Minerals Study Guide
advertisement

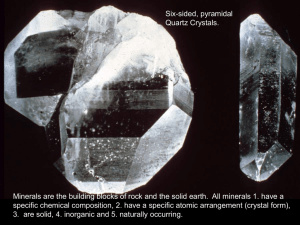
A mineral is a naturally formed, inorganic solid that has a definite crystalline structure. Solid Cannot be a liquid or a gas Naturally Occurring Found in nature, not man-made Inorganic Is not alive and never was, non-living Fixed composition Has a chemical formula, most are formed from compounds of two or more elements, some minerals consist of one element ex. Au Crystal Structure (Crystalline) A definite structure in which atoms are arranged Is it non-living material? Is it a solid? Is it formed in nature? Does it have a crystalline structure? Wood Gold Fossil Topaz Bones Granite Quartz Pearls Talc Icebergs Diamond Coal Rock Salt Minerals Non-Minerals a) Gold a) Wood - once living b) Topaz b) Fossils – once living c) Quartz c) Bone - living material d) Talc d) Granite - intrusive igneous rock e) Iceberg* e) Pearls – made by oysters f) Diamonds Coal - Sedimentary rock g) Rock Salt – Sedimentary rock f) According to IMA – ice is listed as a mineral Color: Physical Property that can be observed without doing anything Streak: Color of the powder it leaves when you rub it along a surface Luster: How it shines; how it reflects light Cleavage and Fracture: The way a mineral breaks Cleavage: Mineral splits easily with a flat surface Fracture: Minerals that break apart in an irregular way Special Properties: Glows Magnifies Magnetic Reactive Density: Mass in a given space; mass per volume Hardness: Mohs hardness scale Scratch test: Minerals can only scratch those minerals softer than it is Crystal Systems: Number and angle of Crystal faces 6 crystal systems