WRITING AND NAMING CHEMICAL FORMULAS

WRITING AND NAMING
CHEMICAL FORMULAS
STANDARDS
• Predict chemical formulas based on the number of valence electrons and oxidation numbers
• Name and write the chemical formulas for simple ionic and molecular compounds, including common polyatomic ions.
(standard list of common polyatomic ions need to be memorized)
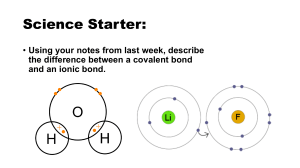
Chemical formula
• Combination of symbols that represent the composition of a compound.
• Formula represents
– elements involved
– ratio of those elements
Structural formula
• Shows how atoms are joined
• Shows kind of atoms and the number of atoms
• used primarily with organic compounds
• example
Interpreting chemical formulas
• practice
Monatomic ions
• Ions formed from a single atom
• Ion – charged atom
– Anion – negative ion
– Cation – positive ion
• oxidation number
– Indicates the general distribution of electrons among the bonded atoms
Oxidation numbers
• periodic table
• handout - memorize
• roman numeral
– Stock system of nomenclature is used to distinguish the ion charge
– Ex. Iron can be +2 or +3
• Silver – transition metal but has only +1 – can be named w/o roman number
Older naming system
• Older naming system –
– when metal forms has more than 1 common oxidation number,
• The ion with the higher charge has a name ending in ic
• The one with the lower charge has a name ending in ous
• Ex – Fe+3 – ferric
• Fe+2 – ferrous
Polyatomic ions
• A charged group of covalent covalently bonded atoms
• Handout
– Make flash cards
Writing chemical formulas
Naming chemical formulas
• Handout - memorize
• chart
• transition elements
Molecular formula
• Formulas for compounds that exist as molecules
Empirical formula
• The simplest formula
• used to help identify unknown substances
• Molecular formula of a compound is always written as some whole-number multiple of the empirical formula
• ionic compounds - always written as empirical formula
Writing empirical formula
• Practice problems