Cells chapter 3, section 2
DO NOW
: 11/29/10
List three differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Objectives:
1. Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell.
2. Explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell.
Cell Review
A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions.
Cell Theory
All living things are made up of cells.
Cells are the smallest working units of all living things.
All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division.
Examples of Cells
Amoeba Proteus
Plant Stem
Bacteria
Red Blood Cell
Nerve Cell
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html
Cell Wall
Some eukaryotic cells have cell walls.
A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to a cell.
The cell wall is the outermost structure of a cell.
Cell Wall, continued
Plants and algae have cell walls made of a complex sugar called
cellulose.
The cell walls of plant cells help plants retain their shape.
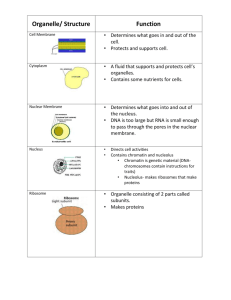
Cell Membrane
All cells have cell membranes.
The cell membrane is a protective barrier that encloses a cell.
In cells that have a cell wall, the cell membrane lies just inside the cell wall.
The cell membrane consists of phospholipids and proteins.
Cell Membrane, continued
The cell membrane controls movement in and out of the cell.
Phospholipid bi(double) layer
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a web of protein fibers in the cytoplasm.
Helps the cell retain its shape and move its organelles.
Nucleus
Directs cell activity
Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane.
Contains genetic material
DNA
DNA contains the information on how to make a cell’s proteins.
Nuclear Membrane
Surrounds nucleus
Made of two layers
Openings allow material to enter and leave the nucleus
Chromosomes
In nucleus
Compacted DNA
Contain instructions for traits and characteristics
Ribosomes
Organelles that make proteins are called ribosomes.
Unlike most organelles, ribosomes are not covered by a membrane.
Proteins are made of organic molecules called amino acids. All cells need proteins to live. All cells have ribosomes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materials are made.
The ER is part of the internal delivery system of the cell.
Substances move through the ER to different places in the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum, continued
Endoplasmic reticulum is either rough ER or smooth
ER. The part of the ER covered in ribosomes is rough
ER. ER that lacks ribosomes is smooth ER.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are the organelles in which sugar is broken down to produce energy (ATP).
Mitochondria are the main power source of a cell.
Mitochondria are covered by two membranes, as shown at right.
DO NOW
: 12/1/10
Pick any organelle that we have discussed so far, and explain what would happen if it was not a part of the cell.
Objectives:
1. Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell.
2. Differentiate between a plant cell and an animal cell.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are organelles in plant and algae cells in which photosynthesis takes place.
Photosynthesis is the process of using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make sugar and oxygen.
Chloroplasts are covered by two membranes.
Golgi Body
The organelle that packages and distributes proteins from the ER.
The Golgi body modifies lipids and proteins to do different jobs.
Final products are enclosed in a piece of the Golgi body membrane, which pinches off to form a small bubble.
Moves materials with in the cell and out of the cell.
Cell Compartments
The bubble that forms from the Golgi body membrane is a vesicle.
A vesicle is a small sac that surrounds material to be moved into or out of cell.
Vesicles also move material within a cell.
Vesicles distribute materials from the ER to the Golgi body, and from the Golgi body to other parts of the cell.
Cellular Digestion: Animals
Lysosomes are vesicles found mainly in animal cells that are responsible for digestion inside a cell.
Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes.
Lysosomes destroy worn-out or damaged organelles, get rid of waste materials, and protect the cell from foreign invaders.
Cellular Digestion: Plants
In plant and fungal cells, vacuoles act like lysosomes.
Vesicles for storage, digestion, and waste removal.
Stores water and other liquids.
Help plants maintain shape.
Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell
Review
What is the cell theory?
What organelles are present in plant cells that are not present in animal cells?