Postwar Period 1945-2001 - Mater Academy Lakes High School
advertisement

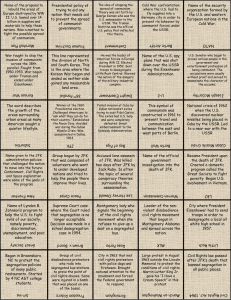
Postwar Period 1945- 2001 Truman & the Beginning of the Cold War Two leading superpowers: United States & Soviet Union Major concerns: 1. survival of the belligerent countries 2.shape of the new postwar world & new political alliances Capitalism V. Communism Power Struggle: Cold War no actual combat Hot “proxy” wars: Korea & Vietnam (fought by the U.S) U.S & Russia never combatted each other. U.S economy growing more dependent on EXPORTS & IMPORTS (metals) 1. Open Trade 2. Friends relations with nations providing metals WWII actually exposed the U.S & S.U ideological differences enemies for the next 40+ years Truman & Foreign Policy Differences between the 2 superpowers became vibrant when S.U refused to recognize Poland U.S supported Polish government (Poland sought refuge in G.B when Hitler invaded) Communist S.U took over Poland and within two years also took over Hungary and Czechoslovakia Propaganda each government portrayed the other as wanted to conquer the world for their own greedy purposes. 1947: Threat of the spread of communism into Greece & Turkey England could no longer prop-op nation Truman asked congress for $400 million Truman Doctrine George Kennan policy of containment (Long Telegram: sent from Germany to Washington, 1946) Prevent the spread of communism & encourage the Soviets to abandon aggressive strategies Continued… U.S Method to gain alliances with other countries give away money Secretary of State George Marshall, Marshall Plan >$12million to Europe to help rebuild after war countries became U.S allies Offered to Eastern Europe & S.U but did not participate Stalin saw as U.S imperialism 1949: North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) Canada, U.S & other Western European countries Berlin: divided as Germany was in 1945 Western Allies planned to unify into one NONcommunist country Soviet set up the Berlin blockade (1948) Berlin Airlift (after 1 yr. S.U surrenders) symbol of Cold War (dismantled in 1989) Discovered that the Soviets also had an atomic bomb, detonated around the time NATO is created/ U.S joins. National Security Council Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) Spy networks and foreign affairs advisors to the U.S President Continued… Asia: Japan’s Reconstruction & Chinese Civil War -U.S occupies Japan after WWII, divides it’s colonies (which included Korea) U.S took over Pacific Islands and southern Korean & USSR took over the northern portion of Korea -Japanese Constitution (General Douglas MacArthur) democratized Japan -China not so successful 20 yr. Civil War U.S sides with Mao Zedong (fighting the communist revolutionaries) U.S eventually pulls it’s support to Zedong Communist take over 1/3 of world communist at this point -French Indochina (Vietnam) Truman aided the French many not aware at this time McCarthyism Anti-Communist paranoia spreads on the home front (Red Scare) 1947: Truman orders investigation of 3 million federal employees searching “security risks previous associations with communists or with any “moral” weakness subject to blackmail 1949: State Department official Alger Hiss guilty of communist affiliations (communist spy) Richard Nixon (congress) responsible for bringing him down Sparks paranoia of communists within our society Senator Joseph McCarthy ruthless accusations the “so-called” list of 200 communists working in State Dept. U.S Army Edward R Murrow’s TV show airing Army- McCarthy hearings fall of McCarthyism H.U.A.C (House of Un-American Affairs Committee) Hollywood 10 Blacklists Truman’s Domestic Policy & 1948 Election Economy now has to mobilize back to a “peace-time” industry Many businesses that produced war goods went out of business laid off employees rise in unemployment there was also an inflation (20%) Truman offers the Fair Deal in an attempt to assist the poor and unemployed not passed into law Anti-unionism (Red Scare) United Mine Workers went on strike shut down energy supplies to other industries Truman: seizure of the mines & threatens a draft to railroad strikers Alliance formed against skyrocketing prices & frustrated about the unions Eightieth Congress (1946) Republicans take over congress Truman alienates many voters: Civil Rights Agenda President’s Committee on Civil Rights goals: end to segregation, poll taxes, anti-lynching laws issued executive order preventing discrimination for government jobs & desegregated the Army Galvanizes African Americans