MBA Module 3 PPT
advertisement

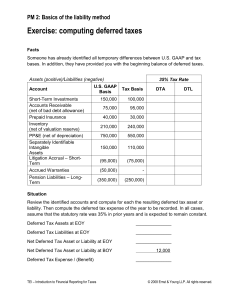
Module 5 Reporting and Analyzing Operating Income Revenue Recognition Revenue recognition criteria 1. 2. realized or realizable, and earned Realized or realizable means primarily that cash is collected or a receivable is collectible. Earned means that the seller has performed its duties under the terms of the sales agreement. Revenue may be questioned, when… Rights of return exist Continuing involvement by seller in product resale Contingency sales Revenue Recognition Challenges Case 1: Channel stuffing Case 2: Barter transactions Case 3: Mischaracterizing transactions as arm’s-length Case 4: Pending execution of sales agreements Case 5: Gross versus net revenues Case 6: Sales on consignment Case 7: Failure to take delivery Case 8: Nonrefundable fees Percentage-of-Completion Method appropriate for sales made with long-term contracts: construction, defense contracts The percentage-of-completion recognizes revenue by the proportion of costs incurred to date compared with total estimated costs. Subject to manipulation of the estimated costs. Percentage-of-Completion Assume that Bayer Construction signs a $10 million contract to construct a building. Bayer estimates construction will cost $4,500,000 the first year and $3,000,000 for the second year. Research and Development (R&D) Expenses Expense all R&D costs as incurred unless those assets have alternative future uses (in other R&D projects or otherwise). For example, a general research facility housing multi-use lab equipment is capitalized and depreciated like any other depreciable asset. However, project-directed research buildings and equipment with no alternate uses must be expensed. How is R&D Reported by Cisco? 13% of sales Restructuring Expenses Restructuring costs typically consists of three components: Employee severance or relocation costs Asset write-downs Other (i.e., contract termination costs, legal expenses, etc.) Accounting standard: A company is required to have a formal restructuring plan that is approved by its board of directors before any restructuring charges are accrued. Also, a company must identify the relevant employees and notify them of its plan. In each subsequent year, the company must disclose in its footnotes the original amount of the liability (accrual), how much of that liability is settled in the current period (such as employee payments), how much of the original liability has been reversed because of cost overestimation, any new accruals for unforeseen costs, and the current balance of the liability. Income Tax Expenses Companies maintain two sets of accounting records, one for preparing financial statements for external constituents, including current and prospective shareholders, and another for reporting to tax authorities. Two sets of accounting records are necessary because the U.S. tax code is different from GAAP. Deferred Tax Liabilities and Assets Deferred tax liabilities Arise when reported income is higher than taxable income. Depreciation. Deferred tax assets Arise when reported income is lower than taxable income. Unearned revenues, bad debt expenses. Loss Carryforwards When a company reports a loss for tax purposes, it can carry back that loss for up to two years to recoup previous taxes paid. Any unused losses can be carried forward for up to twenty years to reduce future taxes. This creates a benefit (an “asset”) on the tax reporting books for which there is no corresponding financial reporting asset and thus the company records a deferred tax asset. Income Tax Footnotes Income tax expense reported in its income statement (called the provision) consists of the following two components (organized by federal, state and foreign): Current tax expense - the amount payable (in cash) to tax authorities Deferred tax expense - the effects on tax expense from changes in deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets Pfizer’s Income Tax Footnote Income tax expense is the sum of 1. Taxes currently payable 2. Deferred income taxes Extraordinary Items The following items are generally not reported as extraordinary items: Gains and losses on retirement of debt Write-down or write-off of operating or nonoperating assets Foreign currency gains and losses Gains and losses from disposal of specific assets or business segment Effects of a strike Accrual adjustments related to long-term contracts Costs of a takeover defense Earnings Per Share Global Accounting – R&D U.S. GAAP expenses all R&D costs IFRS allows capitalization and subsequent amortization of certain development costs that meet a list of requirements.