NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION A four minuet examination
advertisement

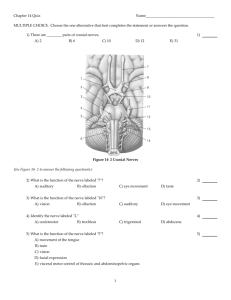
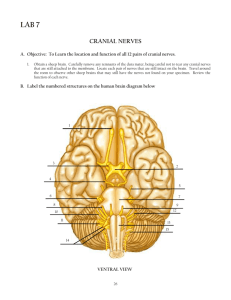
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION A four minuet (or less) examination By Don Hudson, D.O., FACEP/ACOEP Organic Disease ? Signs &/or symptoms that cannot be faked must be examined closely. Examples include, asymmetry in pupils, abnormal retinal exams, nystagmus, muscle atrophy, and muscle fasciculation. Where are the Connections Upper Motor Neurons (UMN) are defined as the connections of motor nerves before they leave the spinal cord Lower Motor Neurons (LMN) are defined as after the synapse (connection) into the peripheral nerve cell bodies. THE EXAMINATION Here’s what you need to examine. Mental Status Cranial Nerves Motor Sensory Coordination Reflexes Mental Status Exam “FOGS” Family story of memory loss Orientation General Information Spelling &/or numbers Recognition of objects Cranial Nerves Cranial nerve 1 (Olfactory) The sense of smell rarely identifies any significant pathology. Use tobacco, soap, smelling salts, etc for some idea to get some idea if they smell. Ammonia stimulates pain endings of CN5 ( Trigeminal) rather than CN1 Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerve 2 (optic Nerve) Central vision- Vision testing a chart, i.e. Snellen. Peripheral Vision- Test one eye at a time Examples of How to Examine CRANIAL NERVES Cranial Nerves 3, 4, 6 Key tests: Lateral and Vertical gaze Pupillary reaction to light Cranial Nerves PERLA- means you checked the pupil constriction at near accommodation. This is rarely done. Therefore it should read PERL. This tests the response of each pupil to light. PUPILS A large dilated pupil on one side with no other ocular abnormalities may be normal. (check license) A dilated pupil in the presence of AMS suggests herniation of the temporal lobe against C3 & the brain stem. Constricted pupils may indicate pontine injuries, narcotics i.e. Demerol, Morphine. Cranial Nerve 5 (Trigeminal) A lesion that effects C5 will usually effect all three segments (ophthalmic,maxillary,&mandibular) so the exam light touch on both cheeks. If you suspect a orbital injury touching the cornea with a wisp of cotton will test the corneal reflex. This tests C5 + transfer to the brain stem then on to C7 Crainal Nerve 7 (Facial Nerve) This is a critical part of the neuro exam. Smile- note any weakness on either side of the mouth Bell’s Palsy- Where the nerve is injured between pons & face there is total facial paralysis i.e., weakness of a corner of the mouth + closing the eye + wrinkling the brow. If the smile test is normal there is little reason to continue the exam. Crainal Nerve 8 Vestibulocochlear Nerve- Conductive defects or sensorineural are found here. Rubbing your fingers together next to the patients ear. Blocked EAC with wax are examples of conductive loss. Ask the patient to hum- in the conductive loss the blocked ear sounds louder, in sensorineural loss the normal ear sounds louder. Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 Glossopharyngeal & Vagus This is basically a gag reflex check Crainal Nerve 11 Accessory Nerve Key test: Shoulder elevation (shrug) Rarely injured except bin neck injuries. Cranial Nerve 12 Hypoglossal Nerve Key test- stick out your tongue The tongue will deviate to the side of weakness. Motor Examination Key tests: Drift of upper & lower extremity Hand grip & toe & foot dorsiflexion Testing of other muscles when their proper function is in question Sensory Extremity Examination Key Test: Pain Sensation- Use simultaneous stimulation (sharp, dull, etc.) Proprioception- Test big toe (position). MS, neurosyphilis, & pernicious anemia may cause loss of lower extremity proprioception. Coordination Key Test: Finger to nose & heel to shin motions Alternating rapid movements of hand & foot. Examples of tapping thumb & index fingers together, or heel on floor & tap toes on floor. Balance test- Tandem gait or Romberg test. Romberg Test Key test: Be sure to check orthostatic (B/P) for changes first Balance is maintained by vision, vestibular sense & proprioception. These feed into the cerebellum either directly or indirectly. If a patient sways with eyes open or close it is considered +. Reflexes Key tests: Triceps, biceps, knee jerk, Achilles & Babinski are the major reflexes. Asymmetry is usually a sign of major pathology. Babinski- This points to a upper motor neuron lesion. A positive test is when the lateral aspect of the foot is scratched & the big toe dorsiflexes & the other toes fan out Examination of Unconscious Pt. Key test: Hand-drop over head Pupillary size & response to light Abnormal eye movements Grimacing, withdrawal to noxious stimuli Babinski reflex V/S, Cardiac, Respiratory & metabolic status Rapid Neuro Exam Mental Status- FOGS, count back from 100, serial 7’s Cranial Nerves- C1- smells tobacco 0r soap; Visual acuity (near/far), gross visual fields, Opth. Exam; CN3,4,6- Pupil light response; lat/vertical gaze; CN5- double stimulation; corneal reflex. CN7- Smile: CN8-finger tips rubbing; hum; CN9,10- gag; CN11 shrug; CN12-stick out tongue Motor- drift of extremities, grasp & foot/toe dorsiflexion; Sensory- double stimulation hands/feet; position of big toe. Coordination- finger to toe; raid movements of fingers/toes; Romberg, tandem gait; Reflexes- check; Kergig or Brudzinski U/C- V/S, hand-drop, abn. eye movements, withdrawal, Babinski, cornea's, doll’s eye reflex. Neuro Exam This is a brief neurological examination. It is not meant to replace a full neurological examination. This is intended to be part of the secondary exam for pre-hospital providers. This exam should not take longer than 34 minutes. How to get good doing the Exam PRACTICE PRACTICE PRACTICE Thanks for your patience, Don Hudson, D.O.