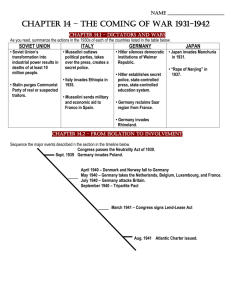
The Road to World War II
advertisement

The Road to World War II • Definitions: – Totalitarian: a political regime based on subordination of the individual to the state and strict control of all aspects of the life and productive capacity of the nation esp. by coercive measures (like censorship & terrorism) – Fascism: a political philosophy, movement, or regime that exalts nation and often race above the individual and that stands for a centralized autocratic government headed by a dictatorial leader, severe economic and social regimentation, and forcible suppression of the opposition. • Anti-Semitism: hostility toward or discrimination against Jews as a religious, ethnic, or racial group. • Scapegoat: one that bears the blame for others. • WWII saw the rise to power of three militaristic, totalitarian states: – Germany under Adolf Hitler – Japan under Hirohito – Italy under Benito Mussolini – Spain under Francisco Franco also had a Fascist & Totalitarian government • Adolf Hitler was one of the most powerful dictators of the 20th century. His attempts to conquer territory for German Lebensraum (living space) brought about World War II (1939-1945). He caused the slaughter of millions of Jews, Sinti and Roma (Gypsies), Slavic peoples, and others in the name of racial purification. • Benito Mussolini led Italy from 1922 to 1943. He founded the first fascist political group and later allied his country with Germany in World War II. Mussolini took the title Il Duce (The Leader). His clenched fist, jutting jaw, fiery speeches, and dramatic poses became his trademarks. • A skirmish between Japanese and Chinese troops near Beijing in 1937 soon boiled over into a full-scale war between the two countries. Japanese Emperor Hirohito is seen here reviewing Japanese troops in 1938. Hirohito allowed a militaristic party to dominate his government from 1926 until the end of World War II in 1945, when Japan’s expansionist policies were ended with his unconditional surrender to the Allies. • 1922: Mussolini is elected Prime Minister of Italy. • 1925: Mussolini installs himself as head of a single party state he called facismo. • 1933: Hitler is appointed Chancellor of Germany. • 1935: Nye Commission investigates US involvement in WWI and decides that weapons deals helped to draw the US into WWI. • 1935: Italy invades Ethiopia. (Ethiopia bordered Italian Somaliland in Africa.) • 1936: Rome – Berlin axis announced. • 1936: Germany invades the demilitarized zone in the Rhineland in direct violation of the Treaty of Versailles. • 1935, 1936, 1937: Neutrality Acts passed in Congress. These acts prevented the United States from – 1. Sailing on “belligerent” ships – 2. Selling or transporting arms to hostile nations – 3. making loans to hostile nations. – (These acts were an attempt to avoid a repeat of the Lusitania.) • 1936-1939: Spanish Civil War begins. Fascist General Francisco Franco takes over. • 1937: Japan invades China. • 1937: President Roosevelt delivers the Quarantine speech encouraging the free countries of the world to avoid trading w/ hostile, aggressive, militaristic nations (like Japan, Italy, and Germany). • 1937: US responds to events overseas w/ “storm-cellar isolationism”. • 1937: US Gunboat The Panay is sunk by Japan in Chinese waters. • 1938: Germany “annexes” Austria. • March 1938: Hitler demands return of the Sudetenland which was incorporated into Czechoslovakia after 1918. • March 1938: At the Munich Conference European leaders give the Sudetenland back to Germany to “appease” Hitler. • Early 1939: Germany annexes the rest of Czechoslovakia. • August 1939: Hitler and Stalin sign a “Non-Aggression” Pact. • Sept. 1, 1939: Germany invades Poland to officially begin WWII. As a result of this action, both Great Britain and France declare war on Germany. • Following the invasion of Poland, Germany quickly invades Denmark, the Netherlands, Belgium, Norway, and France using the blitzkreig attack. Blitzkreig means “lightning war” and included air attacks followed by invasion with troops and tanks. By the summer of 1940, Hitler controlled most of western Europe. • Oct. 1939: Neutrality Act of 1939, also called the Cash and Carry Act passed by Congress. • Oct.11, 1939: A letter written by Albert Einstein is delivered to President Roosevelt. In the letter, Einstein discusses the implications of a nuclear chain reaction and the powerful bombs that could be created using that knowledge. Roosevelt immediately begins a secret military undertaking (later known as the Manhattan Project) that will result in the creation of the atomic bomb. • Early 1940: USSR invades Finland. • March 18, 1940: Mussolini and Hitler announce Italy’s formal alliance with Germany against England and France. Mussolini calls this the “axis” on which Europe will revolve. • April 9, 1940: Germany invades Denmark and Norway. • May 10, 1940: Germany invades Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands. • June 5, 1940: Germany invades France. 10 days later Paris falls. • June 22, 1940: France surrenders. A proGerman government is set up in Vichy. • “Preparedness” Program begins in the US with the goal of building huge airfleets and a two-ocean Navy. • July 10, 1940: The Battle of Britain begins. For four months, German bombers pound London and other strategic points. England destroys 1700 German planes. • Sept. 1940: Congress passes a conscription law. This is the first peacetime draft in US history. • Sept. 2, 1940: Bases for Destroyers Deal: FDR gives 50 old destroyer ships to Great Britain in exchange for the rights to build 8 military bases on British lands around the world. • Dec. 1940: Congress passes the LendLease Law. This allowed the United States to “loan” arms and supplies to victims of aggression. (Germany sees that act as the official end of US neutrality.) The Lend-Lease Act is signed into law on March 11, 1941. • May 21, 1941: The Robin Moor an unarmed US merchant ship is destroyed by German submarines in the Atlantic Ocean. • June 22, 1941: Germany invades the Soviet Union breaking the Non-Aggression Pact. The United States eventually sends $11 billion in Lend-Lease aid to the Soviet Union. • August 1941: The Atlantic Conference: The Atlantic Charter is signed by FDR & Winston Churchill and endorsed by the USSR. Similar to Wilson’s 14 Point Plan, it outlined a plan for lasting peace after the war. • Sept. 1941: US Destroyer The Greer is attacked but not sunk by a German submarine. • The USS Greer • Oct. 1941: German U-boats attack but don’t sink US destroyer The Kearney. 11 US soldiers die in the attack. • Oct. 28, 1941: US destroyer The Reuben James is sunk by Germany near Iceland. • Nov. 1941: President Roosevelt announces a “shoot-on-sight” policy against German submarines. Congress repeals the Neutrality Act of 1939 and allows US merchant ships to be armed. • Dec. 1940-Dec. 1941: US enforces an embargo against Japan. US refuses to sell oil, scrap iron, and gasoline to Japan to protest Japanese aggression in the Pacific. • Dec. 7 1941: Japan attacks Pearl Harbor in Hawaii. • Japan also attacks Malaya, The Philippines, Guam, Wake Island, and French Indochina. • Dec. 8, 1941: The United States declares war on Japan. • Dec. 11, 1941: Germany and Italy declare war on the United States. The U.S.S. West Virginia, Pearl Harbor The stricken U.S.S. West Virginia was one of the eight battleships caught in the surprise Japanese attack at Pearl Harbor, Hawai'i, on December 7, 1941. In this photograph, sailors on a launch attempt to rescue a crew member from the water as oil burns around the sinking ship. (U.S. Army) "DAY OF INFAMY" Franklin D. Roosevelt - December 8, 1941 Full audio speech, "Yesterday, Dec. 7, 1941 - a date which will live in infamy - the United States of America was suddenly and deliberately attacked by naval and air forces of the Empire of Japan." ...