kor_bs_stage6_education_unit

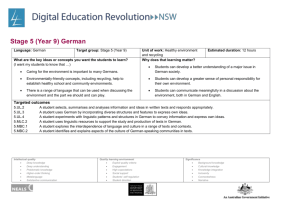
Stage 6 (Years 11 and 12) Korean
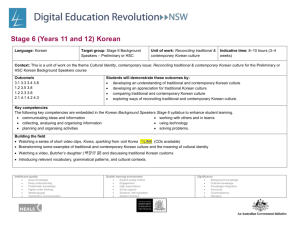
Language: Korean Target group : Stage 6 Background
Speakers – Preliminary or HSC
Unit of work: The place of education in young people’s lives
Indicative time: 8 –10 hours (3–4 weeks)
Context: This is a unit of work on the theme Youth culture , contemporary issue: The place of education in young people’s lives for the preliminary or HSC Korean
Background Speakers course
Outcome/s
3.1 3.2
1.1 1.2 1.3 2.1 2.2 3.8
2.2 2.4 3.2 3.5 3.8
4.1 4.2 4.3
Students will demonstrate these outcomes by:
understanding and identifying the importance of education and its place in young people’s life today
expressing opinions on various pressures from education experienced by young people today
exploring and identifying the place of education in young people’s lives; producing texts which are creative, persuasive and appropriate to the issue
comparing and contrasting the impact of different emphases on education in Australian and Korean cultures
comparing and contrasting the impact on young people of changes in traditional social values regarding education.
Key competencies
The following key competencies are embedded in the Korean Background Speakers Stage 6 syllabus to enhance student learning
communicating ideas and information
collecting, analysing and organising information
planning and organising activities
working with others and in teams
using technology
solving problems.
Building the field
Watching a video clip, Youth Education from ADIC , LINK
Brainstorming the issue, consequences and values of education
Comparing parents ’ and students’ views on and attitudes towards education
Introducing relevant vocabulary, grammatical patterns, and cultural contexts.
Intellectual quality
Deep knowledge
Deep understanding
Problematic knowledge
Higher-order thinking
Metalanguage
Substantive communication
Quality learning environment
Explicit quality criteria
Engagement
High expectations
Social support
Students’ self-regulation
Student direction
Significance
Background knowledge
Cultural knowledge
Knowledge integration
Inclusivity
Connectedness
Narrative
Suggested teaching and learning activities:
Note: teaching and learning activities marked with an asterisk (*) could be used as formal assessment tasks.
LR: Listening and responding, RR: Reading and responding, W: Writing, S: Speaking
1. Group research and threaded discussion (refer to Teaching and learning activity 1 for explanation) activity
1) Students research to compare and contrast the attitudes of students and parents to the education systems in Korea and Australia
2) Students post their findings and thoughts on the class wiki page LINK (or any similar web discussion boards)
3) Students r ead other groups’ postings and add comments.
2. Individual E-portfolio task LINK (RR, W *)
1) Students get a clear idea about what is ePortfolio with teacher demonstration of what it is and how to create it
Evidence of learning
Class discussion and teacher feedback on student contributions
Student use of appropriate vocabulary structures for the contemporary issue
Student ability to sequence ideas
Student use of culturally appropriate behaviour
Teacher observation of level of participation in class discussion and oral feedback.
2) Students collect evidence: looking back and looking ahead
3) Students develop their messages through ePortfolios
4) Students create web pages using Google docs or uploading ePortfolios on the social networking sites.
3. Creating a radio advertisement in groups (S, W *)
1) Students browse a KOBACO LINK site to choose a print form of advertisements in relation to the issue
Direct links to suggested advertisements: LINK1 LINK2 LINK3 LINK4
2) Students analyse the chosen advertisements in groups
3) Students in groups create radio advertisement scripts in relation to the issue
Intellectual quality
Deep knowledge
Deep understanding
Problematic knowledge
Higher-order thinking
Metalanguage
Substantive communication
Quality learning environment
Explicit quality criteria
Engagement
High expectations
Social support
Students’ self-regulation
Student direction
Feedback for students
Ongoing feedback through:
teacher observation
oral/written feedback
student self-evaluation
peer evaluation.
