Chemistry Unit 03 Lesson 01
advertisement

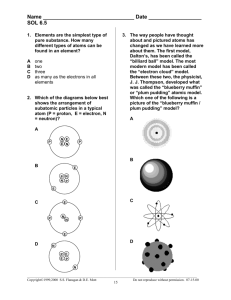
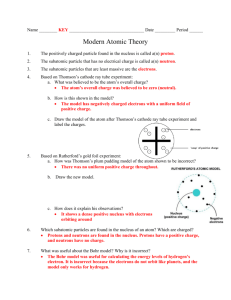
CHEMISTRY Unit 03 Lesson 01 Models of the Atom • Atom A submicroscopic particle that constitutes the fundamental building block of ordinary matter; the smallest identifiable unit of an element • Subatomic particles Any of various particles that are smaller than an atom (Ex. Protons, electrons, neutrons) • Nucleus The very small, dense core of the atom that contains most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge; composed of neutrons and protons • Proton(p+) An electrically positive subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom • Neutron(n0) An electrically neutral subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom, with a mass almost equal to that of a proton • Electrons(e-) Negatively charged subatomic particles with negligible mass that are found in orbitals surrounding the nucleus of an atom, making up nearly all of the atom’s volume • Electromagnetic spectrum The range of wavelengths of all possible electromagnetic radiation • Wavelength (λ) The distance between adjacent crests of a wave • Frequency (ν) The number of cycles (or complete wavelengths) that pass through a stationary point in one second • Photon The smallest possible packet of electromagnetic radiation with an energy equal to hν • Planck’s constant A value of h= 6.626x10-34 J·s which is used in the equation E=hν to calculate the energy in a photon • Speed of light A value of 3.00x108 m/s • Isotope Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons and subsequently a different mass • Spectroscope A piece of equipment used to observe a spectrum of light or radiation from a particular substance • Mass number The sum of the number of protons and neutrons • Atomic number The number of protons in an atom; defines the element • Average atomic mass The average mass of the atoms of a particular element based on the relative abundance of the various isotopes • Nuclear symbol Consists of the atomic number, atomic mass, and the mass of the particular isotope of that element • Hyphen notation Element- Atomic mass (Ex. Carbon- 12) • Write hyphen notation for the following elements: • Lithium(6.9amu), Nitrogen(14amu), Argon(39.9amu) The Atom and the Solar System Analogies: nucleus: Sun electrons: planets ATOM SOLAR SYSTEM > 99.9% of total mass is in nucleus ~ 99% of total mass is in Sun Mostly empty space Mostly empty space Electrons held by mutual attraction with nucleus Planets held by mutual attraction with the Sun Electrons behave as spinning bodies. Planets rotate on their axes. The Atom and the Solar System Analogies: nucleus: Sun electrons: planets ATOM SOLAR SYSTEM Paths of electrons are unpredictable; can only determine probability that an electron can be found within a given space Planets move in relatively fixed, predicable paths. Electrons moving around the nucleus in three dimensions Orbits of planets lie in nearly the same plane. Electrons held by electrical attraction with nucleus Planets held by gravitational attraction with the Sun Electrons repel each other. Planets attract each other. Electrons sometimes “fall” into the nucleus, and sometimes they pass through the nucleus. Motion of the planets prevents them from being pulled into the Sun All electrons are alike. Planets differ greatly from one another. History of the Atom • Leucippus and Democritus proposed the first theory of matter being composed of atomos, small indivisible particles (460-370 B.C.) • In the sixteenth century, the scientific revolution began with works of scientists such as, Francis Bacon, Johannes Kepler, Galileo Galilei, Robert Boyle and Issac Newton Discovery of the Electron • J.J. Thompson, an English physicist, used cathode rays to discover electrons in the late 19th century • In 1909 Robert Millikan, an American physicist, discovered the charge of an electron and confirmed Thompsons theory that an electron is 2000 times lighter than hydrogen Early Models of the Atom • Thompson proposed the plum pudding model Ernest Rutherford • In an attempt to confirm the plum-pudding model, he proved it wrong • Performed a gold foil experiment and discovered that atoms are mostly empty space with a central nucleus Comparing Models • Make a T-chart for the similarities and differences of these models A. B. Model Limitations What are the limitations of the following models? A B Model Limitations • What are the limitations of the following models? C D