EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2
advertisement

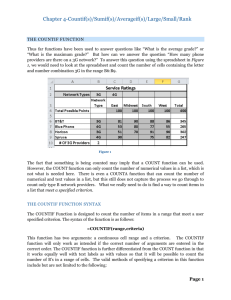
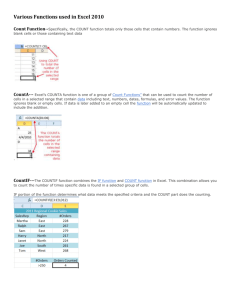
EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Microsoft Excel 2007 – Level 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END ADVANCED FUNCTIONS AND FORMULAS 2-1 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END Performance Objectives • Use named ranges in formulas • Use functions COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • Use functions AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • Use functions SUMIF, SUMIFS • Delete a range name • Look up data using the lookup functions VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP • Analyze financial data using PPMT, PV and NPV • Use conditional logic functions IF, AND, OR, NOT, and IFERROR • Modify text using the text functions PROPER, UPPER, LOWER and SUBSTITUTE 2-2 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END Naming a Range • Assigning a name to a range of cells allows you to reference a range of cells by a descriptive label • A name should describe the range of cells for example, January_Sales • Names can be a combination of letters, numbers, underscore characters or periods up to 255 characters • The first character must be a letter, an underscore or a backslash (\) • Spaces are not allowed, use underscore character or period to separate the words • A valid cell address cannot become a range name • Range names are not case sensitive 2-3 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. Naming a Range…/2 EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions Select the cell or range of cells to be named Click the Name box, type the name, and press Enter • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Click OR Type name and Click OK • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-4 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using a Named Range in a Formula LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS Range names can be used in formulas instead of the references to the cells • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END Using a range name in a formula makes the formula easier to understand 2-5 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END Understanding Functions • A function is a built-in formula • Functions perform complex mathematical, financial, data-manipulation, and logical operations • Functions include: 1. The name of the function 2. One or more arguments - (the data needed to perform the calculations or data manipulations, enclosed in parentheses) 3. No spacebars unless part of a text string 4. Text strings must be enclosed in quotations =function(argument1, argument2, etc.) 2-6 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Entering a Function Functions can be keyed directly into a cell OR Functions can be entered using the Insert Function button on the formula bar • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV OR • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-7 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. Click and choose the desired formula EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Insert Function Dialog Box LINKS TO OBJECTIVES Search for a function by typing a query • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS OR • SUMIF, SUMIFS Select a category and click the function • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE A description of the currently selected function is displayed • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-8 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS Function Arguments Dialog Box Entering arguments for the function … If an argument name is bold, data must be entered in its box Click to select cells in the worksheet • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV The result of the formula will display • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END Click for Help Function Arguments return box appears and is filled in as you select cells 2-9 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. Click to return EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Statistical Functions LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions Excel's statistical functions are used on ranges of data • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-10 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the COUNT and COUNTA Functions LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS Counts the number of cells containing numbers in a given range =COUNT(range) • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Counts the number of cells containing text or a combination of text and numbers in a given range • Features Summary BACK NEXT END =COUNTA(range) 2-11 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions Using the COUNT Function Make desired cell for result active Click Insert Function button Change category to Statistical • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT Select ‘COUNT’, Click OK END 2-12 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions Using the COUNTA Function Make desired cell for result active Click Insert Function button Change category to Statistical • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT Select COUNTA, Click OK END 2-13 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 COUNT and COUNTA Functions.../2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges =COUNT(D8:D24) returns the incorrect result 0 • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions =COUNTA(D8:D24) returns the correct result 17 • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-14 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Using the COUNTIF Function Counts the number of cells in a given range that meet a specific condition =COUNTIF(range,criteria) • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE The range of cells to be counted • Features Summary BACK NEXT The condition that must be met in order for that cell to be counted can be a number, an expression, or text END 2-15 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS Using the COUNTIF Function…/2 Make desired cell active Click Insert Function button • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV Change category to Statistical • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT Select COUNTIF, Click OK END 2-16 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions Using the COUNTIF Function…/3 Enter range name or address • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Type criteria • Lookup Functions Click OK • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Found 4 cells in the range A6:A20 that contained the word ‘Pathfinder’ • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-17 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS Using the COUNTIFS Function Counts the number of cells in a given range that meet multiple criteria The range of cells to be counted • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions =COUNTIFS(range1,criteria1, range2,criteria2) • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE The conditions that must be met • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-18 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges Using the COUNTIFS Function…/2 COUNTIFS formula • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS Multiple ranges and criteria to count • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Result of formula • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-19 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS Using AVERAGEIF and AVERAGEIFS Functions Finds the Average within a specified range that meets a single criterion =AVERAGEIF(range, criteria,average_range) • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions Finds the Average of cells with multiple criteria First range of cells to be tested • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT Conditions that must be met First Range containing values to be averaged =AVERAGEIFS(average_range1, criteria1,average_range, range2,criteria2,average_range) END Second set of arguments 2-20 