Animal Body Systems
advertisement

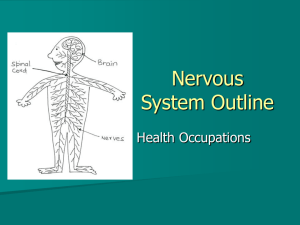
Animal Systems: REGULATION Nervous System The nervous system maintains homeostasis (an internal stable environment) by… Functions of the Nervous System 1. - uses receptors to gather information from all over the body 2. -the brain then processes the information into possible responses 3. -sends messages back through the system of nerve cells to control body parts Evolutionary Trends of the Nervous System Animal Taxon Type of Nervous Tissue Aquatic Invertebrates Flatworms & Roundworms Segmented Worms & Arthropods Vertebrates A simple system with interconnected neurons called ; contain specialized cells for touch and chemical detection (a group of nerve cells) and nerve cords run along the body; can detect chemicals, touch, and some have eyespots occurs which is the concentration of nerve cells in a head region to form ; intense senses in arthropods A well-developed brain evolved from the spinal cord; the size and complexity increases from . planaria, flukes, earthworm, ants, mammals, birds, reptiles, fish, tapeworm, hookworm grasshopper, bees amphibians Picture of system Examples sponges, jellyfish, hydra Structure of the Nervous System: Neuron – 1. - the largest part of the neuron; contains the nucleus and organelles 2. - short, branching extensions spreading out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. - long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body What is a nerve impulse? An signal is sent from the dendrite, along the axon, to the terminal. A message, called a_____ _______ is released from the axon terminals into the _______ , where it travels to the next cell. **Flow of Impulse: _____________ cell body (nucleus) _______ jumps synapse next dendrite** Types of Neurons a. neurons carry messages from sense organs to the brain/spinal cord(CNS) b. neurons carry impulses from the brain/spinal cord (CNS) to the muscles/organs. c. carry impulses between sensory and motor neurons (within the CNS). Reflexes: They are ______________________, happen very quickly, take place _____________ the brain receiving the message, they protect you by triggering an involuntary response to stimuli (stepping on a tack). Divisions of the Nervous System (CNS and PNS) I. Central Nervous System (CNS) – derived from dorsal nerve cord A. Brain- “control center”- _______________ and analyzes information; processes and sends back instructions Cerebrum: controls ______________, language, learning/studying, judgment, & voluntary actions Lobes of the Cerebrum: write what each lobe does…. • • Language and Speech – strokes, tumors, injuries Broca’s Area: – Primary motor cortex in the ______________ that controls muscles – Damage to area means you can understand language but are unable to speak it • Responsible for speech generation Ex – stroke patients Wernicke’s Area: • The posterior part of __________________ • Damage to area means you can speak but unable to comprehend speech • Responsible for hearing speech Cerebellum: controls _____________________ functions of muscles and maintains ________________ Hypothalamus: Controls ____________________ in body (body temperature, water balance, hunger, thirst, biological clock, flight or fight response) Brain Stem: controls involuntary functions Medulla Oblongata & Pons: controls basic primitive body functions such as __________________, heart ______________, blood pressure, etc. II. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) A. Consists of nerves outside the CNS. Nerves: B. Gathers information and ______________________ it to and from ______________ C. PNS divided into two systems: 1. ___________________(voluntary) 2. ___________________(involuntary) Autonomic Nervous System – the_________________________branch of the nervous system Divided into two division: _________________ division _________________ division Sympathetic – “Fight-or-flight” Response to unusual stimulus Takes over to _______________activities (increase heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar level, dilates bronchioles in lungs, dilates pupils) Parasympathetic – “Rest and Digest” Chiefly concerned with promoting normal digestion and elimination of feces and urine and with conserving body energy ( normal low levels of heart rate, blood pressure, etc. pupils constrict) Levels of Organization Interaction with other systems for Regulations Bones of the protect the spinal cord and brain. The brain controls heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing via the and . Glands in the brain control the release of hormones of the and systems. The brain controls muscles both in and . Diseases and Disorders of the Nervous System 1. ___________________- a virus that attacks the spinal cord; eventually causes paralysis 2. _________________________________ (MS)- affects neurons; slows nerve impulses, causing muscle weakness, possibly paralysis. 3. ___________________________________- brain tissue deteriorates; severe memory loss 4. _______________- a blockage in a blood vessel in the brain, causing brain damage 5. ______________________- a bruise to the brain when the brain hits the inside of the skull Fun Facts A human body contains more nerve cells than there are stars in the Milky Way Neurons are the largest cell in the body and do NOT undergo mitosis Nerve impulses move at 100 meters per second or more Longest axon of a neuron is 15 ft! (in the giraffe) Animal Systems: REGULATION Regulation requires - the ability of the body or a cell to seek and maintain stability within its internal environment when dealing with external changes The nervous system maintains homeostasis by… The excretory system regulates the concentration of water and other components of body fluids like salts and nutrients. Every organ system plays a role in maintaining the constancy of the internal environment. – Examples: Homeostatic Control Mechanisms • __________________ within the body is essential for homeostasis. • Homeostasis is accomplished primarily by: – Endocrine system (hormones) – Nervous system (electrical signals) Negative Feedback vs. Positive Feedback Mechanisms Negative Feedback Mechanism – The net effect of the response to the stimulus is to shut off the original stimulus or to _______________ its intensity. – Examples: Thermostat or body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, blood levels Positive Feedback Mechanism – Feedback that tends to cause a variable to change in the same direction as the initial change; __________________ the stimulus – Examples: Blood clotting, birth of a baby – More __________ in the body The Excretory System Evolutionary Trends: Animal Taxon Release Wastes By… Picture of system Aquatic Invertebrates to remove waste across their cell membranes directly into the water Worms and Mollusks Use of _____________________tiny pores along the body excrete waste Insects Vertebrates Using __________________to collect and excrete wastes Use of kidneys, ureters, and a bladder to collect and excrete waste Function- Maintains Homeostasis in 3 Steps: 1. - Filters substances from the blood 2. - Regulate the chemical composition of body fluids by retaining the proper amounts of water, salts, and nutrients 3. - Elimination of wastes in the form of urine Major Organs: Kidneys (renal = kidney) o _____________ organs that receive blood via the o The main filters are tissues called that separate the components of the blood o Every 45 minutes ______________ filter all the __________________in your body o Filtered blood leaves kidneys and returns to circulation carrying nutrients, salts, and water via the o Excess _____________ and toxic waste in the form of ______________ leave the kidney via the ______________________ o Urea is a waste product found in __________ – it contains excess _________________ and is the result of protein ________________________. o Sometimes excess ____________ or minerals in the urine crystallize and form ___________ . When kidney stones block the , they cause great pain. Ureters—tubes that carry urine from Bladder—muscular sac where Urethra—tube that carries urine from to urinary is temporarily stored before being excreted to _________________ the body. Levels of Organization within the Excretory System renal cells nephrons kidney, bladder, ureter, urethra excretory Organism Respiratory system (lungs) remove CO2 from blood. Circulatory systems (blood) brings wastes to lungs, kidneys, skin for excretion. Integumentary system (skin) excretes water, urea, salts, through sweat.