Significance
Background knowledge
Cultural knowledge
Knowledge integration
Inclusivity
Connectedness
Narrative
4) Students use Audacity LINK to record the radio advertisements and upload to the class wiki
5) Students present to the class : students listen and respond to other groups’ advertisements in written and verbal form.
4. Listening and responding (texts from New HSC Online LINK )
1) Students listen to a radio interview (Youth employment pathways) and answer questions
2) Students listen to a dialogue between two high school students (stressful school days) and answer questions
5. Reading and responding
1) Students read some articles and clarify meaning in pairs or groups
2) Students analyse the texts: theme, subjects, text-types, facts and opinions
3) Students summarise the articles and add opinions about the article.
6. Writing a speech (W, S *)
1) Students learn about written and spoken speech: teacher modelling required
2) Students outline their speech using a mind map tool LINK
Points to be included:
- what place education should have in our lives
- is university the only way to success
- what should a person get from life?
3) Write a speech using their essay outline
Listening activities: teacher observation and oral feedback on purpose and content
Speaking activities: teacher provides oral feedback on correct pronunciation and vocabulary and ability to maintain an interaction
Discussion activities: teacher observation and oral feedback on how well students participate and recognise and use the vocabulary
Reading activities: teacher gives oral/written feedback on identifying general or specific information, purpose and content
Written activities: teacher observation and written feedback on purpose and content; peer evaluation
ICT activities: use of internet for research to provide additional activities that allow for independent student progression or group progression.
Intellectual quality
Deep knowledge
Deep understanding
Problematic knowledge
Higher-order thinking
Metalanguage
Substantive communication
Quality learning environment
Explicit quality criteria
Engagement
High expectations
Social support
Students’ self-regulation
Student direction
Significance
Background knowledge
Cultural knowledge
Knowledge integration
Inclusivity
Connectedness
Narrative
4) Deliver the speech to the class: the form of delivery can be face-to-face presentation or video presentation using Adobe Premier Element 7
LINK
Resources
Web resources
ADIC, Youth education video clip : http://www.adic.co.kr/ads/list/showTvAd.do?ukey=85727&oid =
Wiki space : http://www.wikispaces.com/
Google sites for ePortfolio : http://sites.google.com/
Korean Broadcasting Corporations (KOBACO): http://www.kobaco.co.kr/businessintro/about/about_view.asp
Teacher tube Audacity tutorial : http://teachertube.com/videoList.php?pg=featuredvideolist
Mind map tool, CMAP : http://cmap.ihmc.us/conceptmap.html
Adobe Premier Element 7 : http://www.adobe.com/designcenter/premiereelements/
HSC Online, listening tasks: http://www.hsc.csu.edu.au/korean/background/youth/education/youth_tasks/listening/index.html
Text resources
무슨 공부를 하여 무엇이 될까
,
정범모
나한테 꼭 맞는 일을 어떻게 찾나
아이들이 스스로 선택할 수 있도록 도와주는 호주의 교육제도
,
김형아
진정한 인간다운 교육을 기대하며
,
이정재
대학을 안 가도 멋진 직업 많아요
어느 고교생의 일기
입시 교육과 인간 교육
문화 적응상의 가치관 지도
취업을 앞둔 젊은이들에게
공부 잘하는 방법
?
다 자기가 할 탓이랍니다
공부에 습관을 들이자
삶이란 명제
Intellectual quality
Deep knowledge
Deep understanding
Problematic knowledge
Higher-order thinking
Metalanguage
Substantive communication
Quality learning environment
Explicit quality criteria
Engagement
High expectations
Social support
Students’ self-regulation
Student direction
Significance
Background knowledge
Cultural knowledge
Knowledge integration
Inclusivity
Connectedness
Narrative
Evaluation and variation
Considerations: Time allocated for unit; variety of teaching strategies used; opportunities for teacher feedback and student reflection; suitability of resources; suitability of ICT/laptop activities; literacy/numeracy links.
Date commenced: Date completed:
Class Teacher signature: Head Teacher signature:
Intellectual quality
Deep knowledge
Deep understanding
Problematic knowledge
Higher-order thinking
Metalanguage
Substantive communication
Quality learning environment
Explicit quality criteria
Engagement
High expectations
Social support
Students’ self-regulation
Student direction
Significance
Background knowledge
Cultural knowledge
Knowledge integration
Inclusivity
Connectedness
Narrative