Evolution
advertisement

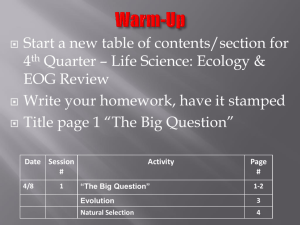
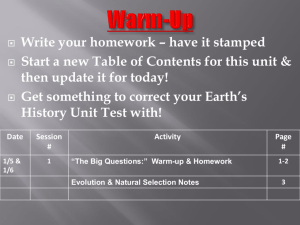
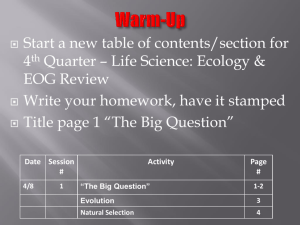
Write your homework – have it stamped Draw a line through your Table of Contents to separate this section of the unit & then update it for today! Get something to correct your Unit Test with Date 12/16 & 12/17 Session # 1 Activity “The Big Question:” Warm-up on Page 1 Homework answers on page 2 Page # 1-2 Evolution Notes 3 Natural Selection Notes & Gallery Walk 4 “THE BIG QUESTION” Does everything evolve? “THE BIG QUESTION PART 2” How do we know everything evolves…what could we use as evidence? Take a few minutes and… Write down any and all questions that come to your mind about evolution - at least 10 - that you would like answered. • •Leave space between your questions so that you can answer them for homework! • Scan the QR code I give you to take you to a website to search the answers…or search on your own! Evolution – The process of change over time evolution can be biological or geological How would they be related? Geological evolution is driven by the idea that Earth itself has changed since it’s formation 4.6 billion years ago. Remember all of our previous evidence? • Law of Uniformitarianism •Geologic Time Scale • Tectonic Plate Movement • Continental Drift & Pangaea • Law of Superposition • Fossils Biological evolution is driven by the changes in Earth…living things evolve in response to changes in their environment. This response leads to a change in genetic material that is passed through generations, or the process of Natural Selection or “Survival of the Fittest.” There are 4 Principles of Natural Selection! Overproduction Definition: When an organism makes more offspring than the environment can support to ensure that at least some survive Example: Variation Definition: Naturally occurring differences in traits due to differences in genetics -these variations or mutations get passed to offspring Example: Adaptation Definition: Inherited trait that gives an organism an advantage in its environment over other members of its species Example: Selection Definition: Organisms with an adaptation will be “naturally selected” to survive and reproduce passing on the adaptation. Example: So how do animals and plants adapt to their environment over time? Elephant Adaptation Video - shows how evolution of the Earth affects the evolution of a species http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?gui dAssetId=0B5B292A-983E-4327-A27DB647383BF293&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US Objective: - Analyze each picture to find examples of the 4 principles of Natural Selection. Activity: - Each photo is numbered, so…in your notebook number 1-10. Next to each number write as many examples of the 4 principles of Natural Selection as you can justify! Sea Turtle Land Turtle VS. Create an additional example that could be added to our gallery walk by finding one ORIGINAL example of Natural Selection that we did not talk about in class, and creating the informational poster about it! EXAMPLE: The warrior ant of Africa can learn to imitate the chemical signal from other ant colonies so they can invade and take over undetected! This is an example of adaptation because… Write your homework – get it stamped! Update your table of contents for today! Get your homework out to be checked, and be ready to share some of the answers you found! Date 12/17 & 12/18 Session # 2 Activity Evidence of Evolution Notes & Images Genotype Vs. Phenotype Analysis Page # 5-6 7 What is evolution? We focused on geological evolution in the last section of this unit, so we are going to focus on biological evolution in this section…HOW DOES BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION HAPPEN? Process by which species change over time in response to their environment. This response leads to a change in genetic material that is passed through generations, or the process of Natural Selection or “Survival of the Fittest.” What were the 4 Principles of Natural Selection again? Would you be selected to survive? Let’s find out from our “Survival of the Fittest Challenge!” Based on the challenges of this environment, what traits or genetic variations are important in giving students the physical advantage or adaptation for survival? What if the environmental demands changed? So, what can you infer about the relationship between variations (which are genetic) and adaptations (which are physical advantages)? The body structure and characteristics are dependent on the genetic code! In other words, the genetic variation leads to the physical adaptation! This idea was the basis used as evidence for evolution! GENOTYPE – genetic code or DNA structure PHENOTYPE – body structures and characteristics Now, when Charles Darwin, “The Father of Evolution,” first proposed the idea that ALL species descend from a common ancestor he needed evidence to support his claim. The major pieces of evidence can be broken into… 1. 2. 3. 