INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
advertisement

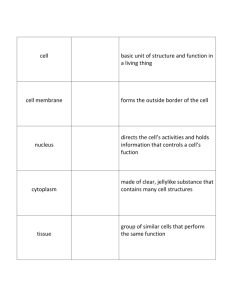
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DEFINITIONS Anatomy - “to cut apart” - Study of Bodily Structure - Includes: * Systemic or Regional * Gross or Microscopic * Developmental * Imaging DEFINITIONS continued Physiology - “study of nature” - Study of Bodily Function - Includes: * Cell Physiology * Pathophysiology * Immunology * Exercise Physiology LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION Chemical - Atoms, Molecules Cellular - Organelles, Cells Tissue - Groups of Cells Organ - 2 or more tissue types - Specific functions - Recognizable shape LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION continued System - Groups of related organs - Work together toward common function - 11 organ systems Organismal - Highest level - All parts of organism 11 Organ Systems Integumentary – external body covering; protection & sensation Skeletal – internal support; protection Muscular - movement Nervous – fast-acting control system Endocrine – hormonal control; secreted by glands 11 Organ Systems Cardiovascular – Transports via circulating blood Lymphatic – Returns fluid leaked from blood; immune defense Respiratory – exchanges gases (O2 & CO2) with environment Digestive –Breakdown & absorption of food; elimination of undigestable food 11 Organ Systems Urinary – Removes most metabolic wastes from the blood as urine Reproductive – produces offspring HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis - Maintaining a relatively stable internal environment, regardless of external conditions. - Allows changes within narrow limits. - “Dynamic Equilibrium” - Regulated by feedback mechanisms Homeostatic Control Mechanisms - 3 Components *Receptor – detects changes *Control Center – to determine set point (normal) and appropriate response to deviations *Effector – responds to change Negative Feedback - Control of Room Temperature Homeostatic Control Mechanisms Negative Feedback System - Common Reverses Change Results in Fluctuations about Set Point e.g. control of body temperature Positive Feedback System - Rare Change is increased May be Harmful (induced by pathogens) e.g. lactation, blood clot formation Positive Feedback – Blood Clot Formation TERMINOLOGY Anatomical Position - Erect Stance, Palms Forward Directional Terms - Explain Relative Location of Body Parts - Many Paired Opposites Regional Terms - Refer to Specific Body Parts, Regions - Divided into Anterior & Posterior Landmarks Directional Terms Regional Terms Some Examples… Cephalic - head Cervical - neck Axillary - armpit Brachial - arm Inguinal- groin Gluteal - buttock Femoral - thigh TERMINOLOGY continued Body Planes & Sections - Frontal (Coronal) * Vertical, Divides into Anterior & Posterior - Transverse * Horizontal, Divides into Superior & Inferior - Sagittal (Para- & Mid-) * Vertical, Divides into Right & Left - Oblique * Diagonal, Between Vertical & Horizontal TERMINOLOGY continued Body Cavities (Protect & Allow for Growth/Change) Dorsal & Ventral form during embryological development - Dorsal * Cranial - Brain * Spinal or Vertebral – Spinal Cord BODY CAVITIES continued - Ventral * Thoracic Pleural - Lungs Mediastinal – Trachea, esophagus, thymus; Between Lungs Pericardial – Heart; division of mediastinal * Abdominopelvic Abdominal (Peritoneal) Pelvic Abdominopelvic Quadrants Abdominal Regions Hypochondriac – spleen & parts of diaphragm, liver, kidneys, pancreas Epigastric – Most of pancreas & parts of stomach, liver, duodenum, IVC, abdominal aorta Lumbar/Lateral Umbilical Iliac/Inguinal Hypogastric