sec2-3ch9 - ChurchillHistory
advertisement

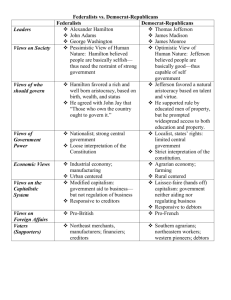
1. To help President Washington carry out his duties, the first Congress a) passed the Judiciary Act. b) created the Bank of the United States. c) created five departments whose heads made up the Cabinet of advisors. d) agreed to place the nation’s capital near his home along the Potomac. 2. Hamilton thought the national government should pay off both national and state war debts because a) it showed the government would act firmly in a time of crisis. b) if it did not, it would lose the trust of future investors. c) it was not fair for speculators to make a profit on the war. d) it would protect local industry from foreign competition. 3. The group of officials chosen to assist the President is called the a) House of Representatives b) Congress c) Cabinet d) Senate Ch. 9 section 2 Creating a Foreign Policy • Main Idea: Washington established authority of the national government at home and avoided war with European powers. -How was American opinion divided over the French Revolution? -Why did Washington want the nation to remain neutral in foreign affairs? -Why was it difficult for the United States to remain neutral? • Why It Matters: Washington’s policies at home and abroad set a precedent (example for later presidents) . Foreign Issues Facing Washington… • Events in Europe had effects in America 1. FRENCH REVOLUTION (In 1789, the French rebelled against their king). – What should the U.S. do? • France had helped us during our revolution • Britain was America’s best trading partner • Americans supported the French people’s desire for liberty BUT they were horrified by the violence in France (divided Americans): Jefferson – supported France Hamilton, Adams – supported Britain The US REMAINS NEUTRAL • The main foreign policy issue facing the President was how to remain neutral (not taking sides in the conflict) while honoring agreements to support France. • Washington decided on a foreign policy (the action that a nation takes in relation to other nations). • He issued the Neutrality Proclamation (the U.S would not side with France or Britain). Foreign Issues Facing Washington 2. American business depended on foreign trade. Problem: -British captured American trading ships in the French West Indies -Washington knew that the country was too weak to fight Solution: -Washington sent Chief Justice John Jay to Britain for talks. Jay’s Treaty -Britain agreed to give up their forts held in the West and pay damages for the ships -Americans paid old debts owed to Britain John Jay • Responsible for Jay’s Treaty. • Jay’s Treaty- agreement that ended the dispute with Britain over American shipping during the French Revolution. Washington’s FareWell Address.. Washington before leaving office, published his Farewell Address. -He advised Americans to avoid becoming involved in the disagreements among European countries. -Advised nation to remain neutral and avoid permanent alliances. -Cautioned against letting political differences divide the nation and cause arguments. Washington’s FareWell Address • Despite Washington’s warnings, political parties developed. • The first two political parties were the Federalists and Democratic-Republicans. • The Federalists, led by Hamilton. • The Democratic-Republicans, led by Jefferson. 1. Many Americans turned against the French Revolution when a) John Jay got the British to sign a treaty. b) Thomas Jefferson criticized the revolution. c) the French started seizing American ships. d) the revolution became increasingly violent. 2. President Washington’s foreign policy proclamation said that a) in the European conflict, the United States would support France. b) in the European conflict, the United States would remain neutral. c) in the European conflict, the United States would support Britain. d) individual Americans could make up their own minds and aid either side. 3. What precedents were set during Washington's Presidency? a) Not to run for third term b) Passed Judiciary Act c) Chose well known leaders to serve in Cabinet d) All of the above 4. Which of the following established the U.S. foreign policy of not taking sides in foreign affairs? a) Neutrality Proclamation b) Alien and Sedition Acts c) Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions d) Pinckney Treaty Ch. 9 section 3 political parties emerge • Why did many Americans distrust the idea of political parties? • How did the views of Hamilton and Jefferson differ? • Why did political parties develop? • How did the election of 1796 increase political tensions? A distrust of Political parties • Americans had seen how factions, or opposing groups within parties, worked in Britain. Members of factions were often more interested in personal gain than in public good. • Political parties could be a threat to national unity. They could lead to “jealousies and false alarms.” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2 7vbHvcRo1s RULES • Every second row reads about Federalists (Hamilton) or Democratic-Republicans (Jefferson). 1. Open textbook to pages 288 and 289. 2. Read starting with the blue title “Differing Views” and “Development of Political Parties.” 3. Find the information about your party and fill in your table [5 minutes.] a) Hamilton-turn to your shoulder partner – talk about your Federalists party while your partner writes the information down [2 minutes]. b) Jefferson-turn to your shoulder partner – talk about your Republicans party while your partner writes the information down [2 minutes]. Federalists Democratic Republicans Jefferson Leaders Hamilton Supporters Elite Wealthy and well educated should lead nation Manufacturing, shipping, and trade Common man People should have power federal state Supported loose interpretation “necessary and proper” Pro-Britain Despised the violence and social disruption Supported strict interpretation Wanted Opposed Favored Gazette of the US Opposed National Gazette Basis of economy (how did they earned their living) Federal or state powers Interpretation of the Constitution Foreign policy Position on issues: -national bank -protective tariff Supporting newspapers: Farming (agriculture) Pro-French Admired French Revolution Development of political parties Leaders in different states organized to support either Hamilton or Jefferson. Jefferson’s supporters called themselves Democratic Republicans. Hamilton’s supporters were called Federalists. Newspapers began to take sides. The two political parties took part in the election of 1796. Election of 1796 Republican Candidates V S. Federalist Candidates Thomas Jefferson for PRESIDENT John Adams for PRESIDENT Aaron Burr for Vice President Thomas Pinckney for Vice President The Winners • John Adams for President • Thomas Jefferson for Vice President Quick check One issue the first political parties clashed over was a) which should be stronger—the central government or the state governments. b) whether the United States should expand beyond its original borders. c) whether George Washington should be permitted to retire. d) whether the Supreme Court should be allowed to declare laws unconstitutional. Quick check In 1796, the person with the most votes became President, and the person with the second highest number of votes became Vice President. One problem this caused in the election of 1796 was that a) the votes had to be counted twice. b) candidates for President and Vice President had to run together on the same ticket. c) the views of the opposing candidates were the same. d) the people chosen as President and Vice President were from opposing parties.