The “brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and
advertisement
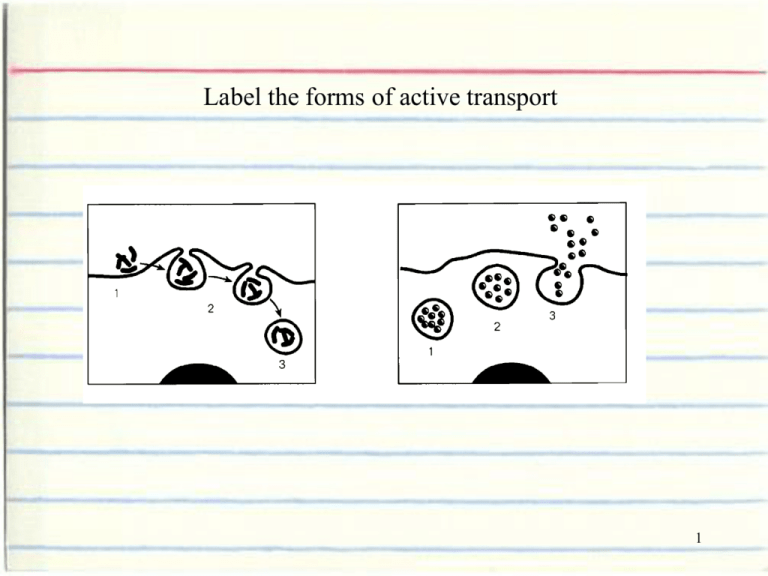
Label the forms of active transport 1 Endocytosis Exocytosis 2 What is the movement from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration? 3 Diffusion 4 Give the type of particle transport that requires input of energy from the cell. 5 Active Transport 6 What happens to cells placed in a hypertonic solution? 7 They shrink due to losing water by osmosis 8 When the concentration s across a cell membrane are the same… Does Osmosis occur? 9 No. Because the cell is at equilibrium in a state of homeostasis 10 Act like little garbage trucks to move around, pick up cell waste, and get rid of it 11 lysosomes 12 Stores wastes, nutrients, and water 13 vacuole 14 Active cells like muscle cells will need a lot of this organelle that carries out cellular respiration 15 mitochondria 16 Site of photosynthesis; green moving disks 17 chloroplast 18 Rigid outermost layer in plant cells 19 Cell wall 20 Larger storage organelle in plant cells than in animal cells 21 vacuole 22 "intracellular highway" because it is used for transporting proteins from the ribosomes 23 Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 24 The “brains” of the cell, that directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA 25 nucleus 26 Make proteins to be transported outside of the cell they are produced within 27 Ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum 28 The framework that anchors organelles within the cytoplasm 29 cytoskeleton 30 Works with the cell wall to maintain turgor pressure within plant cells 31 vacuole 32 _______________ cells have the capacity to assemble into multicellular organisms 33 Eukaryotic 34 What type of cell is shown below? 35 Plant cell 36 A prokaryotic cell lacks a _____ 37 nucleus 38 Label the diagram 39 40 Make conclusions from the graph 41 The rate of an enzyme depends on the temperature 42 Make a conclusion from the graph 43 pH affects the activity rate of enzymes 44 List the four major macromolecules and their functions in a living organism. 45 Carbohydrates – provide and store energy Lipids – store energy and insulation Protein – hormones, enzymes, muscles Nucleic acids – genetic information that regulates MOST cell activities 46 What part of the cell is selectively permeable? 47 Phospholipids of the cell membrane 48 What are the monomers of each macromolecule? 49 Carbohydrates – glucose Lipids – Fatty Acids Protein – amino acids Nucleic Acids - nucleotides 50










