SMART CHEM 1022 Review All questions are adopted from Prof
advertisement

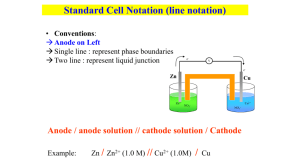
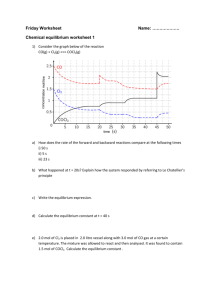
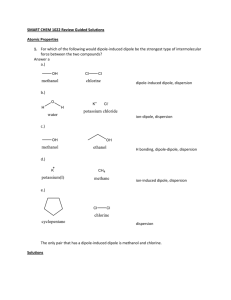
SMART CHEM 1022 Review All questions are adopted from Prof. Leopolds Spring 2007 and 2006 exams Atomic Properties 1. For which of the following would dipole-induced dipole be the strongest type of intermolecular force between the two compounds? a. methanol (CH30H), Cl2 b. water, KCl c. methanol (CH30H), ethanol (CH3CH2OH) d. K+, methane (CH4) e. cyclopentane (C5H10), Cl2 Solutions 1. C6H12O6 is dissolved in 1.00L of H2O whose initial vapor pressure is 23.8 torr. After addition of the sugar, the vapor pressure of the solution drops to 21.4 torr. Using this information, calculate both the mole fraction of the solute and the mass, in grams, used. 2. Which of the following liquids would have the lowest boiling point? a. NaCl (0.75 m in water) b. NaN03 (0.25 m in water) c. methanol (0.25 m in water) d. pure water e. the lowest boiling point cannot be determined 3. Assuming ideal behavior, what is the freezing point of a 0.70m solution of glucose in water? (water has Kf=1.86 °C/m, Kb=0.51°C/m, 18.0 g/mol) a. 1.30 ºC b. 0.36 ºC c. 0.00 ºC d. -0.36 ºC e. -1.30 ºC Rate Laws Initial Rate Experiment 1 2 [𝐴]0 𝑀 4.00 4.00 [𝐵]0 𝑀 4.00 2.00 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐿∙𝑠𝑒𝑐 640.0 80.0 1. An experiment is done to determine the rate law for a reaction which uses two reactants, A and B. Determine the rate law from the following experimental data: 3 4 1.00 1.00 2.00 1.00 20.0 2.5 2. The reaction 2N205 (g) → 02 (g) + 4NO2 (g) is first order in N205. At a particular temperature, the rate constant is 1.0 x 10-4 s-1. If initially the [N205] = 0.0040 M, what is the [N205] after 20,000 seconds. a. 0.0041M b. 0.0026M c. 0.0015M d. 0.00054M e. 0.00020M 3. For a reaction in which A and B react to form C, what is the rate law for the reaction in which the following initial raw data was obtained? a. b. c. d. [A]0 (mol/L) [B]0 (mol/L) Initial Rate of Formation of C (mol/Ls) 0.2 0.4 2.00 0.2 0.8 4.00 0.2 1.6 8.00 0.4 0.4 8.00 0.8 0.4 32.00 rate = k [A]2[B] rate = k [A][B]3 rate = k [A]2[B]2 rate = k [A]2 e. rate = k [A]2[B]3 Properties of solutions 1. 0.500 grams of a non electrolyte is dissolved in 25.0 mL of H2O which decreases the freezing point by 0.180⁰C. Given that the Kf and Kb for H2O is -1.86 and 0.512 ℃ 𝑚 respectively, what is the molar mass of the solute? Equilibrium 1. If the equilibrium for the reaction 𝐶𝑙(𝑔)2 + 2𝑂(𝑔)2 ↔ 2𝐶𝑙𝑂(𝑔)2 is 2.9 × 10−21 , what is the partial pressure of ClO2 from the reaction of 1.00 atm of O2 and equal amounts of Cl2? 2. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. 2A ⇌ B + 2C Initially the concentration of A was 5.5M, B was 2.0 M and no C was present. At equilibrium the concentration of A was 2.5 M. a. 6.3 b. 5.0 c. 4.6 d. 2.4 e. 1.0 Acid Base 1. If 0.050 L of 0.100M acetic acid, with a pKa of 4.76, is titrated with 0.015L of 0.100M NaOH, what will the resultant pH be? 2. What is the pH of 0.90 M NH3 solution? Kb=1.8x10-5 a. 2.56 b. 4.56 c. 7.40 d. 9.10 e. 11.60 Thermodynamics 1. Under what conditions is a reaction non-spontaneous at all temperatures? 2. For the following reaction at equilibrium, which choice gives a change that will shift the equilibrium to the left? ∆H°= 30kJ 2NOBr (g) ⇌ 2NO (g) + Br2 (g) a. b. c. d. e. increase the volume remove Br2 remove NOBr remove NO two of these changes 3. Which of the following results in a decrease in the entropy of the system? a. 02 (g), 300K → 02 (g), 400 K b. H20 (l) → H20 (g) c. 2N02 (g) → N204 (g) d. NH3 (s) → NH3 (l) e. 2H20 (g) → 2H2 (g) + 02 (g) 4. Given N2H4 (l) + 2H20 (l) ⇌ N2 (g) + 4H20 (g) ∆°H = -530kJ at 298K Which of the following is true? a. the reaction is spontaneous at high temperatures b. the reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures c. the reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures d. the reaction is not spontaneous at any temperature Electrochemistry 1. A galvanic cell uses a hydrogen electrode and lithium. Given that the standard reduction potential of lithium is -3.0401 and that of hydrogen is zero, what is the chemical potential of the battery if the initial concentration of ionic lithium is 5mM? 2. An electrochemical cell involves the following half-reactions. Under standard conditions, what species are produced at each electrode? Ag+(aq) + e- → Ag(s) Cu2+(aq) + 2e- →Cu(s) 0.80V 0.34V a. b. c. d. 3. Ag+ (aq) is produced at the cathode and Cu(s) at the anode Ag+ (aq) is produced at the anode and Cu (s) at the cathode Ag (s) is produced at the anode and Cu2+ (aq) at the cathode Ag (s) is produced at the cathode and Cu 2+ (aq) at the anode For the reaction Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) ⇌ Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq) the cell voltage is 1.10 V under standard conditions. What is the voltage if [Cu2+] =0.200M and [Zn2+]=0.060M? a. 1.01 V b. 1.12 V c. 1.19 V d. 1.26 V e. 1.41 V



![CHEM 1520 SI MON, TUES, & WEDNES 1.Calculate [H3O+] in a](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007346334_1-b78d73402f58153c92290299886ff084-300x300.png)