Energy Forms
advertisement

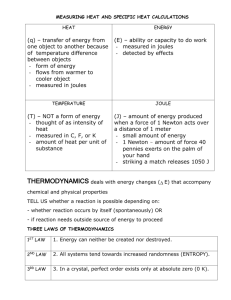
Energy is something that does something to matter. Energy Energy is the ability to do work - make things move. does not have mass or volume (matter) described by the things that it does - its interaction with matter can move by itself or through matter measured in joules (J) E=MC2 James Prescott Joule 1818-1889 Newton’s Second Law: F=ma; force = mass times acceleration A force (f) is any push or pull or any influence that can change the motion of an object such as gravity. Forces are measured in the metric system by a unit called a newton (N). Weight is the force due to gravity. 1 newton equals a force that will give a 1 kilogram mass an acceleration (a = m/s2) of 1 meter per second per second (kg)(m)/(s2). Instead of saying: kg×m/s2 momentum = mass times velocity We say: N Work (W) is defined as force that acts over a distance, or the movement of an object from one location or position to another. Work equals force times distance. The equation for work is: W = f × d Distance (d) in the metric system is measured in meters (m) and force is measured in newtons (N). Instead of using the unit n×m, work is measured using the metric unit joule (J). Ex. If a 500N box is lifted 2 meters, how much work has been done? 500N × 2m = 1000J J = newton × meter Work can also be defined as the change (Δ) in kinetic energy or Metric unit: English unit: calories the change (Δ) in potential energy. 1 BTU = 255 calories = 1055J Energy - 2 Each time work is done energy is transferred or given by one object to another that allows it to do work. So work is also understood to be the transfer of energy. When a certain amount of work is done, the same amount of energy is involved. Energy is therefore measured in joules just like work. Energy can either be used right away or stored for use later. All energy is described by either: 1 2 3 Distance = 0 NO WORK its position / shape / chemistry or so work = 0 W=f*d composition - Potential Energy WORK its motion - Kinetic Energy These are ways that energy is measured – not types of energy! Energy that is stored and is not being used is called potential energy (PE). Since these objects are not moving and are resting, there is no work being done. Potential energy is still measured in joules because of the object’s potential to do work. It is measured by its 1 2 3 position or shape or chemistry. Examples: stretched rubber band or spring heavy object charged battery any type or fuel or food tank of gasoline sugar Energy - 3 Weight is PE due to its position. All food and fuel is PE due to its chemistry. A stretched spring is PE due to its shape. PE can also be measured as weight times height - GPE. A 10 newton object 2 meters above = gravitational potential energy = the ground has a PE of 20J. GPE weight times height Kinetic energy (KE) is energy in motion that is being used. Work is being done. All moving objects have kinetic energy and are doing work. The amount of kinetic energy of an object depends on its mass and speed. The faster an object moves or the more massive it is, the more kinetic energy it has. Kinetic energy is measured in joules (J) by multiplying the mass in kilograms by the velocity squared in meters per second, and then and dividing by two. The equation is: KE = ½ mv2 All energy travels in waves - either through matter or by itself in the form of electromagnetic radiation. An energy wave that travels through matter is called a mechanical wave. The material a wave travels through is called a medium.