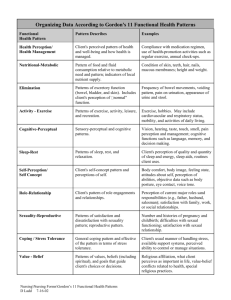
Sensation and Perception - Reading Community Schools

Sensation and Perception
The Basics
• What is sensation?
– Stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission of sensory information to the central nervous system.
-HUH?
Sensory receptors are located along the spine and organs such as eyes and ears.
More BA6
• If that’s sensation Mr. Reardon, then what is
Perception because I sure am lost.
• Perception
– The psychological process through which we interpret sensory stimulation
– WHAT?
Components of Perception and
Perception
• Absolute Threshold
– The weakest amount of stimulus that can be sensed.
– Dog whistle example (see Jesse)
– Can differ from person to person
– This can effect the way we see the world
Components of Perception and
Perception
• Difference Threshold
– The minimum amount of difference between two stimuli
– Stimuli need to be differentiated in order to distinguish what we need to hear versus noise
– Can my music people please pay attention to my next example?....Please?
Components of Perception and
Perception
• Signal Detection Theory
– A method that distinguishes stimuli that takes into account not only strengths but also elements such as setting physical state and attitudes.
– Please pay attention to the following instruction
Components of Perception and
Perception
• Sensory Adaption
– The process by which we become more sensitive to weak stimuli and less sensitive to unchanging stimuli
– Sounds of the country vs. Sounds of the city
Perception
• What is perception?
– Remember your stories and many other memories? How to you perceive them?
– Difference between Sensation and Perception?
– Why is this a major part of psychology?
It’s not you…….It’s me
• The first rule of perceptual organization is known as:
• Closure
– The tendency to perceive a complete or whole figure when there are gaps in what your senses tell you.
Oh, now I see it
• Figure ground perception
– Perception of figures against their background.
– Look out the window tell me what you see?
– We see objects against the background
Rules of Organization
• 1. Proximity
– People are influenced on how they perceive objects based on the proximity of them.
– Take a look
Other Rules of Organization
• Similarity
– People think of objects as being similar to each other.
– See the Next Example
Other Rules of Organization
• Continuity
– People see smooth continuous patterns rather than disrupted ones
– See the Next Example
Other Rules of Organization
• Common Fate
– When you see things moving together, you tend to perceive them as belonging together.
Perception Activity
• Take a look at the following pictures and write down a gut response….you have 30 seconds to write three words to describe your feelings.
• Next we will go back to the picture to further interpret what is going on in the picture
• Next get with one partner and you each will describe what is go
Sleep and Dreams
• We are asleep an average of 1/3 of our lives.
• Why do we sleep, why do we dream
• Why do we experience nightmares
Clocks
• Circadian Rhythms
These are functions for how we live, or biological clocks.
• These rhythms include bodily changes such as body temp, blood pressure, and sleepiness.
• They usually operate on a 24-hour day schedule
• For example, your body temp is at its lowest between 3 and 5am everyday.
Clocks
• The most studies of these rhythms is that of a sleep wake cycle.
• We associate our days with clocks and light, when in reality we are living on this clock and given cues for when we should be asleep or awake.
• If this cycle is hindered, the clock expands to 25 hours.
Stages of sleep
• When we are fully awake we emit beta waves, which are short and quick.
• When we become drowsy and tired we go from beta to alpha waves.
This cycle includes flashing of images or colors and a sensation of falling.
Stages of Sleep
• The move to alpha waves leads us into stage 1
• Stage 1:
Lightest sleep
Go from Alpha to Theta waves
We resemble vivid images and sensations were and if are awakened may seem like we never asleep
Stages of Sleep
• We remain in stage 1 for 30-40 mins if not awakened.
• We move into stages 2,3, and 4
Stages 3 and 4 are the deepest sleep (delta waves) and is the hardest to wake someone up from.
Stages of Sleep
• After about a half hour of stage 4 sleep, we begin to return to level 3 quickly then 2 and finally 1.
• 90 mins will have passed since we fell asleep and something strange begins to happen to us.
• We breathe irregularly, blood pressure rises, heart beats faster, but it is not stage 1 but another stage of sleep….
REM
• Rapid Eye Movement
– Beneath our closed lids our eyes are moving rapidly
– During a typical night of 8 hour sleep, most people go through these stages up to 5 times each constitutes 1 sleep cycle.
– The final period of REM sleep may last a half hour to an hour.
GO TO BED
• If you are not sleeping and are deprived of
REM sleep, tend to try and catch up from that
REM time they missed.
• Seems to serve a psychological function for people and animals.
• Those who get REM sleep tend to learn faster and are “sharper”
Drugs and Consciousness
• Drugs have different effects on individuals. Some drugs can slow a person down while others can spur them into rapid action
• Addiction is when a person takes a drug long enough that the body then craves it to feel normal.
• Alcohol, nicotine, and other drugs are considered addictive.
Depressants
• Depressants are drags that slow the activity of the nervous system and generally give people a sense of relaxation and can have negative effects.
• Two types of depressants are
– Alcohol
– Narcotics
Alcohol
• Small doses can be relaxing to an individual and high doses can put someone to sleep. Too much can be lethal.
• Intoxication is another word for drunkenness and can poison the body and brain.
• Effects:
– Slurring speech
– Loss of Coordination
– Judgment
– Actin da fool
Narcotics
• Narcotics are addictive substances/depressants that have been used to relieve pain and induce sleep
– Heroine, Morphine, Codeine
The use of this drug can impair judgment and consciousness as well as have lethal effects
Withdraws can lead to a deep drop into depression and cause chills, rapid heartbeat, insomnia, vomiting.
Stimulants
• Stimulants increase activity of the nervous system and can speed up heart/breathing rate.
• Nicotine
– This stimulant can spur a release of the hormone adrenaline which causes heart rate to increase and
,make people feel more alert and attentive.
– Decreases Appetite
– People who quit may become nervous, drowsy, headaches, etc.
Amphetamines
• This is another kind of stimulant that are known for helping people stay awake as well as reducing appetite
• First used by soldiers in WWII in order to stay awake during the night.
• If taken in high doses this “high” can last for days at a time.
• The “crash can be devastating and can lead a person into a deep depression and fatigue.
Amphetamines
• High Doses may also effect ones consciousness and can alter ones state of mind.
• Hallucination- is a perception of an object or a sound that seems real but it is not. (Bugs crawling on them)
• Delusion- a false idea that seems real. (Chased by someone)
Cocaine
• This drug can release feelings of pleasure, reduce hunger, deaden pain, and boosts selfconfidence.
• Cocaine can cause muscle loss and lining of the nose and heart to deteriorate
• Crack is a more powerful and chemically impure form of the drug that can cause more problems based on its impurity
Hallucinogen
• Hallucinogen is a drug that produces hallucinations as well as feelings of relaxation and pleasure.
• Marijuana
– Impairs perception and coordination making it difficult to operate machinery
– Increases heart rate
– May become confused or lose sense of self.
LSD
• Also known as acid and can produce intense hallucinations
• “Open New Worlds”
• Intense negative symptoms that can lead to tragic results
• “Flashbacks”
4 Types of Treatment
• 1. Detoxification
• 2. Maintenance Programs
• 3. Counsling
• 4. Support Groups