PS-3-Puffer
advertisement

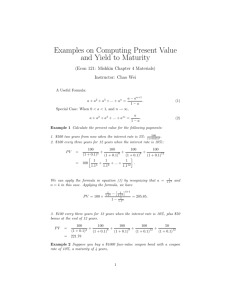
The Credit Crisis and Discount Rate Determination Presentation to the Canadian Institute of Actuaries April 15, 2009 Marlene K. Puffer, Ph.D., CFA www.twistfinancial.com marlene.puffer@twistfinancial.com Agenda Corporate Bond Market Spreads Issuance Opportunities Market Structure Discount Rate Determination Long Term Corporate AA Various Approaches Canadian 10-year Corporate Spreads 600 550 500 450 AA Credit Spreads (bps) 400 A BBB 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Source: RBC Capital Markets 2008 2009 Canadian Net New Bond Issuance Federal, Provincial, Municipal Corporate (Bln. C$) 50 40 30 20 10 0 Source: Standard&Poor’s 08 20 06 20 04 20 02 20 00 20 98 19 96 19 94 19 92 19 90 19 88 19 86 19 84 19 82 19 19 80 -10 Opportunities Canadian corporates Significant new issue supply Mainly investment grade, heavy in financials. Global investment grade credit Liquidity and diversification Detailed credit research required High yield U.S./Europe Equity-like risk characteristics Mainly < 10 year term Emerging markets Good diversifier Growing corporate market Credit derivatives Pure credit exposure Limited currency risk Liquid individual names and indices Increased standardization and central clearing to reduce counterparty risk Market Structure - Trading Source: IIAC Average daily corporate bond trading $580m in 2008 vs. $885m in 2007 Market Structure Corporate Issuance and trading Market Structure Sector Typical trade “Large” trade Typical new issue size Canada $10-25 m >$100 m $1 to $4 b Provincial $10-25 m >$100 m $300 - $600 m Short/mid Corporate $5-25 m >$50 m $300 - $600 m Long Corporate $5-10 m >$10 m $200 - $300 m Gov t of Canada Inflation Linked (RRB) $5-10 m >$25 m $300 - $400 m Provincial RRB Very limited Very limited $ 100 m + Canadian Bond Market - Sectors Percent of Bond Market Value by Sector 60% 3.1% 50% 40% <10y >10y 30% 53.3% 20% 10% 0% 5.0% 5.1% 3.5% 4.6% 2.8% 5.0% 1.2% 3.1% 0.0% 0.8% 1.3% 7.4% 0.5% 2.9% 0.1% 0.1% 0.0% 0.1% Source: CIBC World Markets, ForethoughtRisk Canadian Bond Market - Rating 2% of all corps are over 10 years and rated AA or higher Percent of Bond Market Value by Rating 50% 45% 40% <10y 35% 11.6% >10y 1.2% 30% 25% 20% 15% 33.1% 0.5% 26.6% 3.7% 10% 5% 12.4% $3.5b vs. $32b rated A or lower 10.9% 0% AAA AA A BBB Source: CIBC World Markets, ForethoughtRisk Discount Rate Methodology Methodology Discount liability cash flows using corresponding spot rate that reflects corporate AA spot yields. Term Need full curve, and in particular need to extrapolate beyond 30 year maturity. Potential confusion With a normal upward sloping yield curve, semi-annual yield < annual yield < spot yield. Beware of mixing them up. Long term Government of Canada yield plus “AA” spread Data Bank of Canada long term bond yield available daily. Dealers publish daily indicative yields on select corporate bonds by maturity for both secondary market trades and theoretical new issues. Important to understand source data. Methodology Distinction between secondary trading and indicative new issue levels. Selection of bonds to use is discretionary. “Bootstrap” a spot curve from raw semi-annual yields. Term Maximum 30 year maturity. Data more reliable 10 years and shorter. Usefulness Discretion involved may lead to very different derived discount rates. Standardization is desirable, but some discretion is important in extreme market conditions. CIBC Spot Curve – cash flow matching Data Long vs short term Single dealer New issue concession Theoretical new issue bank spreads (“offered side”). Not a diversified portfolio. Differential between financial and other spreads has increased dramatically recently. Active market in financials under 10 year maturity. Little to no issuance or trading over 10 years. CIBC data only. May differ from other dealers, especially when spreads are wide and volatile. Spreads reflect new issue concession relative to secondary spreads. Wider when spreads are wide and markets are volatile. PC BOND AA Yield Curves Data Bid yields (vs. index mid market ; CIBC spot curve offered). Intended to reflect representative AA rated bond yields at each maturity point. Month end only.; semi-annual and annual yields. Data can very by month i f a new bond is selected at a specific maturity point. Highly dependent on specific bond spread. Long vs short term Active market in corporates under 10 year maturity, but mainly financials. Little to no issuance over 10 years, and tend to use utilities or industrials which may not compare to financials. May use govt yield plus indicative spread in long end. Inconsistent data approach. Single dealer Scotia data only. May differ from other dealers, especially when spreads are wide and volatile. Comparison to CIBC spot curve Derived spot curve can have irregular shape. Derived spot rates have typically been close to CIBC spot curve historically, but have diverged in the past year. DEX long-term AA/AAA bond index yields Data Market value weighted average of all AAA and AA corporate bonds. Long index is > 10 year maturities. Only 5 issuers with these ratings! Semi-annual yield calculation. Term Yields are available for all corporates, or broken down by rating, and/or maturity , or sector. Multiple Dealer Since early 2008, uses all major Canadian dealer data. Gives weight to some dealers who trade very little in the quoted bonds. But omits high and low quotes. Usefulness Long term Index yield data is a useful crosscheck to guage curve movement over time. Not directly comparable yield level to derived 30-year rates. Conclusion Data source CIBC spot curve most consistent and no need to “bootstrap” to derive spot curve. Judgment still required due to single dealer, financials, and new issue concession, especially in volatile markets. Need for new standard based on multi-dealer data and transparent process? Term Extrapolation beyond 30 years subject to subtleties of shape or long end (higher yields around 25 year area vs. 30-years). Judgment Compare to peers, changes in index yields, changes in yields based on Govt bonds plus spread. Biography Dr. Marlene K. Puffer, CFA, Managing Director of Twist Financial Corp., provides strategic advice, analytics, education, litigation support and expert witness testimony, and financing and investment solutions in all areas of fixed income and institutional investment. She was recently appointed to the board of the Hospitals of Ontario Pension Plan (HOOPP). Current projects include pension Liability Driven Investment strategies, mortgage markets, and Asset-Backed Commercial Paper restructuring. Recently, she was an expert witness in the BCE vs. Bondholders case in the context of the BCE leveraged buyout. She has 18 years of capital markets experience, including 13 years on Bay Street and 5 years as a professor of finance at the University of Toronto. Dr. Puffer holds a Ph.D. in Finance and Applied Statistics and a M.Sc. in Business Administration from the University of Rochester William E. Simon Graduate School of Business Administration, and master's and bachelor's degrees in Economics from the University of Toronto. She is a CFA charterholder. Dr. Puffer sits on numerous boards and committees at the University of Toronto, the Toronto CFA Society, and the Canadian Investment Review.