Two body shapes
advertisement

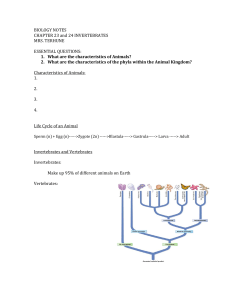
Phylum Arthropoda Characteristics: Symmetry bilateral Jointed limbs, bodies are divided into sections, exoskeleton, well-developed nervous system Phylum Arthropoda Class Arachnida: 8 legs Examples: spiders, ticks Drawing: Class Insecta: Class Crustacea: Gills for breathing in water Examples: crabs, lobster, shrimp 3 body parts: head, thorax, abdomen 6 legs Examples: butterflies, lady bugs, grasshoppers, dragonflies, beetle Drawing: Drawing: Phylum Echinodermata Characteristics: Symmetry Radial Live in the ocean, bodies have 5 equal segments Phylum Mollusca Characteristics: Symmetry bilateral Muscular foot used to move, secretes mucus to help with movement, visceral mass contains organs, mantle covers visceral mass, shell secreted by mantle protects body Examples: snails, octopus, slug, clam How they move: water vascular system and tube feet Drawings: How they eat: sea stars push their stomach outside of themselves into a clam for example, and dissolve the prey with their digestive juices. Examples: sand dollar, sea star, sea urchin Phylum Annelida Characteristics: Symmetry bilateral Body is divided into identical divisions called segments Examples: earthworms, leeches Drawings: Benefits: Phylum Echinodermata Earthworms helpful because they decompose dead matter and make tunnels in soil. Leeches helpful for medical use because they keep blood from clotting and reduce swelling. Drawings: Phylum Porifera Characteristics: Symmetry asymmetrical multicellular, few tissues, no organs Cells and tissues surround a water filled space but there is no true body cavity. All are sessile, (live attached to something as an adult). Has no nervous system. Lives in aquatic environments, mostly marine. All are filter feeders Often have a skeleton of spicules Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Class Amphibia: Amphibians Examples: frogs, toads, salamanders Class Reptilia: reptiles Examples: turtles, snakes, lizards Examples: Class Aves: birds Barrel sponge, branching tube sponge Examples: eagle, blue jay, flamingo, penguin Drawings: Class Mammalia: mammals Examples: lion, humans, mouse, platypus Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Characteristics: Symmetry bilateral Subphylum vertebrata have a backbone to support body Nerve cord surrounded by vertebrae Well-developed brain Skeletons made of bones or cartilage Phylum Cnidarian Characteristics: Tentacles, stinging cells (nematocysts) Two body shapes: Polyp Symmetry: Radial Example: Sea anemone Class Chondrichthyes: Cartilaginous Fish Drawing: Skeletons of cartilage Examples: sharks, rays Class Osteichthyes: Bony Fish Skeletons of bone Examples: trout, bass, puffer fish Class Agnatha: Jawless Fish Medusa Symmetry: Radial Example: jelly fish Skeletons of cartilage Examples: hagfish, lamprey Drawing: Name ____________________________________________ Date ____________________ Block ____________________ The Animal Kingdom Characteristics: 1. Multicellular 2. Eukaryotic 3. No cell walls 4. Develop from embryos 5. Reproduce sexually – some asexually 6. Able to move 7. Have specialized tissues/cells 8. Heterotrophs (consumers