Lecture 31
advertisement

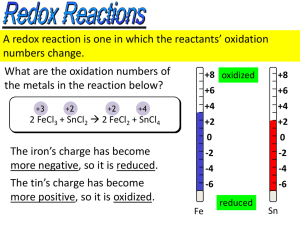
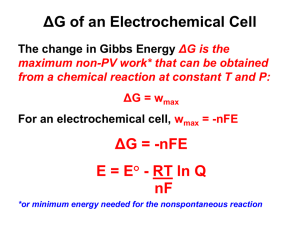
Outline: 4/9/07 due Wednesday… Worksheet #11 answers posted… Final exam in 3 weeks… Special seminar Tuesday/Thursday CAPA 18 Today: Continue Chapter 19 Nernst Equation ( and DG) Coulomb Calculations Redox Applications Spontaneous? o DG = nF Relation to DG Definitions: o = Electromotive force (at STP) Coulomb = unit of charge e = 1.6021019 Coulomb 1 mol of e = 6.0221023 . 1.602 1019 = 9.6485 104 Coulomb F =Faraday Const. = 96,485 C/mol DG, o , and equilibrium.... DG = DGo + RTlnQ..... Then: = o (RT/nF) lnQ Since Which is often written as: Then: = o (0.05916/n) log Q (@298K) (Nernst Equation) What good is this? Can calculate at non-standard conditions! Example What is the voltage produced by the following cell ? o MnO4 +8H+ +5e Mn2+ +4H2O 1.51 O2(g) + 4H+ + 4e 2 H2O 1.23 at pH=7.00, pO2 =0.20 atm, [MnO4] = [Mn2+] = 0.10 M ? First balance redox equation for cell.... Set up expression for Q Solve in Nernst equation Set up redox equation for cell: Which equation gets reversed? MnO4 +8H+ +5e Mn2+ +4H2O 1.51 2 H2O O2 + 4H+ + 4e 1.23 What is n? n=20 MnO4 +8H+ +5e Mn2+ + 4H2O 4 2 H2O O2 + 4H+ + 4e 5 4MnO4 +12H+ 4Mn2+ +5O2 + 6H2O What is o? +0.28V What is Q? Products/reactants : [Mn2+]4 pO25 [H+]12 [MnO4]4 = 3.2 1080 What is ? = o (0.05916/n) log Q = 0.28 0.24 = 0.04 V Using the Nernst equation…. = o (0.05916/n) log Q Example : What is the voltage produced by the concentration cell shown with two copper electrodes. One is immersed in 1M CuSO4 and the other in 0.001M? What is o for this cell? = 0.00 V Only the Q part of the Nernst equation is non-zero….. = o (0.05916/n) log Q What is Q? Products/reactants : [Cu2+] (less concentrated) = 1 103 [Cu2+] (more concentrated) What is ? = o (0.05916/n) log Q = 0.00 (0.05916/2) 3 = 0.089 V Worksheet #12 A galvanic cell is constructed from a silver-silver iodide electrode and a Zn wire in 0.005 M solution of ZnCl2. What is the cell potential? First, what is the galvanic cell? Balance redox equation for cell.... o Set up expression for Q….prods/rcts Solve with Nernst equation = o (0.05916/n)logQ Set up redox equation for cell: Which equations? Which equation get reversed? AgI(s) + e Ag(s) + I 0.152 Zn (s) Zn2+ + 2e +0.762 What is n? n=2 2AgI(s) + Zn(s) 2Ag(s) + Zn2+ + 2I What is o? +0.610 V What is Q? Products/reactants : [Zn2+] [I]2 = (0.005)(1)2 1 = 5 × 103 What is ? = o (0.05916/n)logQ = 0.610 + 0.068 = 0.678 V Problem 2 You need to know: o N2O(g) + 6H+ + H2O + 4e- 2NH3OH+ 0.050 V O2(g) + 2H+ + 2e- H2O2 Answer: + 0.745 V +0.695 V More definitions: Current = charge/time 1 Ampere = 1 Coulomb / second Calculational Example: A lead-acid battery: PbO2+HSO4+2H++Pb 2PbSO4 +2H2O Assume 250 g of PbO2 and that this battery supplies 6 Amps until it dies; how long will it last? Quiz #7 Put away your books & papers When you are finished, turn your quiz into me