Nouns
advertisement

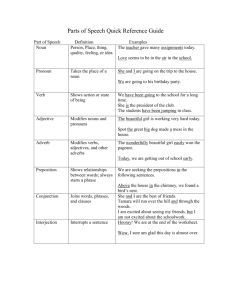
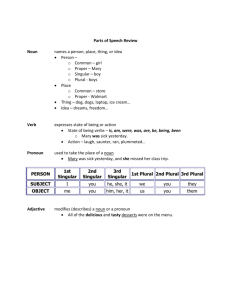
Parts of Speech Nouns Common vs. proper Common-a person, place, thing, or idea Ex. celebrity Proper-a specific person place thing or idea Ex. Katy Perry Common vs. Proper practice Cotton from Egypt has long, silky fibers. Common: cotton and fibers Proper: Egypt Abraham Lincoln was born in Kentucky. Common: none Proper: Abraham Lincoln, Kentucky Paul and his brother stopped to see the animals. Common: brother, animals Proper: Paul Concrete vs. Abstract Concrete: a noun that is material Perceived by the senses you can touch and see this type of noun Ex. chair, house, car Abstract: a noun that is immaterial An idea, quality or state You cannot touch or see this Ex. Kindness, love, hate Concrete vs. Abstract Practice A silver bullet should be used to kill a werewolf. Concrete: bullet, werewolf Stories of monsters have always created suspense. Abstract: suspense Concrete: monsters, stories Compound nouns A noun made up of two words combined together to form one word Ex. Flowerpot, southeast The teacher writes our assignments on the chalkboard. I can see your footprint in the sand. Collective Nouns A noun that appears singular, but denotes a group of persons or objects Ex. Herd, clergy, jury The pack of coyotes tried to eat my dog. A flock of birds flew toward me so I ran away. Pronouns Personal pronouns A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun or another pronoun. Antecedent-the word the pronoun replaces Types of personal pronouns First Person Second Person Singular Plural I, me (my, mine) we, us (our, ours) you (your, yours) Third Person he, him, she, her, it you (your, yours) they, them (their, theirs) Personal Pronouns Replace the noun with appropriate pronouns. Tarzan wondered where Jane was. He wondered where she was. Tarzan and Jane were having a romantic dinner together. They were having a romantic dinner together. Personal Pronouns Identify the antecedent in the following sentences and the pronoun which it replaced. When dinosaurs walked the earth, they were impressive indeed. P-they A-dinosaurs Experts on dinosaurs say that they were the largest land animals ever. P-they A-experts Imagine the excitement a scientist would feel when he or she found dinosaur bones! P-he or she (if the gender is unknown, you must use he or she!) A-scientist Indefinite Pronouns-refer to people, places or things without specifying which one 3 types: singular, plural or both Singular – use with “is” another anybody anyone anything each either everybody everyone everything much neither nobody no one nothing one other somebody someone something Everybody is going to the mall Someone left his or her planner in the classroom. Indefinite Pronouns-Plural Use with “are” both few many others several Example: Both of them are going to the store Example: Several of their friends are going on vacation. Indefinite Pronouns-Singular or Plural all any more most none some Use the subject to determine whether the personal pronoun is singular or plural. Some of the jam is grosse. Jam is singular, so you use is Several of the containers were missing their labels. Containers is plural, so you use the pronoun their Indefinite Pronouns Practice All of the students in the class enjoyed (their, his or her) time away from class. Their-students is plural, therefore the matching pronoun is plural as well Everybody brought (his or her, their) backpack with dry socks and shoes. His or her- Everybody is a singular indefinite pronoun Few in the group could resist (his or her, their) love for outdoor cooking. Their-few is plural so the personal pronoun that corresponds must be plural as well Verbs A word used to express action or describe a state of being 2 different types of verbs 1. action-express an action that the subject of the sentence is carrying out Examples: Donald laughed. Jane wrote a novel. Erma made some soup. (She’s engaged in the making of soup) 2. linking-the verb links the complement back to the subject (the complement must give some information about or description of the subject) Examples: Donald is funny. The novel became a bestseller. The soup smelled wonderful. Transitive Verbs vs. Intransitive Verbs Transitive-an action verb that appears with a direct object Direct object: a person or thing that receives the action of the verb Example: Simon met a pie-man, going to the fair. Example: Simon bought a pie. Intransitive-an action verb without a direct object Example: Sam snores. Example: Sally sneezed. Example: The children snickered. Example: All of the flowers wilted in the sun. Auxiliary Verbs (helping verbs) Combine with verbs to form verb phrases Example: would have been climbing Common auxiliary verbs: be, had, do, might, would, will, must, could, would Hint: To identify verbs, use the WILL test If you can put WILL in front of a word and the result is grammatical, then that word must be a verb. The WILL Test for Verbs Noun-Should we get another round? Verb-The horses round the last post and head for home. Adjective-He put a small, round pebble in his pocket. NOW APPLY THE WILL TEST! Noun-Should we get another (will) round? Verb-The horses (will) round the last post and head for home. Adjective-He put a small, (will) round pebble in his pocket. Adverbs Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs Clue to help you remember: ADVERB-modifies verbs ADVERB-modifies adjectives ADVERB-modifies other adverbs Adverbs Answer the questions where, when, how, and to what extent Where-Put the new bookcases there, please. When-Tomorrow, the painters begin work on our house. How- Speak softly when you come into the nursery, so you don’t wake up the baby. To what extent-The baby’s room is nearly complete. Adverbs Practice I genuinely love teaching. Today, I will be dressed up in a costume. I hope to attain a doctorate in literature someday. Adverbs vs. Adjectives Adverbs 1. Modify verbs, adjectives, and adverbs 2. Answers a. where? b. when? c. how? d. to what extent? 3. Many adverbs end in –ly -don’t overlook the ones that don’t though! Adjectives 1. Modify nouns and pronouns 2. Answers a. what kind? b. which one? c. how many? 3. Common adj. suffixes a. –ous (humorous) b. –ious (hilarious) c. –ible (horrible) d. –able (capable) e. –ent (apparent) f. –ant (tolerant) g. -ic (gothic) h. –al (magical) i. –y (funny) k. –st (last) Adverbs vs. Adjectives Practice State if the underlined word is an adverb or adjective. 1. She rarely brings a pencil to class, and I always give her a different one every day. Rarely is an ________ Different is an________ Every is an _________ 2. Julie is honestly the best dancer I have coached. Honestly is an _________ Best is an ____________ Prepositions Shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence Almost always comes BEFORE the noun That is why it is called a preposition Common prepositions: about, by, during, on, under, to Example: He is going to the store. Preposition: Noun/pronoun: Example: The toy is for you. Preposition: Noun/pronoun: Prepositions Indicate location: The puppy is on the floor. The puppy is in the trash can. The puppy is beside the couch. On, in and beside are showing where the puppy is. Prepositions Compound prepositions: Prepositions formed from more than one word Examples: according to, in place of, because of, and instead of, as of, next to, out of, prior to Can also show location in time: during, since At midnight, Jack and Jill went to a showing of Breaking Dawn: Part II. During the marathon, my legs began to cramp. Prepositional phrase: preposition + object Prepositions Subject + verb preposition “noun” The food is on the table. She lives in Japan. Tara is looking for you. The letter is under your blue book. Pascal is used to English people. She isn’t used to work. I ate before the wedding.