(Progressive Reformers and their Impact).
advertisement

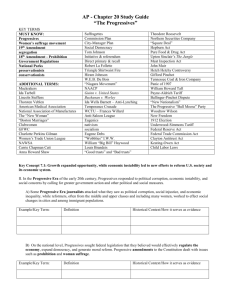
Progressive Era 1900-1916 Reform Movements Populists Farmers Rural Problems Progressives Middle Class Urban Problems Progressives Increase Democracy End Corruption Help Working Class Progressives: Reformers who attempted to rectify the problems caused by the Industrial Revolution & Big Government Muckrakers: writers exposed problems of society Goals of Progressives make government more responsive & responsible limit power of party bosses & political machines increased participation by responsible citizens end laissez-faire trust-busting women’s suffrage conservationism Women Leaders Women’s Rights: Alice Paul Urban: Jane Addams Prohibition: Carrie Nation Civil Rights Racial Equality: Booker T. Washington & W.E.B. DuBois Anti-Lynching League: Ida B. Wells Barnett Reforming State & City Government direct primary system initiative & referendum recall elections tax reform City Commissions Election of Officials fight city bosses & machines Muckrakers: writers exposed problems of society Upton Sinclair, The Jungle Lincoln Steffens, The Shame of the Cities Ida Tarbell, History of Standard Oil Jacob Riis, How the Other Half Lives William R. Hearst, publisher Teddy Roosevelt trust-buster supporter of Labor Anthracite Coal Strike Civil Rights Conservation Movement William Howard Taft Ballinger-Pinchot Controversy on conservation T.R. challenged Taft Progressive (Bull Moose Party) Election 1912 Woodrow Wilson Southern Scholar Federal Reserve Act Clayton Anti-Trust Act Keating-Owen Act Women’s Suffrage controversy