Glacial Landforms (1).
advertisement

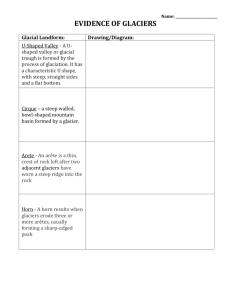
Glacier: Any large mass of ice that moves slowly over land VALLEY GLACIER: CONTINENTAL GLACIER: Valley Glacier: A long, narrow glacier that forms when snow and ice build up in a mountain valley - Found on high mountains - Stay in valley/follow valley Continental Glacier: A glacier that covers much of a continent or large island - Larger than valley glaciers - Spread out in all directions Ice Ages: Times in the past when continental glaciers covered large parts of Earth’s surface Ice Ages: Times in the past when continental glaciers covered large parts of Earth’s surface Form where more snow falls than melts Pressure compacts snow into ice Gravity pulls glacier downhill PLUCKING The process by which a glacier picks up rocks as it flows over the land ABRASION Rocks stick to the bottom of glacier, scrape across the land, and scratch bedrock Till: The sediment deposited by a glacier Fjord: A glacial valley filled with seawater Erosion Fjord: A glacial valley filled with seawater Erosion Horn: A sharpened peak on top of a mountain – glaciers have carved away the sides Erosion Horn: A sharpened peak on top of a mountain – glaciers have carved away the sides Erosion Cirque: A bowlshaped hollow area eroded by a glacier Erosion Cirque: A bowlshaped hollow area eroded by a glacier Erosion Arête: A sharp ridge separating two cirques Erosion Arête: A sharp ridge separating two cirques Erosion Glacial Lake: A long lake, eroded by plucking and abrasion Erosion Glacial Lake: A long lake, eroded by plucking and abrasion Erosion U-Shaped Valley: Shape of a valley created by a glacier Erosion U-Shaped Valley: Shape of a valley created by a glacier Erosion Moraine: A ridge formed by the till deposited at the edge of a glacier Deposition Moraine: A ridge formed by the till deposited at the edge of a glacier Deposition Drumlin: A long mound of till that is smoothed in the direction of a glacier’s flow Deposition Drumlin: A long mound of till that is smoothed in the direction of a glacier’s flow Deposition Kettle Lake: Forms when melting ice forms a depression in till and it fills with water No water = Kettle Deposition Kettle Lake: Forms when melting ice forms a depression in till and it fills with water No water = Kettle Deposition