Job - Cloudfront.net
advertisement
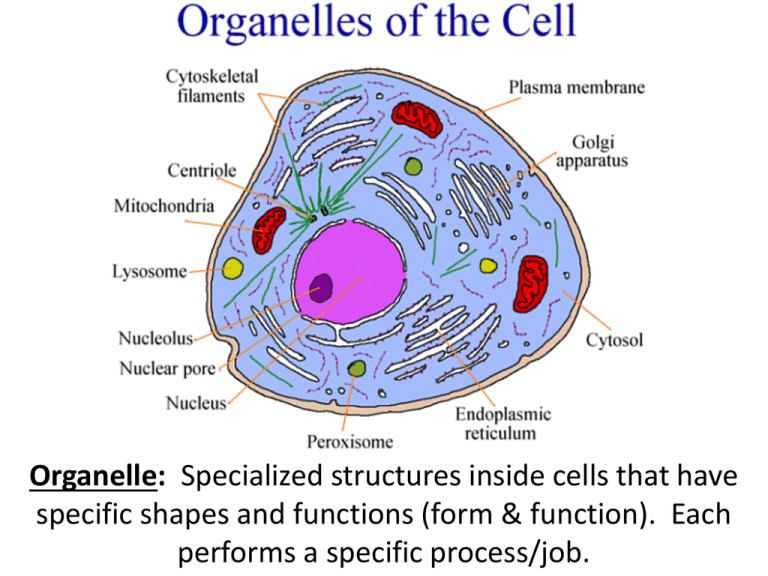
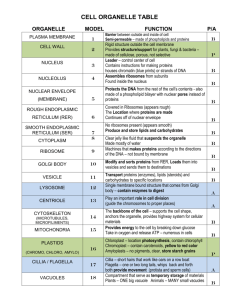
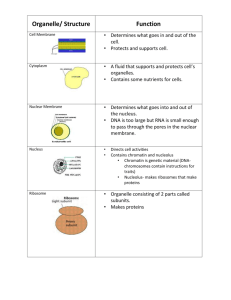
Organelle: Specialized structures inside cells that have specific shapes and functions (form & function). Each performs a specific process/job. Three Sections of the Cell • All cells take in food, rid waste, reproduce • 4 main sections –1) Cytoplasm –2) Plasma Membrane –3) Nucleus Cytoplasm & Cytosol • Cytoplasm: Everything between the plasma membrane & the nucleus that includes the cytosol and organelles. • Cytosol: Jelly-like fluid of the cytoplasm that surrounds organelles. They “float” within this space. – Job: Allow chemical reactions to take place. • Aka: Cell Membrane • Job: Allow materials to enter/exit • Composition: Lipids & proteins • Semi-Permeable: only specific materials may enter and exit – Through pores & protein channels • Job: Controls cell activity – Where DNA is found – DNA holds info to make proteins • Inside: – 1) Chromatin: long strands of DNA – 2) Nucleolus: makes ribosomes • AKA: ER • Rough ER: Tunnel system that transports ribosomes and proteins • Smooth ER: makes fats & breaks down toxins (no ribosomes) • Created by nucleolus – Exit through nuclear pores – Some attached to ER… some free-floating • Transported by the rough ER • Job: Make proteins • AKA Golgi Body • Job: Package and transport proteins out of the cell • Protein Creation Process Review 1) Nucleolus makes a ribosome 2) Ribosome makes protein & travels through rough ER 3) Golgi Body packages the protein into a vesicle and exports them (like a post office). • Membrane-bound sacs. • Job: • Hold materials, like protein, nutrients, or waste. • Transports materials into or out of a cell. Golgi Body in Action Vesicle expels the proteins (blue dots) from the cell Golgi body is placing proteins (yellow dots) into protective vesicles • Powerhouse: Releases energy to the cell • Job: Create ATP (energy molecule) in a process called cellular respiration • Endosymbiosis theory: Mitochondria were once free living organisms that later became parts of modern cells – Evidence: Own DNA, own ribosomes, make proteins, replicate • Contain digestive enzymes • Functions: –1) Break down food –2) Kill bacteria –3) Autolysis: Destroy dying cell • Job: Stores food, water, waste, color pigments • Swells & shrinks with H2O supply • Animal cells: Scattered smaller vacuoles • Centrosomes: Located near nucleus & contain 2 centrioles. –- Centrioles: Cylinders (tubes) found in the centrosomes and contain microtubules. – Job: Aids in cell division. Also forms cilia and flagella. • Used in movement • Cilia = Short hair-like extensions (numerous) • Flagella = Long whip-like extension (very few) That one magical night, sperm cells swam with the aid of a flagella! REview 1) Pick an organelle…any organelle. Describe its function. 2) Name 7 organelles that can be found within the cytoplasm. 3) Describe the pathway that proteins travel from creation to exportation. 4) Which organelle creates ATP energy for cells? 5) Which organelle creates ribosomes? 6) Which organelle fuses with the cell membrane to release proteins? 7) Which molecule holds the information to make a protein? 8) Which organelle helps with cell division? 9) What does it mean when we say that the plasma membrane is semi-permeable?