Volcanoes
advertisement

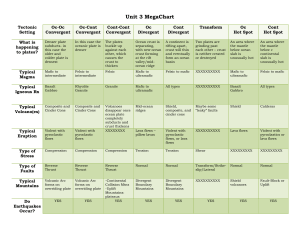
Parts of a volcano Magma chamber Neck ◦ Vent/crater Cone/ash/lava flow Tephra/SO2/gases Steep sided cone Explosive eruptions Lava type: tephra ◦ felsic ◦ Traps gases, thick Example: Paracutin Mexico Plate bound – c/c Rounded sides ◦ Dome Quiet eruptions Lava type: flows and fountains ◦ Mafic – no granite, little gases, flows readily Example: Hawaii Plate bound: o/o Cone not as steep as a cinder cone Layers of tephra and lava flow felsic and mafic Explosive and quiet eruptions Example: Mt. St. Helens, Mt Ranier Plate bound: o/c Pahoehoe: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Quiet Lava flow Finger-like projections Fast flowing like a river Aa - A type of lava having a rough, jagged surface. It is relatively slow moving , thick in the form of massive blocks The blocks size between the size of a football and the size of a house. Pele’s hair ◦ Spun glass ◦ Made by fountains ◦ https://www.youtu be.com/watch?v=O EMyYNziXrc ◦ https://www.youtu be.com/watch?v=Q 8NXO6YxBmU Pele’s tears Volcanic glass A pyroclastic flow a fast-moving current of hot gas and rock (collectively known as tephra), speeds moving away from a volcano of up to 450 mph. Felsic Mafic Temp Low High SiO2 content High > 70% Low <50% Volatile content High 10% water Low <2% viscosity High (very thick) Low (very fluid) Type volcano Type lava Type boundary Dome/shield Hawaii Mafic o/o Hot spot Cinder cone Felsic c/c Mafic and Felsic o/c Vesuvius/Etna Composite/Strato Mt. St. Helen’s Type of Eruption quiet explosive quiet/explosive