4. Fossils Embryology Comparative Anatomy Molecular Biology HUH? What does all that mean? It means that we use both the genetic characteristics and physical characteristics to as evidence to determine how a species has evolved and how they are related to each other! GENOTYPE – genetic code or DNA structure molecular biology PHENOTYPE – body structures and characteristics fossils, embryology, comparative anatomy Fossils – show change in a single species over time or similarities between species Evolution of the Modern Horse Embryology – shows similar developmental stages amongst different species Embryology Challenge: Embryos of a human, chicken, tortoise, fish, rabbit & salamander…which one is which? Homologous Structures – same anatomical structure but different function that arise from different organisms sharing a common ancestor Analogous Structures – different anatomical structure but similar function that arise from common environmental demands Vestigial Structures – Anatomical remnants that were important in an organism’s ancestors, but are no longer used in the same way Molecular Biology - the genetic structure of an organism Key to understanding how traits are passed from one generation to the next Scientists can tell how closely related organisms are – the difference in gene sequences between organisms is very small!! Both the phenotype and genotype are useful in determining the relationships between organisms, but what is the relationship between them? Complete the Genotype Vs. Phenotype Analysis with a partner of your chosing. Complete the Genotype Vs. Phenotype Pros & Cons Chart for homework once you have some experience working with both of them! No homework over break! Update your Table of Contents for today! Get your homework out to be checked…share some of your pros & cons! Date Session # 12/20 & 1/6 3 Activity Survival of the Fittest Scenarios & Natural Selection Nemo Style Page # 8 What is the connection between phenotypes /genotypes and Natural Selection? What does “Survival of the Fittest” really mean? In the next few scenarios, describe the type of animal that would most likely be “selected” to survive… Scenario 1: Drought - There has been a drought and all of the grass has dries up and dies first, but the leaves on bushes and trees are slower to die…who survives the longest? Scenario 2: Predator is Approaching - A predator is approaching the herd, but is not hunting yet…who will know sooner and therefore have a better chance to escape? Scenario 3: Predator Fight - A predator has arrived. It is too late to run away or hide, the animals must fight off the predator…who has the best chance at fighting? Scenario 4: Blizzard - The weather becomes very cold. There is a blizzard and the land is covered in snow…who survives? Scenario 5: Volcanic Eruption - There has been a volcanic eruption. Lava flows down the mountain onto the plains and kills anything in its path…who will make it? Classroom Challenge Mini – Lab 1. 2. 3. 4. There are 4 utensils that need to be tested to ensure your survival, and which habitat you are most suitable for. Each person will receive a utensil, you will rotate the utensils for each round. You will have 30 seconds to test each utensil and then 10 seconds to record your results. Your cup is your “stomach” and your stomach must remain upright on the table the entire time. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LzlUZrt0 Ums Keep in mind: The 4 Principles of Natural Selection The idea of “Survival of the Fittest” Basic scientific information Create an ORIGINAL cartoon or comic strip that illustrates the idea of “Survival of the Fittest” Update your Table of Contents No homework – quiz on Evolution scheduled for next Wednesday Date Session # 4/16 4 Activity Biological Classification Notes Page # 8 What do we use all of this evidence for? To build relationships between organisms and once we have those relationships established we can use them to build evolutionary trees and classify organisms based on the taxonomic system How did this evolutionary tree start? Let’s Find Out… http://www.wellcometreeoflife.org/video/ We know that there are many different species on Earth, but where did they all come from? Speciation – over time the beneficial variations that are passed on to the next generation will accumulate and the result will be an entirely different organism (not just a variation of the original, but an entirely new creature) Isolation Don’t believe that one small change can accumulate into many…let’s try it using Evolution Telephone How does this game of telephone relate to speciation? How are we able to organize and identify all of these different species? Taxonomy – biological classification is also referred to as taxonomy – it is a system to organize & describe all life on Earth What are the benefits of biological classification (taxonomy)? Simple organization Examine relationships between organisms that exist now Construct evolutionary trees to explore the origins of life on Earth Examine relationships between modern & ancient organisms What are the categories we use to classify an organism? Example: Life form: Humans Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primates Family: Hominidae Genus: Homo Species: Sapiens How closely related to the other species in our kingdom, phylum etc. are we? Evolutionary Tree – also known as a phylogenetic tree; like a family tree but shows the relationships between species branching back to common ancestors Technology activity Intro to Reading Phylogenetic Trees Practice with phylogentic trees – beetle activity Next lesson – pull it all together “Story of the Whippo” Update your Table of Contents – write a reminder about the Evolution Test next Wednesday Get your folder so that we can file some quizzes! Last few Vietnam presentations before we go…(4th block only) Date Session # 4/18 5 Activity Nothing to paste in today Page # XXXX 1. Complete any remaining research or additions for your “Big Question.” This page must be ripped out of your notebook and turned in. 2. Complete the “Understanding Evolution” WebQuest * Staple both together & turn in for a class work grade!