NAACP wins initial/ important lawsuits Jackie Robinson (baseball) form alliances with liberal white organizations more political ground Provokes scandalous racism Democrats- “Dixiecrats” (South) Strom Thurmond nominee Continued… Many Democratic populations against Truman’s civil rights tendencies – labor, consumers & Southerners Many believed Truman would be defeated in the 1948 election Became popular with the Republicans with his harsh reactions/ responses to the labor strikes Conservatives passed the Taft-Harley Act (Truman vetoed) prohibited union only work environments, closed shops restricted the right to strike, union funds for political purposes, government broad powers to intervene in strikes On the other hand, Republicans rebuked Truman for his liberal tendencies health care reform, civil rights for blacks, farmers, elderly Recalls former congress to enact platform Congress does not pass a single law in 2 weeks Truman campaigns and ridicules Congress as the “do-nothings” Truman wins re-election 1948 Korean War North Korea (more than likely supported by USSR) invades South Korea War Truman decides to attempt to “reunify” Korea. U.S attack provokes China China enters war & pushes back U.S & South Korea to border Douglas MacArthur recommends a full out war with China (to overthrow the communist government) Truman very hesitant & decides against MacArthur MacArthur publically criticized Truman Truman fires MacArthur War drags on for 2 years and ends once Eisenhower takes Presidency (1952) 1952: Dwight D. Eisenhower runs for office war hero very blunt although now seen as integrity Eisenhower Years (1953-1961) Typical family life Conformity consensus of values reigns : “under God” in pledge & “In God We Trust” on dollar bill. Cause and Effect: G.I Bill of Rights (1944) education, unemployment & housing Many civil rights activist picked up from the advances of the 1940s violent resistance Beatniks Rock ‘n’ Roll Elvis Presley, Little Richard, Jerry Lee Lewis & Chuck Berry Domestic Politics in the ‘50s Sought to balance budget, cut federal spending and ease government regulation of business partly successful Cold War forced Ike to spend more money on the military reduced troops but bought more powerful weaponry systems New Look Army Popularity of New Deal programs difficult for Ike to eliminate deficit spending current circumstances forced Ike to increase the number of Social Security recipients and their benefits Interstate Highway System initially to move soldiers & nuclear missiles around the country easier –BUT- promoted travel and tourism (Holiday Inn & Disneyland) Most important domestic issues Race 1953: Native Americans termination liquidate reservations & subject Native Americans to state law plan failed Civil Rights Movements Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka NAACP Thurgood Marshall Rosa Parks Montgomery bus boycott MLK Jr. Montgomery Improvement Assoc. MLK: encouraged peaceful organizations Greensboro, NC students follow MLK’s advice sit-ins spread across the nation U.S vs. Communism Ike and the Cold War policies: -Secretary of State, John Foster Dulles advised Ike to change the term “containment” to “liberation” as it would make it sound more intimidating. -U.S would eventually free Eastern Europe from USSR Massive Retaliation -Deterrence: fear of punishment USSR feared massive retaliation and would prevent them from challenging the U.S arms race “mutually assured destruction” (MAD) -Brinkmanship - Domino Theory (South East Asia- Vietnam) -Eisenhower Doctrine Continued… Cold War tensions remained high Stalin dies in 1953 & Ike hoped would improve relations with U.S Nikita Khrushchev offered hope against Stalin’s totalitarian rule peaceful coexistence Poland and Hungary rebellions U.S & USSR back as they were during Stalin era USSR explodes H-Bomb a year after the U.S did, sends first satellite- Sputnik into space space race National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Attempts to avoid war with China: Taiwan (U.S Ally) occupied Quemoy and Matsu close to China Brinkmanship: Ike declares that the U.S would defend the islands and hinted on a nuclear attack on China U.S troops stationed in the Taiwanese islands In the next elections, JFK uses this issue against Ike too much $$ into defending the islands. Third World Politics After WWII, Europe’s huge oversees empires breakup countries in Africa, Asia and South America free from European rule Did not ally themselves with either of the 2 superpowers Third World However, both superpowers