Glaciers
advertisement

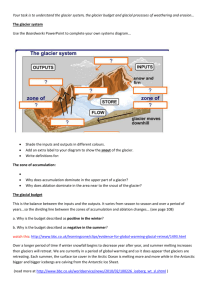
Glaciers Glaciers A GLACIER is a large, slow-moving mass of ice, formed from compacted layers of snow, that slowly deforms and flows in response to gravity and high pressure. Glacial Features Snowline – Area of a glacier that snow/ice stays all year. Snowfield – Motionless mass of permanent snow and ice. Firn – Grainy appearance of ice that melts and freezes (changes overtime). Explain what happens as snow accumulates: Zone of Accumulation – Area of built up snow and ice on a glacier. Zone of Wastage – Area on a glacier that melting is greater than accumulation. The growth of a glacier depends on : The balance between snowfall received and ice lost by melting and evaporation. Glacial Features Types of Glaciers Valley (Alpine) – form at high elevations where temperatures remain cold enough during the summer to keep the previous winter's snow from melting allowing snow and ice to accumulate. Types of Glaciers Continental Glacier – form at high latitudes where temperatures remain cold enough during the summer to keep the previous winter's snow from melting allowing snow and ice to accumulate. Zone of Accumulation – Area of built up snow and ice on a glacier. Zone of Wastage – Area on a glacier that melting is greater than accumulation. Crevasses – Large cracks in a glacier (weak areas of ice). Describe the processes of glacial Advance and Retreat Glacial Advance – occurs when the leading edge of a glacier is able to move ahead faster than it can melt. – Animation Glacial Retreat – occurs when the melting of the front of the glacier happens faster than the forward motion of the glacier. Explain movement of Glaciers Basal Slip Internal Plastic Flow – Movement of glaciers from the slipping of the bottom edge. – Movement in which the ice crystals flow over one another. – (ice skates) – (melting plastic) Glacier Erosion Plucking – It results when glacial ice freezes in the cracks and crevices of a bedrock projection and eventually pulls it loose. Glacier Erosion Ice Wedging – A type of mechanical weathering in which rocks are broken by the expansion of water as it freezes in joints, pores, or bedding planes. Synonymous with frost wedging. Glacial Abrasion – Scratching of underlying rock. Glacial Features Glacial EROSION Cirques – Bowl-shaped depression produced by a valley glacier. Cirques Glacial EROSION Aretes – Sharp, jagged ridge formed between cirques. Glacial EROSION Horns – Sharp, pyramid-like peak formed where several aretes join. Glacial EROSION Hanging Valleys – Small abandoned glacial valley suspended on a mountain above the main glacial valley. Hanging Valley Formation Hanging Valleys Glacial EROSION Striations – Markings on rock from glacial movement. Glacial EROSION Kettle Lakes – Depression in a glacial outwash plain. Kettle Lakes Glacial EROSION ‘U’-Shaped Valleys – Glacial formed valley. U-Shaped Valley Formation Glacial DEPOSITION Drumlins – Long, low tear shaped mound of till. Drumlin Formation Glacial DEPOSITION Eskers – Long, winding ridge of gravel and coarse sand, deposited by a glacier. Esker Formation Glacial DEPOSITION Kames – Irregular shaped hill or mound formed from glacial till. Kames MORAINES Glacial DEPOSITION Moraines –Lateral – Deposited along side of glacier. Glacial DEPOSITION Moraines – End/Recessional – Secondary terminal moraine formed during halt of melting glacier. Glacial DEPOSITION Moraines – Medial – Two or more valley glaciers combine and form along center. Glacial DEPOSITION Moraines – Terminal – Till at leading edge of melting glacier. Glacial DEPOSITION Glacial Sediment – Erratics – Large boulder transported and deposited by a glacier. Glacial DEPOSITION Glacial Sediment – Till – Unsorted Rock material deposited by a glacier. Till Formation Glacial DEPOSITION Glacial Sediment – Outwash – deposit of sand and gravel carried by running water from the melting ice of a glacier and laid down in stratified deposits. Glacial Flow Lab Glacial Flow Lab