What is a property?

Reviewing MATTER
Matter: anything that has mass and volume
Mass – the amount of matter in something
Volume – the amount of space something occupies
Physical and Chemical Properties of
Matter
Why do I care? Understanding the different properties of matter will help you to better classify and describe the world around you.
What is a property?
Property: a characteristic of a substance that can be observed
It can be a physical or chemical property.
Physical Property
- A property that can be observed and measured without changing the material’s composition.
EXTENSIVE Physical Property
Extensive - Properties that depend on the amount of matter present.
• Mass - A measurement of the amount of matter in a object (grams).
• Weight - A measurement of the gravitational force of attraction of the Earth acting on an object.
• Volume - A measurement of the amount of space a substance occupies.
• Length
Extensive Physical Properties
Look at your pencil or pen, if you break it in half, the extensive properties will be different.
The pieces will have a different mass, weight, volume, and length.
Extensive properties depend on size
INTENSIVE Physical Property
Intensive - Properties that do not depend on the amount of the matter present.
Color
Odor
Luster
Malleability
Ductility
Electrical Conductivity
Hardness
Melting/Freezing/Boiling Points
Density
State of Matter
Intensive Physical Properties
Look at your pencil or pen, if you break it in half, the intensive properties will be the same.
It’s still yellow, the graphite still has a hardness of 2, the density of each piece hasn’t changed, and it’s still a solid.
Intensive properties DON’T depend on size
Chemical Properties
Chemical property: a property that can only be observed by changing the composition of the material.
Does it have the potential to change into a new substance?
Examples:
• Will it burn?
•Will it rust?
•Will it react with vinegar
(acids) or other chemicals?
Physical and Chemical Properties can be used to identify matter
Gold or fool’s gold?
Diamond or quartz?
Oak or Maple?
Metamorphic or
Igneous?
Zinc or Aluminum?
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uJ
OGy0dgmUU
Properties song
PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL
CHANGES
Changes in Matter
Change: the act of altering a substance
In science, we talk of two types of changes: physical chemical
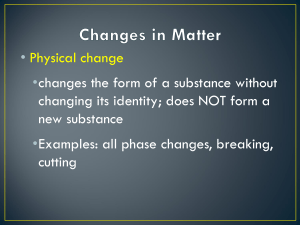
Physical Change
Physical change: a change that occurs that does not change the identity or make up of the substance
Change in state or phase (Freezing, boiling, melting, sublimating)
Changing shape (cutting, folding, twisting, bending)
Dissolving
Physical Changes
Physical changes are changes that alter the size, shape, location or physical state of a substance but not its chemical state.
Its still H
2
O- frozen in snowflakes, as liquid in raindrops, or as a gaseous water vapor, it’s chemical formula has not changed.
Examples
A physical change in a substance doesn't change what the substance is.
Cutting, folding, or crumpling paper –
A physical change in the shape and size of the paper. However, it is still paper!
Dissolving sugar in iced tea-
Sugar is still C
6
H
12
O
6 but now it is spread out in the liquid, it still tastes just as sweet!
What Other Kinds of Changes Are
Physical?
Cutting
Tearing
Shredding
Shrinking
Enlarging
Change in Phase
Relocating
Rotating
Molding (shaping)
Chemical Changes
Chemical change: a change that occurs causing the identity of the substance to change
Burning
Chemically digesting food (acid and bile)
Reacting with other substances
A chemical change is also called a chemical reaction
Chemical Changes
Chemical changes are changes that alter the chemical make up of the substance.
New matter is formed with properties that are different than those of the original matter.
Chemical Changes
If you end up with a chemical or chemicals that you did not start with. . .
It is a chemical change!
Chemical Changes
A chemical change is not easily reversed.
Easy to reverse/change back
Difficult to reverse/change back
Signs That a Chemical Change has occurred
Creation of a gas (bubbles)
Creation or loss of heat
Fire
Rotting/molding
Breaking down (decomposition)
Precipitation (Sour milk clumps)
Cooking
Rusting (oxidation)
Chemical Change
Heat and light are often evidence of a chemical change.
The strike of a match is a chemical change due to the reaction of the chemicals with oxygen.
Burning wood turns to charcoal and ashes.
This is a chemical change .
Is it Physical or Chemical?
Chemical Change
Melting cheese
Burning wood
Milk souring
Folding up paper
Bicycle rusting
Physical
Why do I care?
Physical and
Chemical changes occur around us everyday!
Understanding them will help us better understand our world.
Start physical changes challenge Powerpoint