very interested in bringing in third world countries into their own influence potential markets, raw materials good area to host military bases Third World Countries Nationalism enjoying new found freedom, not interested in any interference with the superpowers distrust HOWEVER, U.S tries to expand it’s influence other ways: offer foreign aid Egypt, Aswan Dam Gamal Nasser suspected this was a Western scheme eventually turn to USSR CIA covert operations forceful strategies of increasing influence in foreign countries newspaper briberies overthrow Iran and Guatemalan governments to re replaced with Pro-American governments Bay of Pigs 1960 Presidential Election & The Turbulent 60s Richard Nixon V JFK Eisenhower warned about new coalition that had grown from the Cold War military might and weapons Vietnam War Turbulent ‘60s -JFK entourage of the “best and brightest” many Americans adored JFK offered hope for the domestic issues New Frontier (poverty, racism & other issues) - 1969: U.S bitterly divided Vietnam War & Civil Rights JFK & Foreign Policy Cuba Fidel Castro (1959) nationalizes over 3 million acres in Cuba owned by Americans (also controlled the country’s electricity & phone service) Cuba signs trade treaty with USSR & depended on USSR for financial and military aid Ike (while still in office imposed a partial embargo and poorly planned an invasion JFK inherits issue Bay of Pigs invasion (1961) Berlin Wall Cuban Missile Crisis USSR missiles in Cuba brinkmanship blockade forced USSR to remove missiles behind the scenes negotiations solved the crisis seemed as if U.S won eventually removed our missiles from Turkey “hot-line” for the purpose of better communication between JFK and USSR is placed Peace Corps humanitarian programs “assimilate” Third World country cultures into anti-communists provided teachers, agricultural specialists, health care, transportation nation building Many countries did not want American-style progress JFK- Domestic Policy Michael Harrington’s book The Other America Opens up JFK’s eyes (along with U.S Society with how the poor were still living) A book does it again! New Frontier unemployment benefits, expanded Social Security, bumped up the minimum wage, aided distressed farmers Women’s rights Presidential committee 1963 remove all obstacles Equal Pay Act (1963) September 1962 JFK enforced desegregation at the University of Mississippi asked Congress to pass the Civil Rights Act but was assassinated LBJ was able to push through congress in 1964 Active period for Civil Rights Movements Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) , sit-ins boycotts & peaceful demonstrations 00> Congress of Racial Equality (CORE), Freedom Riders Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC), voter registrations – Freedom Summer Met with resistance NAACP Director Medgar Evers murdered in 1963, Police brutality in Montgomery, JFK’s assassination LBJ’s Social Agenda Took immediate action towards the Civil Rights issues Civil Rights Act of 1964 BASES OF ALL DISCRIMINATION SUITS TO THIS DAY, most comprehensive piece of civil rights legislation Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) Voting Rights Act of 1965 Great Society LBJ’s social agenda, most sweeping change in U.S government since the New Deal War on Poverty Economic Opportunity Act $1billion in poverty relief Project Head Start education (Sesame Street) Job Corps vocational training Volunteers in Service to America (VISTA) domestic Peace Corps Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) federal aid to low income apt renters Civil Rights Movements 1960’s number of substantial gains Great Society Governmental Support Supreme Court victories under Chief Justice Earl Warren Warren Court extremely liberal Enforced voting rights for blacks Withdraw congressional districts more representation for minorities Prayer prohibited in school Rights of the accused Gideon v. Wainwright right to an attorney even if one cannot afford it Miranda v. Arizona Strict opposition police brutality, KKK, civilians supporting movements killed New Radical Activist in the black community Malcom X (Nation of Islam) Black Panthers Black Power SNCC & CORE segregate themselves by eliminating white supporters MLK assassinated violence breaks out New Left, Feminism & Counterculture New LeftYoung, white, college students- particularly men, made up the “New Left” 1962: Students for a Democratic Society- (SDS) leftist political agenda Port Huron Statement Tom Hayden manifesto; non-ideological call for participatory