Real vs Personal Property
advertisement

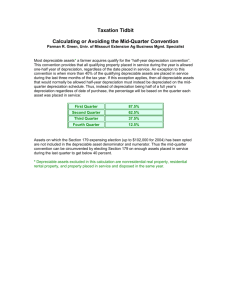
Cost Recovery Personal Property • Tangible Personal (business) Property – generally, use depreciation table 7-1. • Accelerated depreciation (versus straight line). There is a different table for straight line. • Half Year Convention – – – – 3 year – racehorse 5 year – autos, copiers, computers 7 year – furniture, fixtures and equipment. 15 year – land improvements (parking lot) Mid-Quarter Convention • If more than 40% of tangible personal is purchased in the last quarter of the taxpayer’s tax year, then the mid-quarter MACRS tables must be used. • This means that you will be doing four depreciation calculations for the year (one for each quarter), and when the property is disposed of, you would be required to use the mid-quarter table in the year of disposition. Cost Recovery Real Property • Real Property – real estate like buildings. Generally, use table 7-9. • Straight line (versus accelerated depreciation) • Mid-Month Conversion – choose month in the year of purchase and the year of sale. In month of sale, take a half month of depreciation. For example: » Sale in January ………. take ½ month » Sale in March ………… take 2 ½ months » Sale in October ………. Take 9 ½ months etc. etc.h • Residential Real Property – 27.5 year recovery • Nonresidential Real Property – 39 year recovery Additional Depreciation 50% (was 30%) Additional First Year • Applies to tangible personal property only …… not real property. • Applies to property acquired after September 10, 2001 and before Jan 1, 2005. • May 5th 2003 ……. changed to 50% • Election may be made not to take the additional depreciation. • Cost is then reduced by the additional depreciation for calculating the MACRS deduction. Expensing Under Section 179 • Taxpayer can elect to write-off up to $108,000 the cost of tangible personal property. • Annual Limitations: • First, reduced dollar for dollar when property placed in service exceeds $430,000. • Second, the amount expensed under Section 179 cannot exceed the taxable income • Basis is reduced by 179 expense for purposes of cost recovery. Automobiles • There is a limitation on the amount of depreciation that can be taken on expensive automobiles. This is to discourage the business use of cars like BMW’s, Lexus and the like. • If there is personal use of the business auto, then the business portion must be allocated for the deduction. (like 80% business and 20% personal). • If business use falls below 50%, straight line depreciation must be used (versus accelerated). Not only that, but any accelerated depreciation from prior years must be recaptured. Automobiles (con’t) • Maximum depreciation: • • • • Year 1 $2,960 Year 2 $4,800 Year 3 $2,850 Remaining Years $1,675 • Special Limitation on 179 Deduction for nonpassenger vehicles ( > 6,000 lbs.) • Limited to $25,000 Amortization • Intangibles are amortized over a 15 year period beginning in the month that the intangible is acquired. • Intangibles include franchises, copyrights, patents, covenants not to compete and goodwill. Depletion • Natural resources (oil, gas and timber) are subject to depletion. • Land cannot be depleted (nor depreciated) • Two depletion methods: • Cost Depletion – basis is divided by the recoverable assets (like estimated barrels of oil) to get depletion per unit. • Percentage Depletion – percentage rate is applied to gross income (multiplied by gross income) to get depletion, but it is limited to 50% of net income of the property being depleted. In the Year of Sale, what factor do we use to calculate depreciation for the partial year?? Half-Year Convention Mid-Quarter Convention Mid-Month Convention J For the Year D 1 2 1st Quarter 2nd Quarter 3rd Quarter 4th Quarter .5 4 1.5 4 2.5 4 3.5 4 J F M A M J J A S O .5 12 1.5 12 2.5 12 3.5 12 4.5 12 5.5 12 6.5 12 7.5 12 8.5 12 9.5 12 N D 10.5 11.5 12 12