The Federalist Era
advertisement

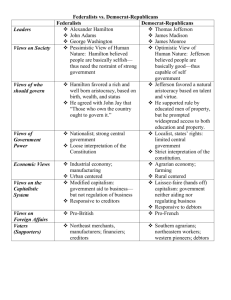
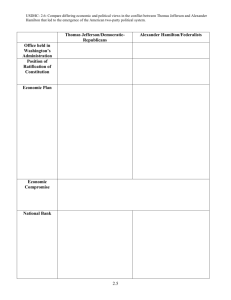
The Federalist Era, 1789-1800 Launching the New Government The First Federal Elections Picking the first president The new Congress James Madison The Bill of Rights John Adams George Washington Filling out the government Washington’s Cabinet Henry Knox: Sec. of War Edmund Randolph: Att. General Thomas Jefferson: Sec. of State Alexander Hamilton: Sec. of the Treasury John Jay: First Chief Justice (SCOTUS) Alexander Hamilton’s Financial Program “Report on Public Credit” •Assumption and creation of national debt “Report on the •Proposed congress national bank” charter a bank “Report on the •Proposed a federal currency Mint" •Program to encourage “Report on Manufactures" domestic industry Political Views: Hamilton versus Jefferson Passionate Politics Partisanship without Parties The New Politician: mobilized voters and created political organizations Expansion of the Press Democratic-Republican Societies Cultural Politics Peter Porcupine Federalist William Cobbett “Peter Porcupine,” scribbles attacks and insults.” Republican political cartoon. Conflicts at Home and Abroad The French Revolution in America The revolution became symbol for both Republicans and Federalists Liberty and the Guillotine Jay’s Treaty, 1795 Treaty agreed to compensate America for cargoes sized in 1793-1794 and to vacate forts in the Northwest territory John Jay Pinckney Treaty (1795): Secured America’s right to navigate the Mississippi River and use New Orleans (also settled boundary of Florida) Map of Spanish Interests in America The Whiskey Rebellion Rebellion over Hamilton’s hated tax on Whiskey in 1794. Call up Militia immediately (F) Negotiate, but have militia ready. Repeal the tax to avoid confrontation (R) Washington chooses the negotiate, but called the militia after negotiations failed The Presidency of John Adams, 1796-1800 Washington’s Farewell Attacked the growing factions and partisanship Advised Americans steer clear of permanent alliances with foreign nations Election of 1796 The XYZ Affair and Quasi-War with France Quasi-War: An undeclared naval war with France from 1798-1800 XYZ Affair (1796): Three French officials demand bribe from Americans to begin negotiations The Alien and Sedition Acts Alien Acts (3 separate laws): Increased government deportation powers/Made it harder to become a citizen Sedition Act: criminalized protesting the government/criminalized speech or expression criticizing the government or its actions. The Election of 1800 Jefferson’s opponents portrayed him as an atheist who drew radical ideas from the French Revolution. In this image the American eagle tries to prevent Jefferson from throwing the Constitution into the flames emanating from the altar of Gallic (French) despotism.