1.2 Practice WKST A: Describing Matter by its Properties
advertisement

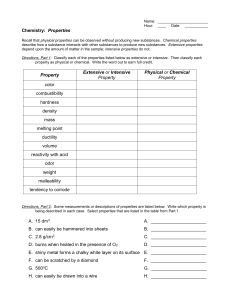
Name:______________________________________ Period _______ Date _______________________ Section 1.2 Practice Worksheet A Describing Matter by its Properties Part 1 Recall that physical properties can be observed without producing new substances. They can be observed with the senses and don’t require destroying the substance. Chemical properties describe how a substance interacts (or fails to interact) with other substances to produce new substances. You can also describe matter by intensive or extensive properties. Extensive properties depend upon the amount of matter present in the sample; intensive properties to do not vary whether there is a little or a lot. Classify the properties listed below as physical or chemical by placing a check in the appropriate box. Then, choose if it is an extensive or intensive property. Physical Chemical Extensive Intensive 1. Color 2. Combustibility 3. Hardness 4. Luster 5. Flammability 6. Reacts with acid to form H2 7. Mass 8. Density 9. Melting Point 10. Can neutralize a base 11. Ductility (easily drawn into wire) 12. Odor 13. Weight 14. Malleability (easily hammered into sheets) 15. Tendency to corrode 16. Length Of the chemical properties you have identified above, were they classified as extensive or intensive? Why? Part 2 In a physical change, the original substance still exists after the change occurs; the substance has only changed in physical form (sold, liquid, or gas). In a chemical change, a new substance is produced. What evidences do we look for in a chemical reaction? A. C. B. D. Remember: Energy (release or absorption) always accompany physical and chemical changes. Classify the following as a physical or chemical change. Write P or C on the line. _______ 1 . Hydrochloric acid reacts with potassium hydroxide to produce a salt, water and heat. _______ 2. A pellet of sodium is sliced in two. _______ 3. Water is heated and changed to steam. _______ 4. Iron rusts. _______ 5. Evaporation _______ 6. Milk sours. _______ 7. Ice melting. _______ 8. Wood rotting. _______ 9. When placed in H2O, a sodium pellet catches on fire as H2 gas is liberated and sodium hydroxide forms. _______ 10. Grass growing in a lawn. _______ 11. A tire is inflated with air. _______ 12. Food is digested in the stomach. _______ 13. Water is absorbed by a paper towel. _______ 14. Sugar dissolved in water. Review: What is the law of conservation of energy?