Chapter 19: Oxidation
advertisement

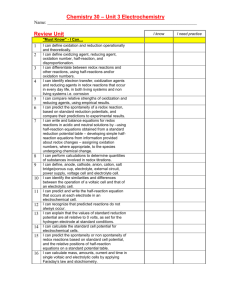
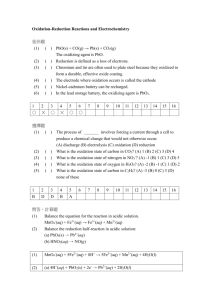
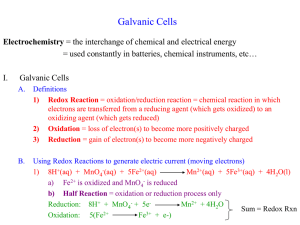
• Explain what must be conserved in redox equations. • Balance redox equations by using the half-reaction method. • The half-reaction method for balancing redox equations consists of seven steps: › 1. Write the formula equation if it is not given in the problem. Then write the ionic equation. › 2. Assign oxidation numbers. Delete substances containing only elements that do not change oxidation state. › 3. Write the half-reaction for oxidation. • Balance the atoms. • Balance the charge. › 4. Write the half-reaction for reduction. • Balance the atoms. • Balance the charge. › 5. Conserve charge by adjusting the coefficients in front of the electrons so that the number lost in oxidation equals the number gained in reduction. › 6. Combine the half-reactions, and cancel out anything common to both sides of the equation. › 7. Combine ions to form the compounds shown in the original formula equation. Check to ensure that all other ions balance. Sample Problem A A deep purple solution of potassium permanganate is titrated with a colorless solution of iron(II) sulfate and sulfuric acid. The products are iron(III) sulfate, manganese(II) sulfate, potassium sulfate, and water—all of which are colorless. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. Sample Problem A Solution 1. Write the formula equation if it is not given in the problem. Then write the ionic equation. KMnO4 + FeSO4 + H2SO4 Fe2 (SO4 )3 + MnSO4 + K 2SO4 + H2O K + + MnO4– +Fe2+ + SO24– + 2H+ + SO24– 2Fe3+ + 3SO24– + Mn2+ + SO24– + 2K + + SO24– + H2O Sample Problem A Solution, continued 2. Assign oxidation numbers to each element and ion. Delete substances containing an element that does not change oxidation state. +7 – 2 +1 + – 4 +2 K + MnO +Fe +3 2Fe 3+ +6 – 2 + 3SO 2+ 2– 4 +6 – 2 + SO +2 + Mn +1 2– 4 2+ +6 – 2 2– 4 + + 2H + SO +6 – 2 2– 4 + SO +1 + +6 – 2 2– 4 + 2K + SO Only ions or molecules whose oxidation numbers change are retained. +7 – 2 – 4 +2 MnO + Fe 2+ +3 3+ +2 Fe + Mn2+ +1 – 2 + H2O Sample Problem A Solution, continued 3. Write the half-reaction for oxidation. The iron shows the increase in oxidation number. Therefore, it is oxidized. +2 +3 3+ Fe Fe 2+ • Balance the mass. • The mass is already balanced. • Balance the charge. +2 +3 3+ Fe2+ Fe + e– Sample Problem A Solution, continued 4. Write the half-reaction for reduction. Manganese is reduced. +7 +2 MnO4– Mn2+ Balance the mass. Water and hydrogen ions must be added to balance the oxygen atoms in the permanganate ion. +7 +2 MnO + 8H Mn2+ + 4H2O – 4 + Balance the charge. +7 +2 MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e– Mn2+ + 4H2O Sample Problem A Solution, continued 5. Adjust the coefficients to conserve charge. e– lost in oxidation 1 – e gained in reduction 5 5(Fe2+ Fe3+ + e – ) 1(MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e– Mn2+ + 4H2O) Chapter 19 Section 2 Balancing Redox Equations Half-Reaction Method, continued Sample Problem A Solution, continued 6. Combine the half-reactions and cancel. Fe2+ Fe3+ + e– MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e– Mn2+ + 4H2O MnO4– + 5Fe2+ + 8H+ + 5e– Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ + 4H2O + 5e– Chapter 19 Section 2 Balancing Redox Equations Half-Reaction Method, continued Sample Problem A Solution, continued 7. Combine ions to form compounds 2+ – + 3+ 2+ 2(5Fe + MnO + 8H 5Fe + Mn + 4H2O) 4 from the original equation. 10Fe2+ + 2MnO4 + 16H+ 10Fe3+ + 2Mn2+ + 8H2O 10FeSO4 + 2KMnO4 + 8H2 SO4 5Fe2 (SO4 )3 + 2MnSO4 + K 2SO4 + 8H2O