major animal phyla
advertisement

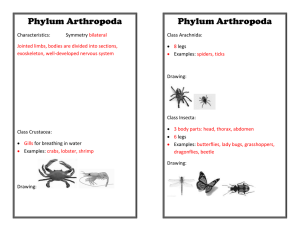
Major Animal Phyla Biology 103 Animal Lab Phylum Porifera • Sponges • Asymmetrical or Radial symmetry • No organs • Most are Marine • Sessile filter-feeders • Asexual Reproduction – Fragmentation • Sexual Reproduction – Hermaphrodites Phylum Cnidaria • Cnidarians • Ex. Hydra, Jellyfish, corals, sea anemone • Radial symmetry • Mostly Marine • Have Nerve Cells • Nematocysts – stinging tentacles • 2 Body Forms: – Polyp – Medusa Polyp Medusa Phylum Platyhelminthes • • • • • Flatworms Bilateral Symmetry Definite Head Thin, solid body Excretory and Digestive System • Oxygen by diffusion • Hermaphrodites • Ex. Planaria, flukes, tapeworms Phylum Nemotoda • • • • • Roundworms Bilateral symmetry Tough outer covering 2 openings Tube-like digestive system • Separate sexes • Ex. Nematodes, hookworms, pinworms Phylum Mollusca • Bilateral symmetry • Mostly Marine • 3 body parts: foot, visceral mass, mantle • Have: heart; digestive, excretory, and open circulatory systems; gills • Mostly separate sexes • Ex. Snails(gastropods), slugs, squid(cephalopods), octopus, clams(bivalves), oysters Phylum Annelida • • • • Segmented worms Aquatic and terrestrial 2 body openings Have nervous, digestive, excretory, and closed circulatory systems; head, nephridia • Ex. Earthworms, leeches, nereis Phylum Arthropoda • • • • Jointed appendages Bilateral symmetry Exoskeleton Separate sexes – internal fertilization in most • Most diverse phyla • 4 classes (next 4 slides) Arachnids • 2 body sections • 2 pairs of mouth parts (chelicerae) • 8 legs • Ex. Spiders, ticks, mites, scorpions Crustaceans • 2 pair of antennae • Aquatic except for pill bug • Ex. Crabs, lobster, barnacles, shrimp Myriapods • Many legs • Ex. Millipedes & Centipedes Insects • 6 legs • 3 body sections • Ex. Grasshopper, bee, butterfly Phylum Echinodermata • Spiny skin • Bilateral symmetry as larvae • Radial Symmetry as adult • Separate sexes • Endoskeleton • Marine • Ex. Starfish, sea urchins, sand dollars Phylum Chordata (vertebrates) • Notochord (nerve cord) • No vertebrae • Gill slits • Ex. Sea squirts, lancelets Phylum Chordata (Vertebrates) • • • • • • Have backbone (vertebrae) Dorsal nerve cord Bilateral symmetry Closed circulatory system Brain 7 classes (next 5 slides) Fish • Class Agnatha – Jawless fish • Class Chondrichthyes – Cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays) • Class Osteichthyes – Bony fish Class Amphibia • Amphibians • Must return to water to reproduce • Aquatic larvae • Semi-terrestrial adult • Moist habitat • Ex. Frogs, salamanders Class Reptilia • • • • Reptiles Dry, scaly skin 3-chambered heart Lays amniotic egg on land • Ectotherms (body temp. depends on environment • Ex. Lizards, snakes, turtles Class Aves • Birds • Endotherms (Internal body heat) • Feathers • Hollow bones • 4-chambered heart Class Mammalia • • • • • • • • • Mammals Endotherms Hair Milk produced in mammary glands Nurse young 4-chambered heart Live birth for most mammals Highly developed brains Ex. Mice, Whales, Humans