Study Aide for Exam over Worms & Mollusks
advertisement

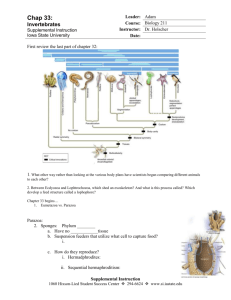
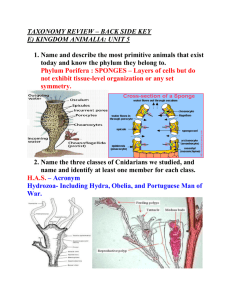
Zoology / Lemmons / Worms and Mollusk Study Aide / 2013 Big Things to keep remembering: Zoology = study of animals Number of species on earth = ~ 8 million Main reasons for species being endangered in our current generation: habitat destruction, pollution, over harvest, competition from species introduced by humans Individual organism, Population (all one species), Community (2 or more species in area), Ecosystem (includes the abiotic variables such as rocks, water = nonliving), Biome (larger scale), Biosphere (entire earth) Eukaryotes have a nucleus; Prokaryotes do not Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, species Domains = Eukarya (eukaryotes); Archaea (harsh environment prokaryotes, such as thermal vents); Bacteria (prokaryotes that are the typical bacteria, such as on your skin) Kingdoms Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia; also the catch-all group Protists for which many Kingdoms are being named Phylum Porifera = sponges (no tissues) Phylum Cnidaria = jellyfish, sea anemones, coral (stinging cells; two tissue layers) Phylum Platyhelminthes = flatworms; e.g. tapeworm & fluke (flat; three tissue layers starting here; acoelomate) Phylum Nematoda = roundworms; e.g. hookworm (complete digestive tract starting here; non-segmented; only group with a pseudocoelom) Phylum Annelida = segmented worms; e.g. earthworm & leech ( true coelom starting here; round, segmentation) Phylum Mollusca = mollusks; e.g. clam, snail, octopus (soft-bodied typically with an external or internal shell; body has a head, foot, and visceral mass) List 10 facts of interest to you from Chapter 27 Worms & Mollusks; Include page #; Show teacher for “approved” status: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10)