Elements of Fiction Handout
advertisement
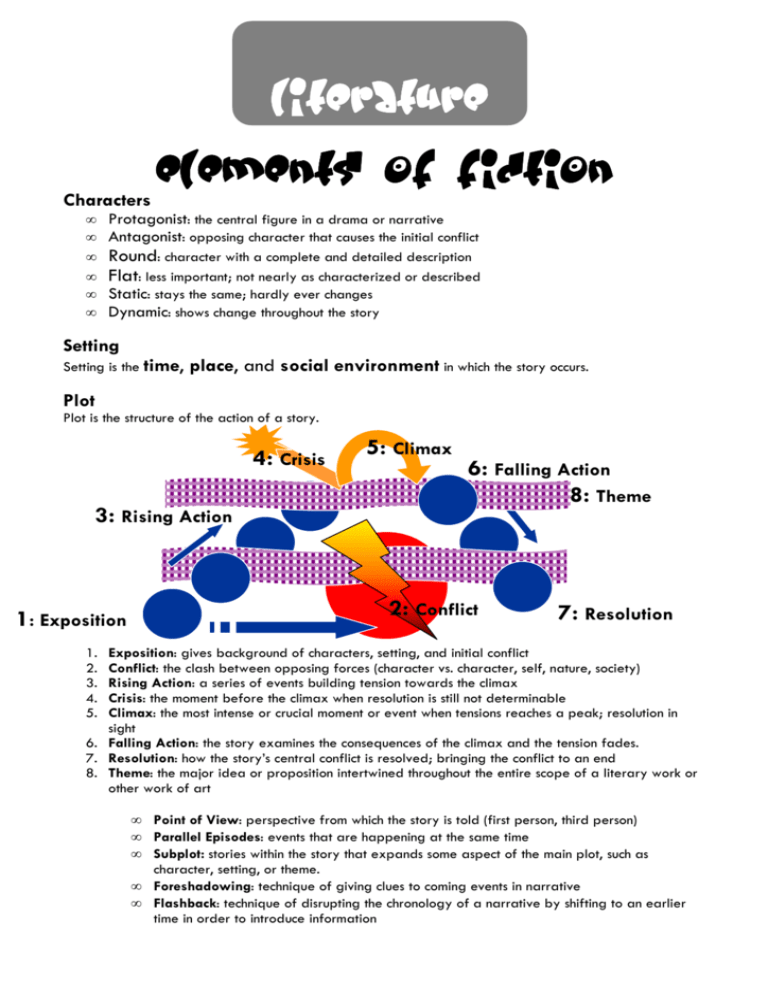
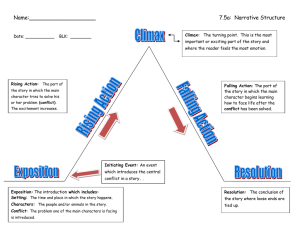
literature Elements of Fiction Characters • • • • • • Protagonist: the central figure in a drama or narrative Antagonist: opposing character that causes the initial conflict Round: character with a complete and detailed description Flat: less important; not nearly as characterized or described Static: stays the same; hardly ever changes Dynamic: shows change throughout the story Setting Setting is the time, place, and social environment in which the story occurs. Plot Plot is the structure of the action of a story. 4: Crisis 3: Rising Action 5: Climax 6: Falling Action 8: Theme 2: Conflict 1: Exposition 7: Resolution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Exposition: gives background of characters, setting, and initial conflict Conflict: the clash between opposing forces (character vs. character, self, nature, society) Rising Action: a series of events building tension towards the climax Crisis: the moment before the climax when resolution is still not determinable Climax: the most intense or crucial moment or event when tensions reaches a peak; resolution in sight 6. Falling Action: the story examines the consequences of the climax and the tension fades. 7. Resolution: how the story’s central conflict is resolved; bringing the conflict to an end 8. Theme: the major idea or proposition intertwined throughout the entire scope of a literary work or other work of art • • • • • Point of View: perspective from which the story is told (first person, third person) Parallel Episodes: events that are happening at the same time Subplot: stories within the story that expands some aspect of the main plot, such as character, setting, or theme. Foreshadowing: technique of giving clues to coming events in narrative Flashback: technique of disrupting the chronology of a narrative by shifting to an earlier time in order to introduce information