Chapter 5 – Practice Problem Sets Stereochemistry
advertisement

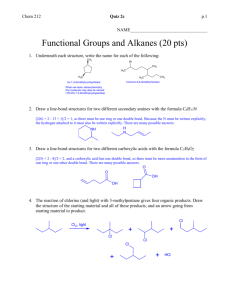
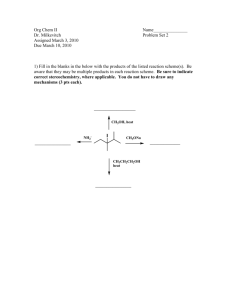
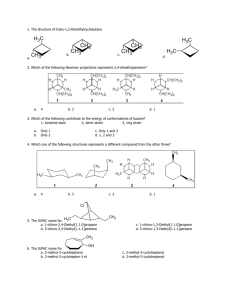
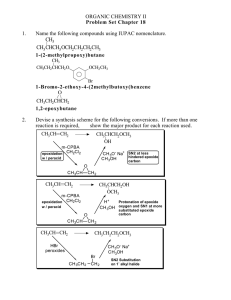
Chapter 5 – Practice Problem Sets Stereochemistry Problem #1: Draw the cis and trans stereoisomers of the following compounds. a) 1 – ethyl – 3 – methylcyclobutane b) 2 – methyl – 3 – heptene c) 1 – fluoro – 4 – iodo – cyclohexane d) 1,3 – dichlorocyclobutane Problem #2: Tetracycline is a broad - spectrum antibiotic used to treat such diseases as Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and acne. Answer the following questions on this antibacterial using the structure shown below. N OH H3C H OH NH2 OH OH O OH O O a) Indicate the hybridization of all carbons. b) Designate all asymmetric carbons with an asterisk. c) Assign a configuration of R or S to each chiral carbon. Problem #3: Provide the correct systematic name (IUPAC name) of the following compounds, including the proper R or S designation. CH(CH 3)2 a) H3C C CH 2Br CH 2CH 3 b) CH 3CH 2 C CH 2Cl CH 2CHCl c) NH2 CH=CH 2 OH d) H OH e) Br CH2CH3 CH2I f) H CH 2C(CH 3)3 H CH2OH OCH2CH3 N(CH3)2 Problem #4: Which of the following cyclic compounds are chiral? Explain. Cl Cl a) Cl b) Cl Cl c) Cl d) Cl 1 Cl Cl e) CH 2Cl Problem #5: Determine whether each of the following pairs are enantiomers, diasteriomers, constitutional isomers, or the same compound. CH 2CH 3 CH 3 H CH3 H3C H H OH HO H H Br H H a) and H b) Br Br Br and H3C H c) H H CH3 and Br H CH 2CH 3 and H CH 2CH 3 Br Br OH e) CH2CH3 and HO CH3 Br CH 3 OH d) H3C H HO Cl Problem #6: Provide the product(s) obtained when the following reagents are reacted with cis–2–butene and trans–2–butene. If the products exist as specific stereoisomers, show which isomers are formed. a) H2O, H2SO4 b) Br2, CH2Cl2 c) Br2, H2O d) 1) Hg(OAc)2, H2O 2) NaBH4 e) 1) BH3/THF 2) –OH, H2O2, H2O f) H2SO4, CH3OH g) HCl h) peroxyacid i) H2, Pd/C Problem #7: Define and describe the following terms. Provide an example. a) racemic mixture b) enantiomers c) diasteriomer d) constitutional isomer e) asymmetric carbon f) meso compounds g) syn addition h) anti addition Problem #8: The specific rotation of (R) – (+) – glyceraldehyde is +8.7o. Determine the percent of (R) – glyceraldehdye in a mixture with the indicated specific rotations. a) 0o b) +1.4o c) –8.7o d) +8.0o e) –3.4o Problem #9: Carbon is not the only element that produces a chiral center. Determine the R or S configuration for the compounds below. If it does not contain an asymmetric element, explain why. CH=CH 2 a) H3C N + H O Cl - b) H3CO CH 2CH 3 P H OCH 2CH 3 2 c) .. NC N H CH 2CH 3 Cl