becomes frequent, soft, threadlike.
Arterial pressure, central venous pressure goes down. A kidney blood streams goes down as a result of hypotension and compensate spasm of kidney arteries
(perfusion of buds).
Oliguria develops.
25
Bleeding
• Haemorrhage, or bleeding, is the escape of blood from the blood vessels into the tissues and cavities of human body or outside, as the result of an injury or defect in the permeability of the blood vessel wall.
30
Anatomical classification (according to kind of bleeding vessel)
• Arterial hemorrhage;
• Venous hemorrhage;
• Capillary hemorrhage;
• Parenchymatous hemorrhage.
Classification according to mechanism of beginning
Symptoms of acute anemia
• persisting paleness;
• trembling and small pulse;
• progressing decrease of blood pressure;
• dizziness;
• nausea;
• vomiting;
• syncope.
Symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding
Some types of internal bleeding have specific name
• Haemobilia – haemorrhage from diliary ducts;
• Haematuria - haemorrhage from kidneys and urinary system;
• Haemoperitoneum - haemorrhage in abdominal cavity;
• Haemothorax - haemorrhage in pleural cavity;
• Haemopericardium - haemorrhage in pericardial cavity;
• Haemartrosis – haemorrhage in joint cavity;
• Metrorrhagia – uterine bleeding;
• Proctorrhagia – rectal bleeding;
• Hemorrhagic insult – cerebral hemorrhage.
Classification according to the time of beginning:
• primary;
• secondary (early and late).
Classification according to clinical course
•
acute;
•
chronic.
Classification according to degree of severity
(V.I.Struchkov and E.W.Lutzevich )
• I level
• II level
• III level
• IV level
The compensatory-adaptive mechanisms during acute blood loss
• Spasm of veins;
• Interstitial fluid inflow;
• Tachycardia;
• Oliguria;
• Hyperventilation;
• Peripheral arteriolespasm;
• Sympaticoadrenal system’ activation;
• Activation of fibrillation system and haemopoiesis stimulation.
Difficult Airway