Study Guide – Unit 8 Test
advertisement

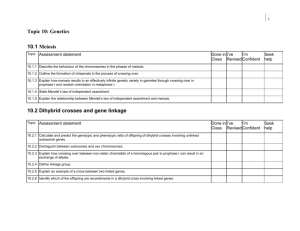
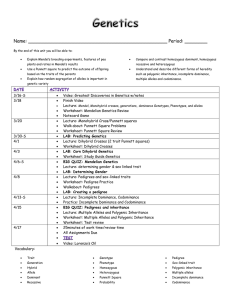
Study Guide – Unit 8 Test Introduction to Genetics April 20, 2012 Format In order to successfully complete the test, a student must be able to: correctly answer 25-30 multiple choice questions (some requiring diagram interpretation and/or Punnett squares) correctly predict the expected genotypes and phenotypes resulting from monohybrid crosses, dihybrid crosses, incomplete dominance, codominance, and epistasis problems correctly interpret polygenic and pleiotropic inheritance patterns 3-5 short answer questions Important Terms In preparation for the test, a student should understand the meaning of the following terms: meiosis fertilization haploid diploid homologous pair tetrad crossing over synapsis variation genetics trait Gregor Mendel true- (pure-) breeding hybrid self-fertilization gamete gene allele parent (P) generation first filial (F1) generation second filial (F2) generation dominant allele recessive allele genotype phenotype homozygous heterozygous Law of Segregation Law of Independent Assortment Law of Dominance Punnett square probability monohybrid cross dihybrid cross incomplete dominance co-dominance polygenic trait multiple alleles pleiotropy sickle cell disease incomplete dominance codominance ABO blood group universal donor universal recipient multiple alleles epistasis polygenic trait pleiotropy karyotype linked genes Thomas Hunt Morgan Important Concepts In preparation for the test, a student should be able to: Explain the difference between a diploid cell and a haploid cell. Be able to calculate the diploid or haploid number given the other. Explain why sexual reproduction is advantageous for a species’ survival. Explain the movement of essential organelles and chromosomes in each phase of meiosis (p. 276-277). Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis. Explain why meiosis is important. Understand how meiosis contributes to variation in sexually reproducing organisms. Explain why Mendel chose peas for his genetic experiments. Know the difference between a purebred and a hybrid. Understand the results of Mendel’s pea experiments. Describe the difference between a dominant allele/trait and a recessive one. Know the difference between homozygous and heterozygous. Determine an organism’s phenotype from its genotype and vice versa where applicable. Know Mendel’s Laws. Explain how each law predicts a physical reality of gamete formation and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. Explain how probability is used in Punnett squares to predict possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring. Correctly complete monohybrid and dihybrid crosses using a Punnett square. Compare and contrast incomplete dominance, co-dominance, epistasis, polygenic traits, and pleiotropy. Use presented evidence and Punnett squares to interpret incomplete dominance, co-dominance, and epistasis problems. Interpret inheritance patterns that involve multiple alleles. Explain the difference between polygenic traits and pleiotropy. Know examples of how environment may influence phenotypes.