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS Using the AVERAGEIF Function Make desired cell active Click Insert Function button • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV Change category to Statistical • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT Select AVERAGEIF Click OK END 2-21 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges Using the AVERAGEIF Function…/2 Enter range to be tested • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Type criteria Enter range to be averaged • Lookup Functions Click OK • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Returns the average of those cells that meet the criteria • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-22 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Using the AVERAGEIFS Function Make desired cell active Click Insert function button Change category to Statistical • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Select AVERAGEIFS Click OK • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-23 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS Using the AVERAGEIFs Function…/2 Enter range address or range name Enter range to scan and the criteria to meet • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Enter next range and condition • Features Summary BACK NEXT END Can enter up to 127 ranges and criteria; scroll to enter more 2-24 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. Click OK EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Math and Trig Functions LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV Excel includes many math and trigonometric functions to perform a wide variety of calculations • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-25 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Using the SUMIF Function Calculate the total of only those cells that meet a given condition or criteria =SUMIF(range,criteria,sum_range) the range of cells to be evaluated • Features Summary the condition or criteria the cell is to meet to be included in the sum - can be a number, an expression, or text BACK NEXT END 2-26 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. the range of cells to sum EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the SUMIF Function…/2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END Add only those commissions on sales greater than or equal to $40,000 2-27 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS Using the SUMIFS Function Calculate the total of only those cells that meet multiple conditions or criteria • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT =SUMIFS(sum_range, the range of cells to sum criteria_range1,criteria1, criteria_range2,criteria2, …) the range of cells to be evaluated END 2-28 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. the condition or criteria the cell is to meet to be included in the sum EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges Managing Range Names Click Create a new name • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT Select a name, then click to make changes or delete it END 2-29 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Lookup and Reference Functions LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV Excel's Lookup and Reference functions provide a way to extract information from a list • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-30 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions Using the VLOOKUP Function Search for a value in the leftmost column of a table and return a value from a different column, from the same row as the value found =VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num [,range_lookup]) • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT False for an exact match the value to look up in the first column of the table the lookup table or range of information the column number in the table that contains the value to be returned True is default END Brackets [ ] indicate an optional argument 2-31 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the VLOOKUP Function…/2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES This function scans down the first column for the largest value that is less than or equal to the lookup value • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END Use an absolute reference if you enter a cell address and plan to copy the formula 2-32 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. Table’s first column must be in ascending order EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions Using the HLOOKUP Function Search for a value in the top row of a table and return a value from a different row, from the same column as the value found =HLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, row_index_num [,range_lookup]) • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT False for an exact match the value to look up in the first row of the table the lookup table or range of information the row number in the table that contains the value to be returned END Brackets [ ] indicate an optional argument 2-33 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the HLOOKUP Function…/2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT Same as VLookup, except that the table is set up so the scan is horizontal from left to right END 2-34 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. Table’s first row must be in ascending order, left to right EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Financial Functions LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV Excel includes many financial functions used for calculating loan details, annuities, and investment analyses • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-35 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Arguments Used in Financial Functions Present value – PV - the current value of amounts to be received or paid in the future discounted at some interest rate OR the amount that must be invested today at some interest rate to accumulate to some specified future value Number of periods – NPer - the number of payments that will be made to an investment or loan Payment – PMT - the amount paid or collected for each period Future value – Fv - the value of a loan or investment at the end of all the periods • Features Summary Rate - the interest rate being charged or paid BACK NEXT END Type - payments can either be made in arrears (at the end of each period) or in advance 2-36 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the PMT Function LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Calculate the periodic payment of a loan based on constant payments and a constant interest rate =PMT(rate,nper,pv) • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT interest rate per payment period END 2-37 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. total number of payments to be made present value of the amount borrowed EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the PMT Function…/2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES annual rate of interest must be divided by 12 for monthly payments • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS the number of years times 12 months (5 x 12 = 60) • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE cash you pay out is represented by a negative number • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-38 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Using the PPMT Function Calculate that portion of a loan payment used to reduce the principal, based on periodic, constant payments, and a constant interest rate =PPMT(rate,per,nper,pv,fv,type) in arrears or in advance • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END interest rate per payment period period for which the principal payment is made 2-39 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. total number of payments to be made balance at the end of the loan - usually 0 present value of the amount borrowed EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the PPMT Function…/2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES annual rate of interest must be divided by 12 for monthly payments • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS period of payment • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names the number of years times 12 months (5 x 12 = 60) • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE amount of money borrowed • Features Summary BACK NEXT balance at the end of the loan -0 if blank END 2-40 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges PMT and PPMT Examples Compare two loans … • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END =PMT(C4/12,C5*12,C6) =PPMT(C4/12,1,C5*12,C6) 2-41 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. =PMT(E4/12,E5*12,E6) =PPMT(E4/12,1,E5*12,E6) EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT Using the PV Function Calculate the present value that the total of a series of constant future payment amounts is worth today, assuming a constant interest rate over the life of the annuity =PV(rate,nper,pmt,fv,type) interest rate per period payment in arrears made each or in total number period advance future of payments value to be made END 2-42 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the PV Function…/2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES the Formula bar displays the function as it is being entered • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT functions may include cell references END 2-43 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Using the NPV Function Calculate the value of an investment today using a discount rate and incorporating a series of cash inflows or outflows related to the investment =NPV(rate,nper,pmt,fv,type) • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END interest rate per period payment in arrears made each or in total number period advance of payments future to be made value 2-44 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the NPV Function…/2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES the Formula bar displays the function entered • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-45 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Logical Functions LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV Excel's logical functions perform logical tests to return a result, based on whether a condition is true or false • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-46 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions Using the IF Function Set up a conditional statement to test data • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS =IF(logical_test,value_if_true,value_if_false) • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT condition that can be evaluated as being true or false END 2-47 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. that returned if the logical test is true that returned if the logical test is false EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Using the IF Function…/2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE calculate commission, based on the Commission code • Features Summary BACK NEXT END You may enter values or cell references 2-48 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT 2-49 END IF Function Operators Comparison Less than Greater than Less than or equal to Greater than or equal to Equal to Not equal to All conditions must be True At least one condition is True True becomes False, False becomes true Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. Operator No spaces in functions < > <= >= = <> AND OR NOT EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Examples of IF Functions Simple conditions: =if(C6="FT","Salaried","Part-Time") =if(D6>50000,“High",“Low") Must be both full-time and make over $50,000: =if(and(C6=“FT”,D6>50000),“Bonus",“") • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT May either be full-time or make over $50,000: =if(or(C6=“FT”,D6>50000),“Bonus",“") Must not be full-time: =if(not(C6=“FT”),“Bonus",“") Shows nothing if false END 2-50 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions Using the IFERROR Function Use to trap errors in formulas and return a message or value • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS =IFERROR(value, value_if_error) • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE value, cell reference, or formula • Features Summary BACK NEXT END message to display, value, cell reference, or formula =IFERROR(A2/B2, "Error in calculation") If A2 or B2 contain invalid numbers, message will display 2-51 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Text Functions LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions Excel's text functions can be used to format or modify text • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-52 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions Text Functions A3 contains text, each example typed into C3 Capitalize the first letter of each word: • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS =proper(“annual report”) C3 shows • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS =proper(A3) C3 shows cell A3’s text, capitalized Annual Report • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END Convert text to uppercase: =upper(“annual report”) C3 shows ANNUAL REPORT Convert text to lowercase: =lower(“ANNUAL REPORT”) Insert new text in place of old: C3 shows annual report C3 shows =substitute(A3,”Annual”,”2010”) 2010 Report cell A3 contains Annual Report 2-53 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES Features Summary How do you name a range? • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names select the cell or range of cells to be named • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-54 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. click the Name box, type the name, and press Enter EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names Features Summary How do you enter a function into a cell? Type the function directly into the cell, starting with the equal sign = OR Use the Insert Function button on the formula bar • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV OR • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-55 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. Click and choose the desired formula EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES Features Summary How do you change a range name? • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS Click the Name Manager button in the Formulas tab • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-56 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT Features Summary What is the difference between the functions COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, and COUNTIFS? COUNT counts cells that contain numbers COUNTA counts cells with either text or numbers COUNTIF counts cells in a range, based on a single condition COUNTIFS counts cells in a range, based on multiple conditions END 2-57 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions Features Summary How must you set up a table of lookup values for the VLOOKUP function ? • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Leftmost column must contain values in ascending order, top to bottom It is advisable to create a range name for the table to simplify entering the arguments for the function • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-58 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions Features Summary How must you set up a table of lookup values for the HLOOKUP function ? • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE Top row must contain values in ascending order, left to right It is advisable to create a range name for the table to simplify entering the arguments for the function • Features Summary BACK NEXT END 2-59 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc. EXCEL 2007 Chapter 2 Coming Next LINKS TO OBJECTIVES • Naming Ranges • Functions • COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS • AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS • SUMIF, SUMIFS • Managing Range Names • Lookup Functions • PPMT, PV, NPV • Logical Functions • PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTITUTE • Features Summary BACK NEXT END WORKING WITH TABLES AND DATA FEATURES 2-60 Copyright 2007, Paradigm Publishing Inc.