democracy New Left: progressive groups. Called for the elimination of poverty, racism and Cold War Policies University of California, Berkeley (1964) Free Speech Movement Colleges changed classes to cater to the members of the New Left Did not include women women became frustrated second class citizens Feminism – 1963: Betty Friedan, The Feminine Mystique Challenged society’s assumptions of acceptable women’s roles Credited for restarting the women’s movement (feminist movement) National Organization for Women (NOW) fought for legislative changes (“Equal” Rights Amendment added to the constitution) Feminism… Continued & Counterculture Fought against discrimination in hiring, pay, college admissions and loans. Reproductive rights 1965 Griswold v. Connecticut & 1973 Roe v. Wade Gay Pride movements commence during this time too (1960s) Stonewall Riots Counterculture: “against mainstream” Rebellion against “the establishment” (roots in 1950s) Hippies communes, long hair, ripped jeans, tie-dyed shirts, drug use, sexual revolution (designers catered to the interest of the hippies & so did record companies…) Music lyrical weapons Bob Dylan, Jimi Hendrix, the Beatles, Rolling Stones Woodstock New Left, Feminists & Counterculture huge divide in U.S society Vietnam War Other movements: Hispanics Cesar Chavez Table Grape Boycotts United Farm Workers Native Americans National Indian Youth Council (NIYC, 1961) preserving native fishing rights in the Northwest group expands to include civil rights issues (1968) American Indian Movement (Aim) occupy Alcatraz Seized the Bureau of Indian Affairs in D.C (long march from California to Washington DC Siege at Wounded nee U.S Involvement in Vietnam Truman Administration -1991: Cold War U.S felt they had the right to intervene anywhere communism was being spread (to protect U.S interests) Vietnam huge failure divides the country unlike ever before since the Civil War Origins – Series of events: WWII French Colony (rice, rubber & metals) fostered resistance (Vietminh) led by Ho Chi Minh lived in France Treaty of Versailles (1919) Wilson’s fourteen points (self determination) Ignored Japan invades Vietnam (WWII) Vietnam and Allies united by common enemy hoped for independence Drafted their declaration of independence (U.S & French) U.S does not recognize independence (Bao Dai) Vietnam & France fight war of independence (1945-1954) U.S funds 80 % of war (in favor of France) Battle of Dien Bien Phu ends that war Continued… 1954 – Geneva Accords 17th Parallel Communist Forces get the North “democratic” forces get the South (pounced autonomous by Diem) Division to last only 2 yrs & free elections would be held elections never took place U.S breaks agreement U.S joins forces with Ngo Dinh Diem CIA organizes raids against the North & hoped for communist retaliation U.S forms SEATO (SouthEast Asia Treaty Organization) with G.B, France, Thailand, Pakistan, Philippines, New Zealand & Australia Diem tyrannical leader imprisoned political enemies, persecuted Buddhist monks, closed newspapers who publically opposed him Many southerners joined the North Vietnamese side (Vietcong) U.S continued to support Diem JFK sends in the Green Berets (advisors) CIA helps stages a coup but assassinates Diem and his brother JFK killed that same month LBJ U.S involvement in Vietnam (1964-68) LBJ took office & had opportunity to withdraw Advisers assured LBJ was winnable LBJ committed to total victory U.S didn’t care who ran the Vietnamese government, as long as not communist U.S starts bombing Laos N.V shipping weapons to Vietcong 1964 -Reports stated N.V had attacked U.S destroyer ships @ Gulf of Tonkin LBJ/ Gulf of Tonkin Resolution floods Vietnam with U.S troops “Americanization” Many men leave to escape the draft Tet Offensive (1968) Major turning point Fighting strategies Tigers v Elephants U.S felt lied to (opposition) My Lai Massacre opposition grows larger and angrier 1968 As a result, LBJ announces he will start making peace negotiations and that he won’t run again in upcoming elections Summer & Election of 1968 Eugene McCarthy, Robert (Bobby) Kennedy an Hubert Humphrey ran for the Democratic ticket that year. April 1968- MLK murdered violence breaks out (riots) in over 150 towns Kerner Commission “separate AND unequal” June 1968- Bobby Kennedy murdered Democratic Convention in Chicago violence convention decides on Humphrey instead of the anti-war candidate McCarthy many anti-war democrats decide to vote Republican Richard Nixon promises to end U.S involvement in war Third Party