National Income Definitions, Calculations
advertisement

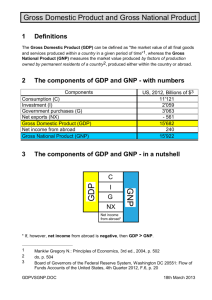
Economics – may revision NATIONAL INCOME DEFINITIONS National Income Income which accrues to the permanent residents of a country from current economic activity in the production of goods & services during a specific period, usually a year. NNP@FC It includes income in kind but excludes transfer payments Net National Product The total of all payments for productive serves accruing to the permanent resident s of a country. It is calculated using a value added approach Gross Domestic Product The output produced by the factors of production in the domestic economy irrespective of whether those factors are Irish or foreign owned. It is the value, in money terms, of the final output in the economy over a specified period, usually 1 year Gross National Product The value at current market prices of goods & services produced in the economy in a specified period ie the total expenditure on the output of goods & services of the national economy valued at the prices paid for them Transfer Pricing When multinational companies try to reduce their total tax bill by underpricing ( or price at zero profit) components/services supplied from subsidiaries in higher corporate tax economies, to subsidiaries in lower corporate tax economies. This increases the apparent value, added in the low corporate tax economy, over inflating GDP figures and reducing the company’s total tax bill. GNP V’s GDP The difference between GNP & GDP is Net Factor Income from Abroad ( NFIA ). NFIA is comprised of profit, interest & wages earned by Irish people living abroad, less similar payments from foreigners living in Ireland. As a result of large scale repatriation by multinationals operating in Ireland, NFIA is negative & when added to GDP to calculate GNP, it makes it a smaller figure. GNP is a more accurate measure in Ireland. Due to the presence of large multinational sector which repatriates profits back to the courtiers which their primary base of operations are located. GDP overstates income per capita in Ireland, This problem is exacerbated by the low corporate tax rate in Ireland which leads to transfer pricing by multinationals, which over states the profits actually earned by the economic activity which took place in Ireland. Net Factor Income from Abroad Profits, wages, Interest earned by Irish people living abroad and Irish owned subsidiaries abroad, less similar payments from foreign people living abroad and foreign owned subsidiaries in Ireland Income in Kind Non money income. It can refer to government provided services such as food stamps, education, medical aid, housing assistance or any good/service that can be consumed. For example, the benefit received from the use of a company car A farmer consuming some of his produce Transfer Payments A redistribution of income by the government. The payments are for providing non productive services paid for out of the tax revenue. Social welfare payments are an example Fiscal Deficit The balance between the amount of money the government collects (taxes, source of income ) less the expenditure ( goods/services, transfer payments ) In a recession, unemployment rises, taxes revenues fall. If the government spends more than it receives then it must borrow to make up the difference. Balance of Payments A record of the countries transactions with the rest of the world. BOP deficits are Imports are greater than Exports. Ireland is a small open economy. Small = Irish firms have a small share of the world economy Open = refers to the importance of International trade in the economy Domestic V National Domestic includes all income from the multinationals National is Irish, the income/money that stays in Ireland The only difference between them is NFIA Unemployment Unemployment A person is regarded as “unemployed” if they are out of work but are willing to accept a job at the going rate for what they are qualified for. Frictional This occurs as workers spend time searching for jobs. Even at full employment such frictional unemployment will occur. As some firms close, others open. Some people lose their jobs, people switch between jobs Structural This arises due to the mismatch between the types of jobs available & the skill of the workforce. This can be as a result of a change in the structure of an industry brought by technical progress, competitive forces, and changes in relative factor costs. Whole regions & sectors may decline & many people may never work again Deficient demand or Cyclical This is the most frequent type of unemployment. Deficient demand in the economy can give rise to unemployment. This can be brought about by the changes in activity associated with the business cycle Classical This occurs when wages are too high – above the level that equates to supply/demand. It can be caused by either the exercise of Trade Union Power or by legislation which forces minimum wage above the equilibrium wage Seasonal Simply some jobs are seasonal i.e. Agriculture, tourism, Xmas. Double Counting Double counting would occur if expenditure on intermediate goods was included in the calculation for national incomes i.e. include the price paid for the car but not the price the manufactured paid for the tyres. Double counting should be avoided and shall not be included in the calculation for national income. We use the value added approach to avoid this Inflation Inflation is a continuing or persistent tendency for the price level to rise. It is a continuous decrease in the purchasing power of money. The most usual measure of consumer prices is called the consumer price index CPI. Non Marketed/Government services Government provides certain services without a direct charge eg, police, ambulance, street lighting These should be included in the national accounts but at cost price as there is no selling price Figuring out National Income Formula’s C + I + G + (X - M) = GDP@mp NNP@fc = National Income GNDI = GDP@mp + NFIA + NTFA Once you know GDP@mp you can figure everything else out. From MP to FC GDP@mp - InTax + Sub = GDP@fc From Gross to Net GDP@fc - Dep = NDP@fc From Domestic to National NDP@fc + NFIA = NNP@fc Income method By adding together the income received by all of people in the economy for the factors of production they supplied during the year. Only income received for productive activity should be included, therefore, income in kind should be included & transfer payments should excluded. Expenditure Method The calculation of the total amount spent on goods and services and on net additions to capital stock and goods in the country in the course of a year. Output method The calculation of the total output of consumer ( or final ) goods and services that produced during the year. Uses To indicate the standard of living For standard of comparison To calculate the rate at which income is growing Relationship between different parts of the economy To assist the government in managing the economy The business Cycle Nominal GNP = Real GNP x price level When GNP changes it is important to distinguish between changes due to changes in the price level and changes to the volume of output ( real GNP ) Year 1 2 Nominal GNP 1,000,000 2,000,000 = Real GNP 500,000 500,000 X Price Level 100 200 Although nominal GNP has doubled, real GNP was unchanged, so the standard of living i the economy remain unchanged. Improvements in the standard of living only come through changes in real GNP