Warm-Up - mssarnelli
advertisement
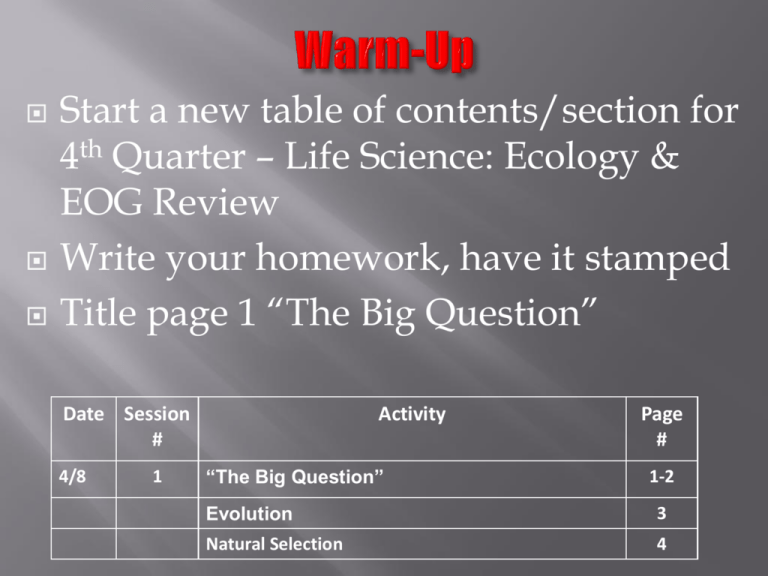
Start a new table of contents/section for 4th Quarter – Life Science: Ecology & EOG Review Write your homework, have it stamped Title page 1 “The Big Question” Date Session # 4/8 1 Activity “The Big Question” Page # 1-2 Evolution 3 Natural Selection 4 Step 1: Write the following statement at the top of page 1: Everything Evolves. Step 2: Come up with as many questions as possible about this statement as a class. Write down everybody’s questions on page 1! IMPROVING THE QUESTIONS You might have these two kinds of questions in your list: • Closed-ended questions – they can be answered with “yes” or “no” or with one word. • Open-ended questions – they require an explanation and cannot be answered with yes” or “no” or with one word. • Identify each question with an “O” or a “C” www.rightquestion.org Select ONE of the questions as a priority question and write it on the top of page 2. You will investigate this question over the next week and a half. You can add notes/reflections from lessons, pictures from online, research info, other questions that are prompted from your connection question… Evolution – The process of change over time evolution can be biological or geological How would they be related? Geological evolution is driven by The Theory of Plate Tectonics and the idea that Earth itself has evolved Remember… Geologic Time Scale Tectonic Plate Movement Continental Drift & Pangaea Law of Superposition Fossils Biological evolution is driven by the changes in Earth…living things evolve in response to changes in their environment. This process is known as Natural Selection or “Survival of the Fittest.” There are 4 principles of Natural Selection: Overproduction Variation Adaptation Selection OverproductionVariation Definition: Definition: Example: Example: AdaptationSelection Definition: Definition: Example: Example: So how do animals and plants adapt to their environment over time? Elephant Adaptation Video- shows how evolution of the Earth affects the evolution of a species http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?gui dAssetId=0B5B292A-983E-4327-A27DB647383BF293&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US Objective: - Analyze each picture to find examples of the 4 principles of Natural Selection. Activity: - Each photo is numbered, so…in your notebook number 1-10. Next to each number write as many examples of the 4 principles of Natural Selection as you can justify! Sea Turtle Land Turtle VS. Find ONE original example of Natural Selection that we did not talk about in class! EXAMPLE: The warrior ant of Africa can learn to imitate the chemical signal from other ant colonies so they can invade and take over undetected! This is an example of adaptation. Look back at your “Big Question” – summarize any information you learned today that helps you answer your questions…write until the bell rings! Update your Table of Contents Get your homework out to be checked Write your new homework – have it stamped Date Session # 4/10 2 Activity Page # Evidence of Evolution Foldable 5 Evidence of Evolution Worksheet 6 Evidence of Evolution…(start a list on page 5) What were the 4 Principles of Natural Selection again? Would you be selected to survive? Let’s find out! When Charles Darwin, “The Father of Evolution,” first proposed the idea that ALL species descend from a common ancestor he needed evidence to support his claim. The major pieces of evidence can be broken into… 1. 2. 3. 4. Fossils Embryology Comparative Anatomy Molecular Biology HUH? What does all that mean? Fossils – show change in a single species over time or similarities between species Evolution of the Modern Horse Embryology – shows similar developmental stages amongst different species Homologous Structures – same anatomical structure but different function that arise from different organisms sharing a common ancestor Analogous Structures – different anatomical structure but similar function that arise from common environmental demands Vestigial Structures – Anatomical remnants that were important in an organism’s ancestors, but are no longer used in the same way Molecular Biology - the genetic structure of an organism The key to understanding how traits are passed from one generation to the next is DNA analysis Scientists can tell how closely related organisms are by studying their DNA There does not have that much of a difference in a gene sequence to be a different organism! Update your Table of Contents Get your homework out to be checked