Nominee George Wallace (pro-segregation support of the South) Nixon and Wallace big threat from Humphrey Very close election Nixon wins “Vietnamization” and Détente Vietnamization handing the war back to South Vietnam with as little support from the U.S as possible Began to withdraw troops BUT also increased bombing campaigns Nixon was a former war vet (WWII) and believed in using military power the U.S MUST win Cambodia airstrikes and ground attacks root out war supplies and the Vietcong 1973: Secretary of State, Henry Kissinger Peace negations for a treaty with North Vietnam Nixon’s Success: USSR increased trade with U.S, number of arms treaties. China U.S previously decided not to acknowledge China, Nixon travels to China and ease tensions, leverage with USSR Détente eased tensions. Countries would respect others differences Nixon Doctrine (1979) U.S would withdraw it’s troops from several overseas nations, relied on alliances with local governments to check on communism. Nixon’s Domestic Policy Successful with foreign Policy but not as successful with domestic economy worsened, stagflation 90 day price and wage freeze efforts did not produce their intended results Politically: Society divided both sides seen the other as an enemy of the American Way Kent State University, Ohio demonstration four protestors killed incident is perfect example of the division of youth and middle America (older America) Many continue to move to the suburbs due to the heightened crime in the urban area 1972: Nixon won re-election one of the greatest landslide victories against Senator George McGovern house was still Democratic Watergate & Nixon’s Resignation 1971- Pentagon Papers are published revealed numerous military miscalculations and lies the government told the U.S public Nixon fights to prevent publication (nothing on Nixon on this tapes) BUT afraid would destroy current credibility Nixon grows more and more paranoid investigators/ plumbers Watergate Hotel arrested White House begins to cover up the scandal White House Tapes – executive privilege The Washington Post Bob Woodward & Carl Bernstein (FBI Deep Throat) August 1974 Nixon resigns Gerald Ford Who had already replaced VP Spiro Agnew pardon Gerald Ford & Jimmy Carter Presidencies Gerald Ford: Selects Nelson Rockefeller as VP first time neither President and VP elected by public Not very popular/ bad credibility pardon – deal with Nixon? Weak economy – W.I.N Oil embargo – O.P.E.C inflation + unemployment media – Saturday Night Live, Chevy Chase 1976- Jimmy Carter Inherits weakening economy inflation >10% stagflation Tries to balance budget, unable to. Economic issues OPEC oil alternatives Department of Energy – nuclear power plants – Three Mile Island High Point: Peace Agreement between Israel & Egypt SALT II w. USSR USSR invades Afghanistan withdrawal of treaty Sandinistas supported until Sandinistas allied themselves w/ USSR & Cuba Lowest Point: Iran Hostage situation Born again Christian support of the “conservative group” 1979 Jerry Falwell finds the “moral majority” Reagan’s target Reagan, G.H.W. Bush, Clinton & G.W. Bush 1980-2001 **Neither DBQ nor FRQ (Parts B & C) deal exclusively with this periods – but expect to see multiple choice questions. Ronald Reagan: Due to all the events in previous decades, U.S wanted to return to a more conservative times major change Washington “outsider” stressed positive aspects of America Wins 1980 election by a landslide Supply-side economics “Reaganomics” Military Spending & Budget Deficits Reduce the size of federal government New Federalism shift power from national government to states Increase military spending S.D.I “Star Wars” escalated arms race Tax cuts, increased military spending escalated federal budget deficit Foreign Policy Under Reagan Reagan sought to end the Cold War anyway and anywhere he could. Supported anti-communist groups across the world Grenade, Nicaragua “Contras” Iran-Contra affair Lebanon (240 marines killed) Greatest success: U.S- USSR relations Mikhail Gorbachev perestroika (reform) & glasnost (openness) USSR collapses & Fall of Berlin Wall (although happens after his presidency, it was because of his diplomatic relations with the nation. After his 2nd term, still had a very high approval rating George H.W Bush Moral majority had spoken 1988 election progressive liberalism was destroyed “read my lips, no more taxes” 1990 – Saddam Hussein invades Kuwait oil Persian Gulf War Operation Desert Storm U.S foreign policy would now focus on Middle East and on Human Rights