File
advertisement

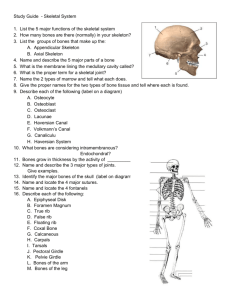
Chapter 5 Section Two Notes The Axial & Appendicular Skeleton The Axial Skeleton • Forms the longitudinal axis of the body • Divided into three parts • ______ • ______ column • _______ thorax The Skull • Two sets of bones • Cranium • Facial bones • Bones are joined by sutures • Only the _______ is attached by a freely movable joint Paranasal Sinuses • Hollow portions of bones surrounding the nasal cavity • Functions of paranasal sinuses • Lighten the skull • Give resonance and _______ to voice The Hyoid Bone • The only bone that does not ______ with another bone • Serves as a moveable _____ for the tongue • Aids in swallowing and speech The Fetal Skull • The fetal skull is large compared to the infant’s total body length • Fetal skull is ____ body length compared to adult skull which is ____ body length • Fontanels—fibrous membranes connecting the cranial bones • Allow skull compression during birth • Allow the brain to _____ during later pregnancy and infancy • Convert to bone within ____ months after birth The Vertebral Column • Each vertebrae is given a name according to its location • There are ____ single vertebral bones separated by intervertebral discs • _____ cervical vertebrae are in the neck • _____ thoracic vertebrae are in the chest region • _____ lumbar vertebrae are associated with the lower back The Vertebral Column • ____ vertebrae fuse to form two composite bones • Sacrum • Coccyx The Vertebral Column • Primary curvatures are the spinal curvatures of the ______ and sacral regions • Present from birth • Form a ____-shaped curvature as in newborns • Secondary curvatures are the spinal curvatures of the cervical and lumbar regions • Develop after birth • Form an ____-shaped curvature as in adults Sacrum and Coccyx • Sacrum • Formed by the fusion of ____ vertebrae • Coccyx • Formed from the fusion of ____ to ____ vertebrae • “Tailbone,” or remnant of a tail that other vertebrates have The Bony Thorax • Forms a cage to protect major organs • Consists of three parts • Sternum • Ribs • True ribs (pairs 1–7) • False ribs (pairs 8–12) • Floating ribs (pairs 11–12) • Thoracic vertebrae The Appendicular Skeleton • Composed of ____ bones • Limbs (appendages) • Pectoral girdle • Pelvic girdle The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle • Composed of ___ bones • Clavicle—collarbone • Articulates with the sternum ______ and with the scapula ______ • Scapula—shoulder blade • Articulates with the clavicle at the acromioclavicular joint • Articulates with the arm bone at the glenoid cavity • These bones allow the upper limb to have exceptionally free movement Bones of the Upper Limbs • Humerus • Forms the arm • ____ bone • Proximal end articulation • Head articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula • Distal end articulation • Trochlea and capitulum articulate with the bones of the forearm Bones of the Upper Limbs • The forearm has two bones • ________—medial bone in anatomical position • Proximal end articulation • Coronoid process and olecranon articulate with the humerus • _____ —lateral bone in anatomical position • Proximal end articulation • Head articulates with the capitulum of the humerus Bones of the Upper Limbs • Hand • ______ —wrist • _____ bones arranged in two rows of four bones in each hand • Metacarpals—palm • Five per hand • _______ —fingers and thumb • _______ phalanges in each hand • In each finger, there are three bones • In the thumb, there are only two bones Bones of the Pelvic Girdle • Formed by ____ coxal (ossa coxae) bones • Composed of ____ _____ pairs of fused bones • Ilium • Ischium • Pubis • Pelvic girdle = 2 coxal bones, sacrum • Bony pelvis = 2 coxal bones, sacrum, coccyx Bones of the Pelvic Girdle • The total weight of the upper body rests on the ______ • It protects several organs • Reproductive organs • Urinary bladder • Part of the large intestine Gender Differences of the Pelvis • The female inlet is larger and more circular • The female _____ as a whole is shallower, and the bones are ____ and _____ • The female ilia flare more laterally • The female _____ is shorter and less curved • The female ischial spines are shorter and farther apart; thus the outlet is larger • The female pubic arch is more rounded because the angle of the pubic arch is greater Bones of the Lower Limbs • ______ —thigh bone • The _____, _______ bone in the body • Proximal end articulation • Head articulates with the acetabulum of the coxal (hip) bone • Distal end articulation • Lateral and medial condyles articulate with the tibia in the lower leg Bones of the Lower Limbs • The lower leg has two bones • _____—Shinbone; larger and medially oriented • Proximal end articulation • Medial and lateral condyles articulate with the femur to form the knee joint • _______—Thin and sticklike; lateral to the tibia • Has no role in forming the knee joint Bones of the Lower Limbs • The foot • ______—seven bones • Two largest tarsals • Calcaneus (heel bone) • Talus • _______—five bones form the sole of the foot • Phalanges—fourteen bones form the toes Arches of the Foot • Bones of the foot are arranged to form three strong arches • Two longitudinal • One transverse