Chapter 12
advertisement

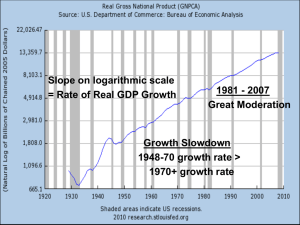
Chapter 12 Production and Growth 1 Outline International comparisons of real GDP per capita What is productivity, its determinants, and its impact on economic growth Link between productivity, economic growth and a nation’s public policy 2 Real GDP per capita and living standards Country Period Japan 18901997 18701997 19001997 18701997 19001997 Canada China USA India Real GDP per person Real GDP per Growth rate at beginning of person at end Per year (%) period (1997 Can $) of period (1997 Can $) 1656 32392 2.82 2616 30261 1.95 789 4942 1.91 4413 39784 1.75 743 2699 1.34 3 Living standards 4 Productivity Productivity is the amount of goods and services produced from each hour of a worker’s time Productivity determines the living standards of a nation as the latter depends on the nation’s ability to produce goods and services Determinants of Productivity: – – – – Physical capital Human capital Natural resources Technological knowledge Y=A F(L, K, H, N) 5 Economic Growth and Public Policy Can public policy raise productivity and living standards? Encourage Savings and Investment – Recall that capital is a produced factor of production – Tradeoff between capital investment and consumption goods – Correlation between growth and investment (reverse causality?) – Diminishing returns to capital 6 Diminishing returns and the catch-up effect Diminishing returns is the property whereby the extra benefit from an extra unit of an input declines as the quantity of input increases In the production process, capital is subject to diminishing returns As a result of diminishing returns to capital: – In the LR, higher savings leads to greater accumulation of capital and therefore higher level of productivity and income BUT not to higher growth in productivity and income – Catch-up effect is the property whereby countries that start off poor tend to grow more rapidly than countries that start off rich 7 Economic Growth and Public Policy (contd) Investment from abroad – FDI – Foreign portfolio investment – Foreign investment raises GNP (income) less than it raises GDP (production) – Source of state-of -the-art technologies Education- investment in human capital – Positive externalities – Opportunity cost of schooling is higher in poor countries – Brain-drain- negative externality 8 Economic Growth and Public Policy (contd) Property rights and political stability – Coordination of economic activities through market prices – Corruption impedes coordinating power of markets – Discourages domestic savings and foreign investment Free trade – Infant- industry argument – Small size of the economy – Landlocked countries 9 Economic Growth and Public Policy (contd) Control of population growth – – – – Population growth reduces GDP per capita Huge burden on education system Malthus theory on population growth Raising opportunity cost of additional children Research and Development – Knowledge is a public good – Tax breaks and patent system encourages R and D 10 Economic Growth and Public Policy (contd) Cross-country growth studies show that per capita growth is related to : – – – – Initial income level of the country Geographic and resource structure of the country Market orientation of the economy National saving rate Is productivity slowdown in industrialized countries a result of slow technological progress? 11