Short Stories Literary Terms
advertisement

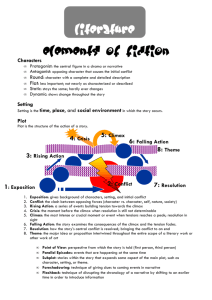
Introduction to Short Stories Plot triangles, literary terms and reading strategies What is a plot triangle? A plot triangle shows the typical progression of events in a story. There are five parts of a plot triangle: exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. Also known as Freytag’s Pyramid Freytag’s Pyramid (Plot Triangle) Climax Rising Action Exposition Falling Action Resolution Exposition (introduction): The beginning of a story that introduces characters, setting and conflict. Rising Action: Conflict is established and intensifies. Climax: Highest point of action in story or turning point in the story. Falling Action: Conflict is in process of being resolved; all action following climax Resolution: Conflict is resolved and “loose ends” are tied up. Assignment Choose a fairy tale: “Little Red Riding Hood,” “Three Little Pigs” or “Hansel and Gretel.” As a group, retell the story. Create a plot triangle for your group’s fairy tale. Literary Terms Definitions and Examples Setting The time and place a story takes place Example: Monster takes place in a prison/courtroom in New York City around 2000. Simile A comparison of two unlike objects using like or as. Example: The water hit me like a bull running a full speed. Metaphor A direct comparison of two unlike objects. Example: The sun is a bright yellow beach ball floating in the sky. Personification Giving a non-human object human characteristics. Example: The tree limbs waved hello to me from the distance. Protagonist The main character of the story (not always the good guy) Example: The protagonist of Monster is Steve. Antagonist The character who causes problems or opposes the main character (not always the bad guy) Example: The prosecutor, Petrocelli, is the antagonist in Monster. Conflict A struggle or clash between opposing characters or opposing forces. Example: Two students arguing over who is right. Two types of conflict Internal Conflict External Conflict A struggle within the mind of a character. Person vs. himself Example: A character cannot decide whether to skip school or go to class. A struggle with an outside opposing force. Person vs. person, person vs. nature, person vs. society . Alliteration Repetition of the same consonant sounds at the beginning of words that are close together in a passage or poem. Example: The beautiful baby boy waved bye-bye to his brother. Onomatopoeia A word whose sound imitates its meaning. Examples: The bee buzzed my ear. The thud of the book landing on the carpet scared me. Theme Central idea of a work or literature (moral of the story) Example: The theme of Monster was to be careful who you hang around because you will be judged by the company you keep. Hyperbole A gross or extreme exaggeration of a truth to show strong emotion or for humor. Example: When my mom saw my report card, she was so mad I thought her head would explode. Foreshadowing Hints and clues to events that will happen later in the story. Pun A play on words using 1. Two words that sound the same but have different meanings. 2. A word with more than one meaning.