Write your new homework – have it stamped Date Session # 4/12 3 Activity Survival of the Fittest Scenarios & Natural Selection Nemo Style Page # 7 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LzlUZrt0 Ums What do you notice about the evolution of a species…in other words, what changes? Changes occur in the body or structure of an organism…this is referred to as an organisms phenotype. PHENOTYPE – body structures and characteristics Natural Selection Or “Survival of the Fittest” What does “Survival of the Fittest” really mean? In the next few scenarios,describethe phenotype that would most likely be “selected” to survive… Scenario 1: Drought - There has been a drought and all of the grass has dries up anddies first, but the leaves on bushes and trees are slower to die…who survives the longest? A. B. C. D. Animals with short legs but long necks Animals with long legs, but short necks Animals with both long legs and long necks Animals with both short legs and short necks Scenario 2: Predator is Approaching - A predator is approaching the herd, but is not hunting yet…who will know sooner and therefore have a better chance to escape? Scenario 3: Predator Fight - A predator has arrived. It is too late to run away or hide, the animals must fight off the predator…who has the best chance at fighting? Scenario 4: Blizzard - The weather becomes very cold. There is a blizzard and the land is covered in snow…who survives? Scenario 5: Volcanic Eruption - There has been a volcanic eruption. Lava flows down the mountain onto the plains and kills anything in its path…who will make it? Classroom Challenge Mini – Lab 1. 2. 3. 4. There are 4 utensils that need to be tested to ensure your survival, and which habitat you are most suitable for. Each person will receive a utensil, you will rotate the utensils for each round. You will have 30 seconds to test each utensil and then 10 seconds to record your results. Your cup is your “stomach” and your stomach must remain upright on the table the entire time. Create a cartoon that illustrates the idea of “Survival of the Fittest” Keep in mind: The 4 Principles of Natural Selection The idea of “Survival of the Fittest” Basic scientific information Update your Table of Contents Put your Survival of the Fittest Cartoon in the basket No homework – quiz on Evolution scheduled for next Wednesday Date Session # 4/16 4 Activity Biological Classification Notes Page # 8 We know that there are many different species on Earth, but where did they all come from? Speciation – over time the beneficial variations that are passed on to the next generation will accumulate and the result will be an entirely different organism (not just a variation of the original, but an entirely new creature) Don’t believe that one small change can accumulate into many…let’s try it using Evolution Telephone How does this game of telephone relate to speciation? How are we able to organize and identify all of these different species? Taxonomy – biological classification is also referred to as taxonomy – it is a system to organize & describe all life on Earth What are the benefits of biological classification (taxonomy)? Simple organization Examine relationships between organisms that exist now Construct evolutionary trees to explore the origins of life on Earth Examine relationships between modern & ancient organisms What are the categories we use to classify an organism? Example: Life form: Humans Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primates Family: Hominidae Genus: Homo Species: Sapiens How closely related to the other species in our kingdom, phylum etc. are we? Evolutionary Tree – also known as a phylogenetic tree; like a family tree but shows the relationships between species branching back to common ancestors How did this evolutionary tree start? Let’s Find Out… http://www.wellcometreeoflife.org/video/ So what are the evolutionary predictions for the next million years? That’s Your Job… With your group create the next branch on the evolutionary tree! “Our prediction is that the temperature on Earth will continue to rise therefore humans will have to adapt by having scales to resist the heat” The name and specific characteristics including the kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus & species – this is a new organism so you can MAKE IT UP! Update your Table of Contents We are going to go over directions for the computer lab and then we will leave Complete all activities to be turned in for a grade Date Session # 4/18 5 Activity Nothing to paste in today Page # XXXX