Physical Properties of Minerals
advertisement

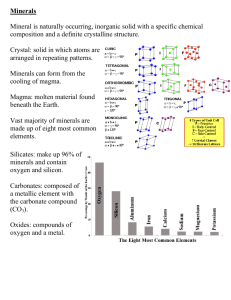
Tue 1/19 1. What is a mineral? Minerals are naturally occurring They are not made by humans Minerals are inorganic They have never been alive and are not made up from plants or animals Minerals are solids They are not liquids (like water), or gases (like the air around you) Minerals have a definite chemical composition Each one is made of a particular mix of chemical elements Minerals have an ordered atomic arrangement The chemical elements that make up each mineral are arranged in a particular way - this is why minerals 'grow' as crystals Crystal – the atoms that make up the mineral are arranged in a particular pattern. Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Luster • Surface reflection • metallic = shiny like metal • non-metallic = dull, non-shiny surface Pyrite has a metallic luster Calcite has a non-metallic luster Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Hardness • How easily a mineral scratches materials • Mohs Hardness Scale • Scale from 1 (softest) to 10 (hardest) • Test by seeing if the mineral can scratch different objects (like human fingernail, copper, penny, glass, steel file) Wed 1/21 2. What is a “Carat”? One carat weighs 200 milligrams, or one-fifth (.2) of a gram. This standard has been in use worldwide since 1914, when it was proposed by the International Committee on Weights and Measures. Fri 1/22 3. Name the mineral. Can be scratched by Topaz but not Feldspar. Quartz Mon 1/25 What happens when a mineral breaks? Tue 1/26 Why is a minerals streak more reliable than color? Streak is the same , even if different color. Thur 1/27 How do minerals form? What is the difference between a rock and a mineral? Fri 1/22 3. Name the mineral. Can be scratched by Topaz but not Feldspar. Quartz Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Color • Can be misleading • Can vary with the type of impurities Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Streak • The color of the powdered form of the mineral • The color of the streak can be different than the mineral • Minerals must be softer than the streak plate Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Luster • Surface reflection • metallic = shiny like metal • non-metallic = dull, non-shiny surface Pyrite has a metallic luster Calcite has a non-metallic luster Mon 1/25 What happens when minerals break? How do minerals form? • 1) Cooling of magma (hot, liquid rock and minerals inside the earth (from the mantle)) – Fast Cooling = No Crystals (mineraloids) – Medium Cooling = small crystals – Slow Cooling = large crystals • 2) Elements dissolved in liquids (usually How do minerals form? water)