polyatomic ion
advertisement

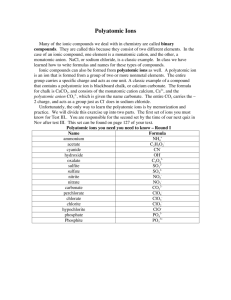
Chapter 7 cont. What are polyatomic ions? Review How does an atom form a negative ion, a positive ion? In a formula, the subscript tells you what kind of information? In a formula, a superscript tells you what kind of information? Many atoms can form one ion. A simple ion is called monoatomic, meaning “one atom”. The term polyatomic ion means a charged group or two or more bonded atoms that functions as a single ion. Atoms in a polyatomic ion are covalently bonded , but the ion as a whole forms ionic bonds with other ions in the same way that simple ions do. Most polyatomic ions consist of atoms of several elements. Compounds with monoatomic ions. Calcium bromide CaBr2 Sodium oxide Na2O Barium iodide BaI2 Compounds with polyatomic ions Sodium nitrate Na2SO4 Calcium chlorate Ca[ClO3]2 Ammonium nitrate NH4NO3 * Each polyaotmic ion is treated as a single unit and is kept together within a pair of brackets. Naming a polyatomic ion The names of polyatomic ions can be complicated. There is no logical way of naming these types of compounds, but.. There are rules that help determine the names of polyatomic ions. Many polyatomic ions contain oxygen. The endings –ite and –ate show the presence of oxygen. Such ions are called oxyanions. The prefix oxy stands for the presence of oxygen. The presence of hydrogen in a polyatomic anion is often indicated by the ion’s name starting with hydrogen. The prefix mono- and di- are also used. For example: HPO4 is called monohydrogen phosphate. and H2PO4 is called dihydrogen phosphate. So how do you name polyatomic compounds???? First, In order to understand naming, you must be able to identify the cations and anions in the formula. NaClO3 K2SO3 (NH4)2CrO4 Na+ , ClO3- Let’s Practice Write the name of the compound with the formula K2CO3 ? Step 1: Name the cation (positive charge) K2 Potassium Step 2: Name the compound Potassium carbonate If you look at Table 5-7 on page 178, you will 2see that CO3 ion is called the carbonate ion. Writing the formula Step 3: Name the anion (negative charge) [K]2[CO3]3 K+ K+ CO 23 You must balance the charges: total of 2 positive charges and 2 negative charges. More practice Write the formula for the compound containing a polyatomic ion. calcium dihydrogen phosphate. Step 1: Use the table to determine the formula and charge for the polyatomic anion. - dihydrogen phosphate is H2PO4. Step 2: Determine the formula and charge for the cation. If you look at your chart from your notes, you will be able to find the charge of the anion. Calcium is Because calcium has two positive charges, dihydrogen phosphate needs two negative charges. Ca2+ Therefore you write the balanced equation as follows: Ca[H2PO4]2 Ca2+ H2PO4- - H2PO4 *there must be two dihydrogen phosphates. Oxidation Numbers Where do you write the charge of an ion ? The charges listed for ions are used to show a transfer of electrons in the forming of an ionic bond. Atoms within polyatomic ions are bonded covalently. In the next chapter you will learn that in covalent bonds electrons are shared between atoms. Unlike transferred electrons in ionic bonds, shared electrons in covalent bonds are not considered part of either of the atoms. For example, the bonds between sulfur and oxygen atoms in SO42-, contain shared electrons. Neither Sulfur or Oxygen is an ion in SO4 Chemists have come up with a way for polyatomic ions and molecular compounds to describe the distribution of electrons among bonded atoms. This convention is called oxidation number. Oxidation number- a number assigned to an atom in a polyatomic ion or molecular compound based on the assumption of complete transfer of electrons. Some Guidelines for Assigning Oxidation Numbers Figure 5-13 shows a list of guidelines that can be used in assigning oxidation numbers. How to use the guidelines Assign oxidation numbers to all of the atoms in the compound: KOH 1st- determine the cation and the anion 2nd- determine whether they are monoatomic or polyatomic. 3rd- Read the rules to assign oxidation numbers. How To: Assign Oxidation numbers to all atoms in S2O72-this is a single polyatomic anion, there is no cation bonded to it. So different rules apply to polyatomic ions. Step 1 - If you know an elements oxidation number, start by placing those oxidation numbers above the elements (shown in red). - From rule 6, you know that oxygen has an oxidation number of -2. -2 S2O72- Step 2- If more than one atom of an element is present, calculate the total charge by those atoms by multiplying the individual atom by it’s subscript in the formula. For oxygen the total charge is calculated as follows O: (-2) 7 = -14 -2 S2O72-14 Step 3- Determine the charge needed to reach a net -2 for the ion. 2S + O7 = -2 2S + ( -14) = -2 2S = +12 Step 4- Divide the charge by the number of atoms to determine the oxidation number for each atom. S = 12/2 S = +6 In S2O72-, the oxidation number assigned to S is +6 and O is -2.